Notably, the VCSEL/CIC showcases superior thermal management capabilities compared to VCSEL/GaAs.
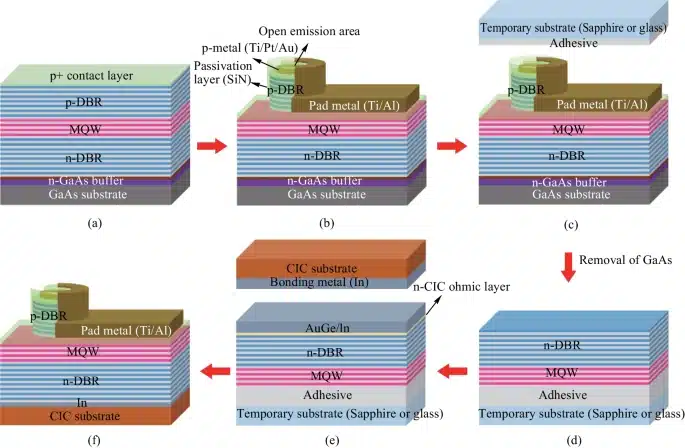
Researchers led by Prof. Ray-Hua Horng, at Yang Ming Chiao Tung University (NYCU), Hsinchu, Taiwan, China have published a research paper titled ‘Study on the performance of thin-film VCSELs on composite metal substrate’. Thin film vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers (VCSELs) operating at a 940 nm wavelength have been successfully developed on a composite metal substrate.
The substrate is made of Copper/Invar/Copper (CIC) using twice-bonding transfer and substrate removal techniques. The CIC substrate consists of a sandwich structure featuring a 10µm thick Copper (Cu) layer, a 30µm thick Invar layer, and another 10µm thick Cu layer. The Invar layer is a mix of Iron (Fe) and Nickel (Ni) in a 70:30 ratio. This composite metal’s thermal expansion coefficient is well-matched to that of the GaAs substrate, enabling the VCSEL layers to be transferred onto the CIC metal substrate without any cracking.
Comparative analysis between top-emitting VCSEL/GaAs and thin-film VCSEL/CIC at 1mA current reveals that their voltages are 1.39V and 1.37V, respectively. Additionally, the optical output power of the VCSEL/GaAs is 21.91mW, while the VCSEL/CIC demonstrates a slightly higher power of 24.40mW. The CIC substrate, with its thickness of 50 µm, significantly enhances heat dissipation, which in turn improves the electrical and optical characteristics of the thin-film VCSELs/CIC.
Notably, the VCSEL/CIC showcases superior thermal management capabilities compared to VCSEL/GaAs. The data gathered indicates that using a composite metal substrate like CIC not only significantly impacts the thin film VCSEL’s performance characteristics but also substantially enhances the device’s overall thermal efficiency.
The implications of Prof. Horng’s research are vast, with potential transformative effects on telecommunications, data centers, and optical communication sectors, among others. The study points to new prospects in laser systems used for data transmission and signal processing across various industries.






