
Integrating wireless control into brushless direct current (BLDC) motor systems opens up exciting possibilities for applications such as remote-controlled cars, robots, and other innovative systems.
BLDC motors are commonly operated using a driver or a remote-controlled controller paired with an electronic speed controller (ESC).
Adding Wi-Fi connectivity to enable control via a laptop or personal computer further enhances their versatility.
This motor system utilises a BLDC motor, an ESC, and an ESP32 to enable wireless operation.
POC Video Tutorial
Table of Contents
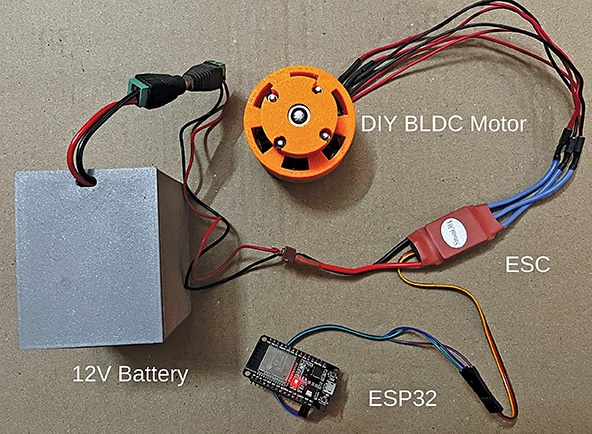
The Bill of Materials table lists the required components, while the author’s prototype of the BLDC motor controller is depicted in Fig. 1.
| Bill of Materials | ||
| Components | Quantity | Description |
| ESC controller | 1 | 30A Simonk ESC controller |
| NodeMCU ESP32 (MOD1) | 1 | ESP32 development kit |
| Battery | 1 | 3S 12V battery |
| Jumper | 2 | Female to male jumper |
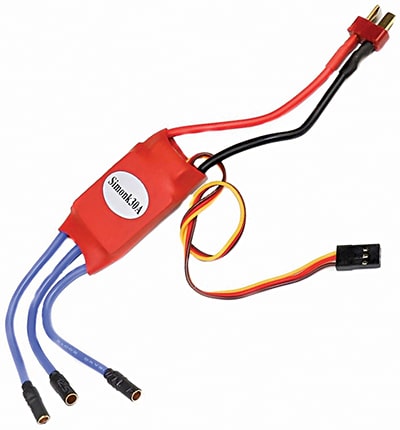
An ESC is vital in operating BLDC motors. It regulates the motor’s speed, direction, and overall performance by controlling the power delivered to the windings.
The 3S 12V battery powers the BLDC motor and other components, ensuring efficient system operation. Its stable output makes it suitable for driving ESCs and maintaining consistent power for the ESP32 module. Fig. 2 shows an electronic speed controller.

Working Principle
The ESC manages the timing and duration of current flow through the stator windings, effectively controlling the rotor’s rotation. It operates on principles such as pulse width modulation (PWM), phase sequence, sensorless control, and sensor-based control.
The ESC uses PWM signals to control transistors, managing voltage and current delivered to each phase. It simulates a rotating magnetic field by rapidly switching phases on and off.
The ESC energises windings in a specific sequence (A, B, C) to create continuous rotation. As the rotor moves, the ESC adjusts which windings to energise based on sensor feedback or back electromotive force (EMF).
Many ESCs utilise sensorless controllers that estimate rotor position from back EMF generated during motor operation, simplifying designs and reducing costs. In some applications, sensor-based controllers (like Hall effect sensors or encoders) provide precise feedback on rotor position, enabling accurate control.
ESP32 for BLDC Motor
Controlling a BLDC motor with an ESP32 in access point (AP) mode offers a flexible wireless solution for speed control in robotics, drones, or automated systems.
The ESP32 creates its own Wi-Fi network, enabling direct connection from any web browser-equipped device, such as a smartphone or laptop, without an external router or internet connection.
Fig. 3 shows an ESP32 module.

The ESP32 serves as a controller and web server, generating PWM signals via its general-purpose input/output (GPIO) pins to control the motor’s speed through the ESC. A basic web interface hosted on the ESP32 features a slider to adjust the PWM duty cycle.
The web page allows users to adjust motor speed in real-time by modifying the slider value, which directly influences the PWM signal sent to the ESC. The PWM signal regulates the power supplied to the motor, ensuring smooth and precise speed control.
The AP mode eliminates the need for additional network infrastructure. This setup is easily programmable using the Arduino integrated development environment (IDE), with straightforward code to manage the Wi-Fi network and control the motor via PWM signals.
Circuit and Working
The ESP32 creates a Wi-Fi network (AP mode), which you can connect to from a smartphone, tablet, or laptop. The ESP32 hosts a web server that serves a basic HTML interface with a slider to control the motor speed.
The PWM signal generated by the ESP32 is sent to the ESC, controlling the motor’s speed based on the slider value. The duty cycle of the PWM signal directly corresponds to the engine’s speed, with higher duty cycles resulting in faster speeds and lower duty cycles resulting in slower speeds.
Fig. 4 depicts the circuit diagram of a BLDC motor with a web-based speed controller using ESP32. It is built around (MOD1), an ESC controller, a 3S 12V battery, and several jumpers.







