- These buck devices are ideal for high-duty-cycle ranges and effortless startups below 5-V input.
- The Simple Switcher’s integrated FET in an inverting buck-boost configuration offers an efficient, compact power supply adept at managing varying voltage conditions.
Light Detection and Ranging is a remote sensing technology that uses light as a pulsed laser to measure distances. This technology has revolutionised various fields due to its ability to generate precise, three-dimensional information about the shape of the Earth and its surface characteristics. Its applications extend to autonomous vehicles, where it provides critical data for navigation and obstacle detection, and in archaeology, where it reveals previously hidden features beneath dense vegetation. LiDAR’s precision and versatility make it a vital tool in modern technology, offering unparalleled insights into our natural and built environments.
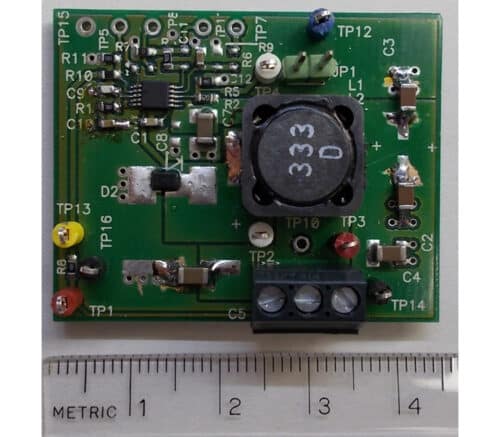
This PMP30942 reference design by Texas Instruments is a tiny inverting buck-boost that provides negative voltage up to -45 V out of input voltage 5.2 V for lidar applications. Maximum load current is limited to 120 mA. This setup is cost-effective, utilising a single inductor alongside a standard buck device. This approach not only simplifies the design but also reduces the overall component count, leading to savings in both space and cost.
It can produce sinusoidal input and output ripple. This characteristic is particularly beneficial in reducing conducted emissions, a critical factor in maintaining compliance with electromagnetic interference (EMI) standards. By ensuring that the waveforms are free from these anomalies, the Simple Switcher helps maintain the integrity of nearby radio frequency communications, making it an ideal choice for applications where electromagnetic compatibility is a priority. This power supply’s maximum output current (Iout) capability is 0.12 amperes, suggesting it is designed for low-current applications. Furthermore, it has an output power capacity of 5.4 watts, a reasonable output for a device operating within these voltage and current ranges. This power rating indicates the total energy the supply can deliver to its load. It suits small-scale electronic devices or specific components requiring a stable, negative voltage supply.
Mechanically scanning LiDAR systems are gaining prominence in the automotive sector, offering advanced vehicle sensing capabilities. In the industrial domain, it finds diverse applications. It is utilised in drone vision to enable drones to accurately navigate and map their surroundings. In the context of industrial robots, it serves as a critical component, empowering these machines with spatial awareness and precision in complex tasks. Additionally, mobile robots in industrial settings increasingly rely on LiDAR for navigation and obstacle detection, ensuring efficient and safe operation in dynamic environments.
Texas Instruments has thoroughly tested this reference design, which includes a Design Guide, Bill of Materials (BOM), schematics, Gerber files, Printed Circuit Board (PCB) layout, and more. Please visit the company’s website for further information on this reference design. To explore this design in greater detail, click here.