Researchers have developed a telepresence system based on a humanoid robot that allows users to virtually navigate remote environments and interact with people in these environments
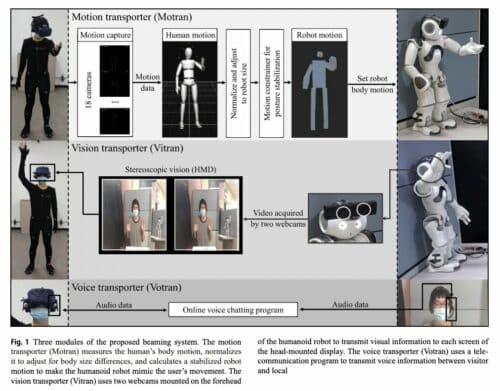
Currently, telepresence systems let you move geographical barriers, allowing real-time, two-way collaboration between people at different locations. To improve the immersiveness and performance of the current system, researchers at Hanyang University and Duksung Women’s University in South Korea have invented a promising telepresence system based on a humanoid robot, a head-mounted display, a motion transporter, a voice transporter, and a vision transporter system. This would enable human users to fully embody a humanoid robot in a remote location, using its body to navigate the environment and interact with others in it similar to their physical presence over there.
“The present study aims to develop a beaming system that provides full body ownership through a humanoid robot and investigate users’ telecommunication experiences as roles of visitor and local with different levels of controllability,” Myeongul Jung, Jejoong Kim, Kyungsik Han, and Kwanguk (Kenny) Kim wrote in their paper.
Researchers performed various tests in which participants interacted with each other in pairs, where one controlled the humanoid robot and the other interacted with it. The pairs completed three trials. Initially, the robot was static and could not be moved at all by users, in the second it could only turn its head and its movements were synchronized with those of users, and in the third, its whole body could move in ways that mirrored a user’s movements. Researchers note that when users had greater control over a humanoid robot’s body and the robot mirrored their movements, their eye contact, emotional, verbal, and gesture communication style was more aligned with those of the humans they were interacting with.
“Forty participants were assigned to both visitor and local roles, and their copresence, usability, eye-contact, emotion, verbal, and gesture communications were investigated,” Jung, Kim, Han, and Kim wrote in their paper.
Researchers envision that the proposed system will enhance telepresence applications that entail users’ remote interaction with other humans and inspire the creation of similar systems based on humanoid robots.
Click here for the Published Research Paper





