A sustainable technological revolution aims to reduce carbon footprint and dependence on rare materials through advanced manufacturing and recycling solutions.
Organic electronics possess the potential to play a significant role in decarbonization efforts while simultaneously reducing the demand for scarce and valuable raw materials. To achieve this, it is crucial to advance manufacturing processes and establish technical solutions for recycling from the early stages, including the laboratory phase.
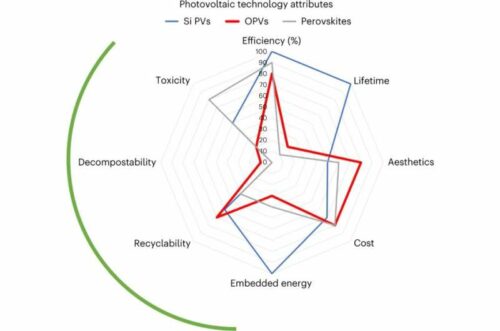
Materials scientists from Friedrich-Alexander University (FAU), along with researchers from the United Kingdom and the United States, published a call to adopt this circular strategy in the renowned journal “Nature Materials” in June 2023. Organic electronic components, like solar modules, offer flexibility and diverse applications compared to crystalline materials. Their carbon-based photoactive substances reduce reliance on rare and costly materials like iridium, platinum, and silver. They are especially booming in Organic Light-Emitting Diode (OLED) technology, primarily for TV and computer screens.
More efficient synthesis and more robust materials
Developing organic electronics involves using new materials and efficient manufacturing processes to reduce energy and costs. The researchers have proposed eco-friendly methods like water-based deposition and inkjet printing to replace high-energy vacuum deposition. The challenge lies in finding non-toxic solvents and developing materials for inkjet printing, potentially replacing precious metals in OLED screens. Enhancing material durability is crucial, as complex encapsulation protects carbon layers and reduces weight. Robust material combinations can substantially save energy, weight, and resources.
Planning the recycling process in the laboratory
To assess the environmental impact of organic electronics accurately, the entire product lifecycle must be considered. While organic photovoltaic systems have a lower output than silicon modules, they emit 30% less CO2 during manufacturing. Maximum efficiency isn’t everything; fewer manufacturing steps and a smaller environmental footprint may be critical. The shorter lifespan of organic modules is relative due to difficulties in recycling silicon-based modules. Biocompatibility and biodegradability are crucial for product and packaging design. Recycling considerations should start in the laboratory, using recyclable substrates and multilayer designs for easy separation and recycling. Adopting a cradle-to-cradle approach is vital for establishing organic electronics in the renewable energy transition.
Reference: Iain McCulloch et al, Sustainability considerations for organic electronic products, Nature Materials (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41563-023-01579-0






