Threats include phishing trends due to the pandemic, ransomware and critical security supply chain weaknesses
As per the fourth Keysight Security Report featuring key network security trends over the past year from Keysight’s Application and Threat Intelligence (ATI) Research Center, three areas of critical concern to network security have been highlighted. These are:
- Phishing attacks rapidly increased by 62 per cent in 2020 over 2019. Most of them took place in March and April when the pandemic took center stage.
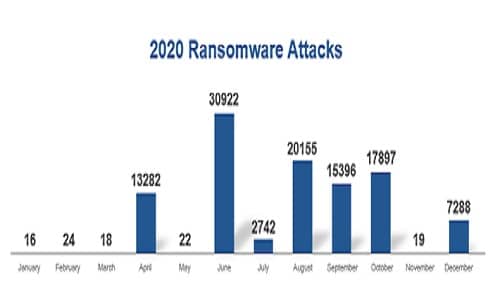
- There was a huge uptick in ransomware deployment starting in June. While this trend was directed across all industries, healthcare was hit especially hard (59 per cent of the attacks occurred during the second half of 2020).
- The supply chain continues to be a weakness and the SolarWinds attack reinforced the need for security architects to embrace a holistic and comprehensive approach.
Strategic Insights from the Keysight Security Report, 2021
- Phishing and additional social engineering attacks will continue to take advantage of pandemic-related headlines.
Keysight’s recommendation: People need to recognise social engineering vaccination scams and network security teams must be aware that bad actors target personally identifiable information (PII) in a healthcare and government setting.
- Ransomware is highly popular because it makes a lot of money for bad actors. While it’s not going away, business models continue to mutate along with malware variants.
Keysight’s recommendation: It’s critical to keep enterprise threat detection systems up-to-date with the latest signatures and behavioural patterns, as ransomware builders are getting better at obfuscation and avoiding detection. Network security teams should also be aware that exploitation practices evolve.
- An organisation’s supply chain is more than just components. There is a tendency to think of a supply chain as outside entities that either supply a company with software and hardware components or the supplies used when building a product.
Keysight’s recommendation: The supply chain is critical to the operation of a business, including utilities, email, cloud providers and even coffee suppliers. Network security must consider non-traditional components that may touch an organisation and IT systems.
- Zero-trust is more than just a buzzword. It does not mean limiting what users can see when they connect to an organisation’s network.
Keysight’s recommendation: A successful zero-trust implementation requires that systems and users can only access the internal or external resources that they absolutely need.
- Assume an organisation is breached and behaves accordingly.
Keysight’s recommendation: Organisations need visibility into their networks and cloud resources. If network security teams cannot spot anomalies hiding in their network (whether on-premises, in the cloud or a remote user), then they are allowing breaches to remain undetected indefinitely.
“The report combines lessons learned in 2020 with impactful insights for network security professionals for 2021. Both the data and insights are based on research conducted by Keysight’s Application and Threat Intelligence (ATI) Research Center,” said Scott Register, vice president, security solutions for Keysight. “Cybercrime did not take a holiday during the pandemic. Cybercriminals leveraged phishing, ransomware and supply chain vector attacks to strike networks for financial gain. We believe that these network security trends will continue in 2021.”
The report draws on Keysight’s in-depth experience in network security testing, as well as the company’s expertise in network and cloud visibility. The globally distributed team of dedicated cybersecurity professionals that make up Keysight’s ATI Research Center monitor and analyse evolving indicators that threaten the security of enterprise IT networks, leverages input to the research process from multiple sources (including honeypots placed worldwide, which actively seek threats in the wild), exploit databases, the Dark Web, scans of security news alerts and crowdsourcing, as well as social media and partner feeds.






