There are numerous parameters that must be analysed to quantitatively and qualitatively assess a given network’s performance at a time and deal with any bottlenecks that might exist. The goal is to increase network availability and minimise the time for data transfer.
With the push towards digitalisation and 5G, a strong network is of foremost importance. As a user, we know that it has always been the case, and the only thing that matters is that we receive the requested service as we expect. We all know how annoying it is when we want to place an order for a product, but the server crashes due to traffic. Nobody likes a website that takes forever to load, or a disconnected call, or a video that keeps buffering.
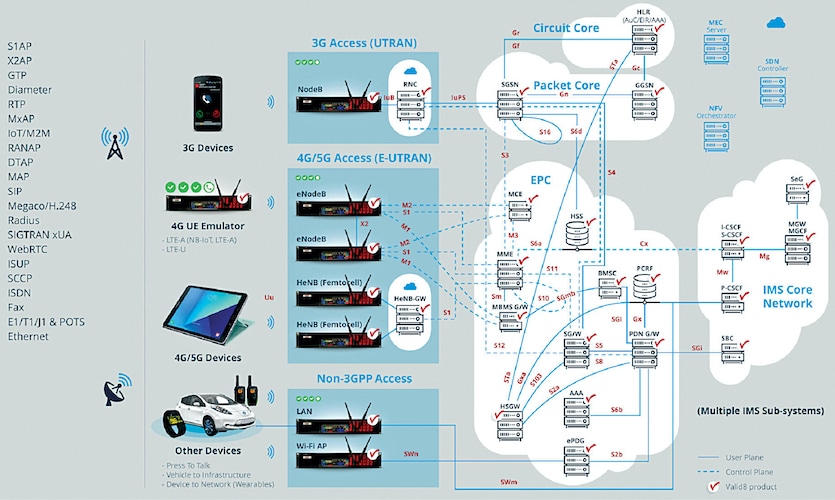
There are multiple factors why a network may not perform optimally, with one or more parameters deviating from the ideal range. By proactively identifying the potential problematic elements in a network, chances of crisis in the future are reduced. For this, understanding how the infrastructure works—both hardware and software—is crucial.
All hardware components, that is, routers, switches and cables, and servers, should be designed to meet requisite system demands based on the application. Other details like knowing the number, type and location of all devices, understanding network security architecture, operating systems, IP addresses, and wireless protocols, in advance, are highly beneficial when it comes to optimal infrastructure. Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is the standard set of networking protocols that allows two or more computers to communicate and exchange data, and together with the Internet Protocol (IP) defines how packets of data are transmitted through a network.
Madhukar Tripathi, head, Optical Business & Marketing, Anritsu India, says, “Testing in wireless networks is entirely different as compared to wired networks. The wireless network is unpredictable due to various radio frequency (RF) transmissions and its harmonic generation for many non-visible, uncontrolled reasons, including illegal transmitters. Such a scenario is often seen in over-the-air (OTA) interference testing, while wired testing is free of such scenarios. OTN analyser or Ethernet analyser or OTDR are some of the popular wired technology testing tools that are used in connected mode with the network.”
When applications become complex, testing on every level gains the utmost importance. If the design does not consider variations that exist in real-life applications when compared to a simulation environment, the extra cost is incurred after repairing the faults. Also, it is very common for cybercriminals to redirect traffic on the connected devices to fulfill their malicious intent. Since maintaining network security is an absolute necessity for any application, regardless of its scale, methods for mitigating issues like security breaches due to trojans need to be chosen such that intensive bandwidth requirements are avoided.
Parameters impacting network performance
There are numerous parameters that must be analysed to quantitatively and qualitatively assess a given network’s performance at a time and deal with any bottlenecks that might exist. The goal is to increase network availability and minimise the time for data transfer. A few of them are discussed next.
Packet loss
Packet loss occurs when data transmitted in the form of packets fails to reach its destination. This can be caused by congestion, inadequate infrastructure, software bugs, among others. Although it depends on the application, a loss above two to three per cent is considered significant. It also results in a reduction of the speed or throughput of a network, leading to problems like incomplete transmission of documents. Analysing the root cause and taking measures like updating hardware and software regularly can help reduce the loss.

Latency
Latency, measured in milliseconds (ms), is defined as the amount of time taken for data to travel from one place to another. Lower the latency, better the network performance. There are multiple reasons why the latency in a network may be higher. For example, if one link is experiencing heavy traffic, TCP/IP protocol places packets in a queue for later processing to avoid traffic. Other factors include a large number of routers and a high refractive index of optical fibre. Latency is lower in wired networks.
Bandwidth
The term bandwidth is a theoretical measure of the amount of data that can be possibly transferred over a given time period. It tells us about the capacity of a channel for both wired and wireless networks. It depends on the number of concurrent devices as well as the distance from the router. It is usually measured in bits per second.
Throughput
In telecommunication, throughput is a metric that determines the rate of successful data delivery over a network or communication channel in a pre-defined time frame. Throughput includes the sum of all data rates delivered to individual terminals to calculate speed.
Jitter
Jitter is the variation in time delay or increased latency for the data packets sent over a network, resulting from network congestion and route changes. Jitter is measured in milliseconds (ms) and should be as low as possible to avoid packet loss. Jitter values of a few ms are not even perceptible, but high jitters must be avoided, especially in streaming and gaming.
Testing and measurement
By capturing and analysing network data, problems like slow response time and intrusion can be identified. Key players in this market include Anritsu, Rohde & Schwarz, Fluke Networks, National Instruments, Agilent Technologies, Electro Rent, and so on. The increasing demand for accurate and reliable procedures and tools, especially for testing wireless networks in real time, is pushing the companies to use tools that incorporate remote diagnostic capabilities to figure out the root cause, among other advanced features, for better user experiences.
