Modern vacuum robots, enhanced with accurate vision and proximity sensors, ensure efficient cleaning in intricate settings.
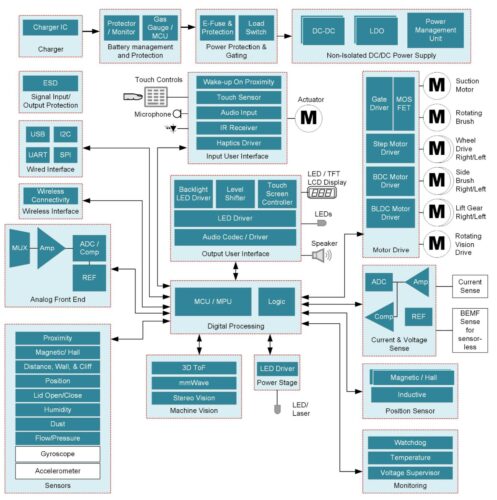
Vacuum robots are increasingly being adopted and favoured, often replacing traditional manual vacuum cleaners in homes and businesses. These robots must process extensive environmental sensory data for optimal performance in intricate and sometimes messy settings. They rely on specific mapping protocols to clean designated areas thoroughly and safely, steering clear of potentially damaging situations. Emerging trends in these robots, like cloud-based wireless connectivity, enhanced sensor systems for varied surroundings, and voice recognition for home automation, drive their intelligence and efficiency to new heights. Texas Instruments (TI) has developed the reference design for a vacuum robot with maximum battery duration, low audible noise and high-performance robot vision that meet Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS) requirements.
The reference design for the vacuum robot prominently features the integration of accurate robot vision and proximity sensors, which guarantee smooth navigation and effective object detection. Equally vital are reliable and precise battery protection, gauging, monitoring, and charging systems to ensure longevity and consistent performance. Furthermore, these robots are equipped with high-speed, compact motor controls that deliver powerful suction and facilitate effortless movement across surfaces. Additionally, to enhance user experience and remote operation, these designs incorporate secure, robust, and energy-efficient wireless or mobile connectivity options.
The heart of the vacuum robot control unit is the processor. TI offers specialised Sitara processors designed for quick and adaptable designs in vacuum robot applications. Running on Arm Cortex-A cores, these processors come equipped with diverse, flexible peripherals, unified software support, and connectivity options, catering to a broad spectrum of vacuum robot needs and use cases. The design is equipped with a proximity sensor that detects objects in the vicinity and can gauge their distance when required. Enhancing vacuum robot vision using 3-D Time of Flight (ToF) technology allows the robot to precisely identify objects from a distance and create detailed maps of its surroundings. By determining the best vacuuming routes, the robot can achieve comprehensive surface cleaning and reduce cleaning times, all while preventing collisions, tumbles, and trapping scenarios.
TI provides avenues for embedding communication functionalities into its processors. The TI WiLink, 8 series of connectivity modules, equips developers wanting to design a vacuum robot with tools to integrate both 2.4- and 5-GHz versions of Wi-Fi along with dual-mode Bluetooth 4.0 into their design. The design also has integrated Digital Signal Processors (DSPs) that facilitate voice recognition. These DSPs excel in isolating clear speech from background noises, ensuring clear audio and voice inputs. An expansive range of power-management integrated circuits (PMICs) caters to various devices, encompassing energy-efficient solutions ideal for vacuum robots.
TI has tested this reference design. It comes with a Bill of Material BOM, schematics, etc. You can find additional data about the reference design on the company’s website. To read more about this reference design, click here.