Includes a fast-charging architecture for ultra-fast charging in flagship smartphones and other mobile devices

In this 5G era, smartphones consume significant power, creating a high demand for fast charging. The first generation of fast charging IC that was launched in 2017 improved the smartphone charging from 10W to 40W. However, the battery requirements kept increasing with increasing powerful APPs and games on smartphones, which asked for higher charging power up to 60W, or even 120W to shorten the charging time and cool the charging temperature.
Now, the 2nd gen charge pump fast charging IC, the NU2205 from NuVolta Technologies aims to improve that with the one-of-its-kind 100W charge pump fast charging IC that is optimal for 2S battery with 4:2 charge pump fast-charging architecture for ultra-fast charging applications in flagship smartphones and other mobile devices. The innovative 2S battery fast charging architecture enables the charging power from 60W to 120W, which can be further increased to 200W.
Higher Efficiency
High efficiency is the most critical parameter in fast-charging applications. The NU2205 not only improves the work efficiency through the internal innovative structure but also can adjust the efficiency through the operating frequency. In the 4:2 mode, the highest efficiency can reach 98%. Under the 10V AC-DC adaptor input, the charging efficiency of the 2S battery in the 2:2 mode can reach up to 99.2%. In high power charging application, it provides the possibility of pulse switching between 4:2 and 2:2 modes to reduce the heat of the system. The NU2205 can also support both 2:1 and 1:1 1S battery fast charging modes.
Temperature Rise
At 25°C ambient temperature and 16V input, when 2S batteries are charged at 10A and 20A current, the temperature rise is 44.9°C/46.8°C respectively shown as follows.
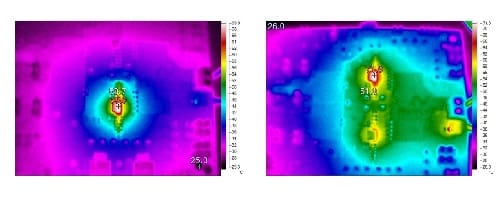
The EVM board of a single NU2205 can output a 10A current stably while two EVM boards with NU2205 can output a stable current of 20A.
Advantages of 2S Battery Architecture
When the internal resistance of the battery is only 5mΩ, the power loss exceeds 0.7W. Higher current brings more heat that induces huge challenges to the design of the battery protection board and the internal resistance of the battery cell. Since the resistance of MOSFET has been reduced from 5mΩ to 1.1mΩ to meet the application of fast charging and high current, the 1S battery fast charging encounters the charging power limitation. To overcome this challenge, the 2S battery fast charging solution doubles the battery voltage at the charging output terminal, reducing the current into the battery by half at the same charging power and bringing down the battery heat to 25%.
Architectural Benefits
The 4:2 charge pump architecture of the NU2205 and the integrated FET has been optimised to achieve a 50% duty cycle. The architecture lowers down the current of the USB cable to half of the charging current that further reduces the loss of the charging cable and limits the temperature rise in the application. The two-phase architecture lowers down the input capacitance requirements while improving the output voltage ripple.
Furthermore, NU2205 supports charging parallelly. When two NU2205 ICs are used in parallel, the charge pump ICs will output 120W power. When three NU2205 ICs are in parallel, the charging power exceeds 200W.
Safety Protections
In high-power charging applications, efficiency and heat are the most important considerations. Another important consideration is charging safety. NU2205 integrates up to 34 levels of safety protections, such as protections of input and output voltage and current, battery voltage and current, and temperature, etc. That protects the system and prevents abnormal conditions that damage the battery and system.