Tripathi says, “Selection of right testing tools and accessories is very important for any network testing. Testing tools with automation features save time and provide reliable results. There are many tools available for network testing. It depends on the element or network component system under test. Network testing tools must have easy to use Graphical User Interface (GUI) and future technology support proof. Testing tools must have automation tools to support easy, faster, and reliable testing. Automation tools save a lot of time and help deliver quality products in the market. The testing tool must be flexible and scalable for future use.”
Tripathi adds, “For wireless network testing, spectrum analysers such as Spectrum Master MS2720T and Field Master Pro are some well-known industry tools. Field Master Pro MS2090A measures all RF parameters for 5G network 5G NR base station measurement—validate the performance of the gNB base station with essential measurements that are in full compliance with 3GPP TS 38.104V15, including frequency error, time offset, cell/sector ID, modulation quality, unwanted emissions, occupied bandwidth, adjacent channel leakage ratio, transmitter spurious to 12.75GHz, and EIRP synchronisation signal block (SSB) and can be used for coverage mapping and interference hunting/testing as well.”
Out of the numerous tools available for monitoring, managing, and troubleshooting network issues in the market, one of them is WAN Killer by SolarWinds. It enables testing network performance for Wide Area Network (WAN) to ensure that it can handle large volumes of traffic when the need arises. This helps in load balancing by rerouting traffic to the available servers to prevent downtime.
For security checks, take the example of the cloud-based network scanning tool, Intruder. There are thousands of security vulnerability checks possible with the tool, including detection of bugs necessary for debugging later, configuration weaknesses, and the like. Similarly, Acunetix detects network vulnerabilities and misconfigurations such as weak passwords, gaps in firewall and router security, among others.
5G and cloud have given rise to numerous new use cases. Data collected from all connected devices reach the cloud these days, in contrast to the traditional infrastructure. Mobile networks are extremely complex structures. There need to be cost-effective test networks and services to support these applications. Test and measurement will play a central role in the adoption of 5G devices, networks, and services. Internet of Things (IoT) solutions provider Cavli Wireless has joined hands with Maker Village, the Indian IoT and hardware innovation hub, to launch a 5G network test lab in India in the third quarter of this year.
The department of telecommunications (DoT) has recently launched its ‘5G Hackathon’ to shortlist ideas that could be converted into workable 5G products and solutions. The government received applications from companies like Airtel, Vodafone Idea, Reliance Jio, and BSNL.
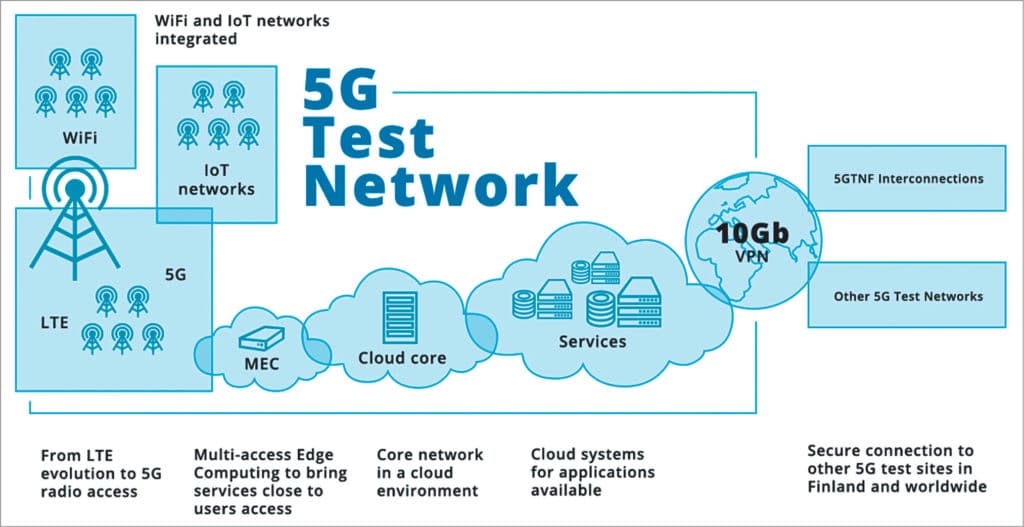
Challenges
It is not possible to accurately model the performance of a network hundred per cent. Although parameters like negligible delays are not that perceptible, it is necessary to address the challenges involved in testing and measurement of networks and make accurate decisions. The cost of production of equipment is often on the high end. While improving test capabilities such that these are user-friendly, cost and testing time also need to remain low. Managing a specialised skill-based workforce can be quite challenging too.
Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) suggested that DoT could impose a six-month limit for a company to conduct tests on its landline and fixed-line broadband networks before commercial launch. While rules already existed for players offering wireless services in India, these draft recommendations were floated in December. Only when a connection is provided to the employees and partners, there would be no time limit for testing.
In 5G, factors like choice of the higher frequency spectrum and dense networks present newer challenges. The management of multiple tools in itself becomes an intimidating task for IT admins.
Tripathi says, “While 5G ecosystem is expanding day by day across the world, co-existence of standalone 5G (SA) and non-standalone (NSA) networks will be a real challenge in 5G testing. Interoperability with legacy networks is another important and challenging area in 5G. IoT ecosystem is full of various technologies, and therefore testing is complex. This is due to ever-increasing and evolving standards for various wireless connecting technologies and applications.”










