A smart Indoor Air Quality Monitor (AQM) tracks CO2, PM2.5, humidity, and temperature, storing data on an EEPROM, displayed on OLED, and uploaded to Google Cloud.
Indoor air quality is a significant concern in offices and homes due to its impact on health, comfort, well-being, and productivity. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), approximately seven million people die annually from exposure to fine particles in polluted air, leading to various health issues like stroke, heart disease, lung cancer, and respiratory infections. Therefore, it is crucial to have reliable air quality monitoring systems in place for continuous monitoring. An Air Quality Monitor (AQM) is a real-time monitoring system that measures key airborne contaminants such as Particulate Matter (PM2.5), Carbon Dioxide (CO2), humidity, and temperature levels indoors. These smart AQMs can transmit the collected air quality data to a cloud server, smartphone, or other devices through wireless communication. This data can then be used to control air purification systems, inform HVAC control systems, and facilitate early maintenance of indoor air delivery systems.
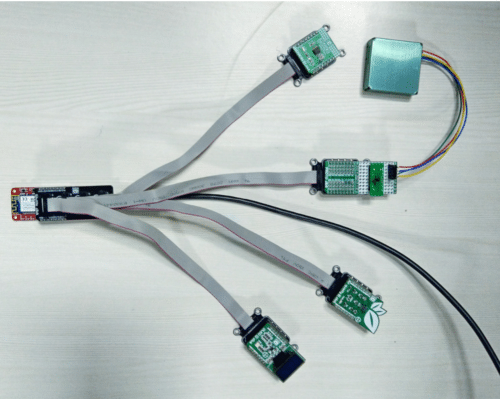
The Indoor Air Quality Monitor (AQM) is built using the AVR-IoT WG development board, sensors, and MikroElektronika click boards, all from Microchip. The board includes Microchip’s ATmega4808 MCU, ATECC608A CryptoAuthentication secure element, and ATWINC1510 Wi-Fi module. It tracks indoor humidity, temperature, Particulate Matter (PM2.5), Carbon Dioxide (CO2), and Total Volatile Organic Components (TVOC). The MCU processes these readings to calculate the Air Quality Index (AQI) based on the PM2.5 sensor data, which, along with other parameters, is stored on an external EEPROM, displayed on an OLED screen, and uploaded to Google Cloud.
The AQM measures CO2 levels from 0 to 10000 ppm (good range 0-1000 ppm), PM2.5 levels from 0 to 12 ug/m3 (good range), humidity from 0 to 100%, and temperature from -40°C to +125°C.
Utilizing the microcontroller’s ADC, RTC, Event System, and I2C peripherals, the AQM measures main airborne contaminants, humidity, and temperature. Data can be displayed on a 3″ OLED screen and logged to the EEPROM for trend analysis. Processed data can be wirelessly transmitted to a smartphone or cloud-based server via a Wi-Fi module, with encryption provided by the CryptoAuthentication secure device.
The sensor node application, like AQM, involves measuring analogue signals from various sensors. In a noiseless scenario, achieving a high-quality digital representation is straightforward (using single ADC conversions triggered at fixed intervals). However, most analogue signals are affected by noise. One potential solution is filtering the ADC samples in software, which would require extra CPU resources. The ATmega4809 device includes a successive approximation Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) with a maximum conversion rate of 150 kbps at 8-bit resolution or 115 kbps at 10-bit resolution.
Microchip has tested this reference design. It comes with a Bill of Material (BOM), schematics, etc. You can find additional data about the reference design on the company’s website. To read more about this reference design, click here.





