Reference design for low-power PIR detector to sense motion with wireless capability and approximately more than ten years of battery life.
Automation systems use motion detectors to control functions based on human presence. Wireless sensor nodes reduce installation costs, but battery power is a limitation. Texas Instruments (TI) has launched a low-power Passive infrared (PIR) detector with wireless connectivity enabling 10-Year coin cell battery life to simplify the design process. The reference design utilizes nano-power operational amplifiers, comparators, and SimpleLink™ ultra-low power sub-1GHz wireless microcontroller unit (MCU) to demonstrate a low-power wireless motion detector. This PIR sensor can detect movement up to 30 feet away while consuming only 1.65 µA in standby mode. The design is suitable for various applications such as intrusion detection, occupancy detection, motion detection, room monitors, etc.
The reference design is based on the ultra-low power CC1310 Microcontroller Unit (MCU) that achieves an extended battery life for sensor end nodes. The MCU includes a powerful ARM Cortex M3 processor with up to 48-MHz clock speed and 128KB of programmable flash memory. Signal amplification and filtering are necessary at the output of the PIR sensor to ensure that subsequent stages in the signal chain receive sufficiently large signal amplitudes for useful information. Hence an operational amplifier LPV802 is included in the reference design due to its low current consumption benefit. A low-current consumption window comparator circuit is employed to convert the filtered sensor output into digital signals for the MCU input. The design is powered by a CR2032 lithium-ion coin cell, chosen for its widespread availability in small form factor systems like sensor end nodes. The reference design utilizes the Murata IRS-B210ST01 PIR sensor, selected for its surface-mount package and analog output, enabling the demonstration of a low-power circuit in an area-efficient footprint.
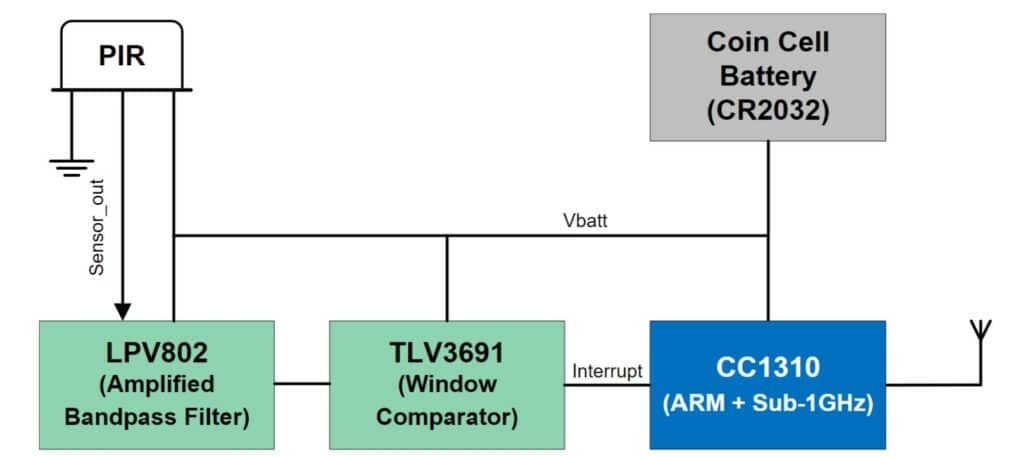
The low-power PIR motion detector features average active-state current consumption of 1.12mA and average standby-state current consumption of 2.3 μA. The battery life with the coin cell battery is estimated to be more than ten years. The motion-sensing range of the design is approximately 30 feet. The system’s operating temperature is limited by CR2032 coin cell batteries and ranges from –30°C to 60°C. The design includes a standby mode with only the PIR sensor active, consuming a low standby current of 1.65μA. The reference design comes with interrupt-driven sub-1GHz wireless communication of motion for increased power savings. The Reference Design detects motion by sensing differences in Infrared (IR) energy. Amplification and filtering are used to boost the small sensor output while minimizing false triggers. The scaled analog output is converted to digital signals using a window comparator function, which saves power by waking up the MCU only when needed.
This reference design has been tested by TI. It comes with a Bill of Material (BOM), schematics, Gerber file, Printed circuit board (PCB) layout, computer-aided design/ computer-aided engineering (CAD/CAE) symbols, Assembly drawing, etc. You can find additional data about the reference design on the company’s website. To read more about this reference design, click here.







