The design combines processors and mmWave sensing for applications in industry, smart cities, and drones, offering seamless integration with open-source software for rapid development.
Autonomous robots are increasingly becoming indispensable across various sectors due to their ability to enhance efficiency, safety, precision, and cost-effectiveness. They can operate continuously without the need for breaks, significantly boosting productivity in industries such as manufacturing, logistics, and agriculture. Additionally, by taking on dangerous or repetitive tasks, autonomous robots reduce the risk of injury to human workers, making them invaluable in hazardous environments like nuclear plants or in critical operations like bomb disposal. Their capability to perform tasks with high levels of precision and consistency is particularly crucial in fields like surgery, where accuracy is paramount. Over time, the deployment of autonomous robots can lead to substantial cost savings, making them a key component in the future of automation and technological advancement.
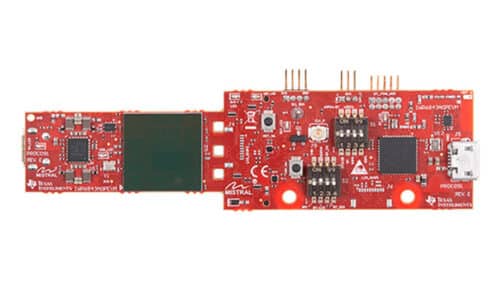
TIDEP-01006, the reference design from Texas Instruments (TI) features autonomous robotics using Processor SDK Linux on the Sitara AM57x processor and the mmWave SDK. It showcases an embedded robotic system where mmWave radar sensing data is processed by the processor running the Robot Operating System (ROS) for system control. The design combines advanced processor SoCs and sensors with open-source software components. It supports the IWR6843 antenna-on-package mmWave sensors, offering reduced costs, simplified design, smaller sensor size, and faster time to market. This design is an excellent starting point for evaluating autonomous robotics with Sitara processing and mmWave sensing, facilitating rapid development of robotics applications using TI’s hardware and software components.
The applications of this technology span across various fields. In the industrial sector, it is used in robotics for tasks such as object detection and localization, sorting, quality control, inspection, and packaging in industrial, logistics, delivery, service robots, and forklifts. In smart cities, it is applied for security monitoring and road inspection. For drones, the technology is utilized for obstacle avoidance, path planning, and flight control.
The features of this technology include an embedded ROS on the System on Chip (SoC), ensuring seamless integration of the mmWave sensor, including the antenna-on-package variant, with the processor. The processor controls the mobile Kobuki platform to navigate and avoid obstacles detected by mmWave sensors. There is real-time visualization of navigation on a remote Ubuntu Linux box with ROS Rviz. The technology comes with a step-by-step guide to establish a fully operational robotic system with sensory data and a mobile base. The open-source ROS implementation enables easy adjustments or enhancements to existing modules and the addition of new modules.
TI has tested this reference design. It comes with a Bill of Material (BOM), schematics, etc. You can find additional data about the reference design on the company’s website. To read more about this reference design, click here.