This unique innovation addresses the common problems associated with non-temporary, space-occupying furniture, among others.

Due to ever-increasing shortage of free space in enclosed rooms and the non-feasibility of setting up permanent arrangements within a temporary structure such as a camping tent, foldable furniture act as an attractive solution for fixing these kinds of issues. However, a piece of single foldable furniture serves only a single purpose, either for sitting (chair), keeping things on it (table) or for lying down (bed). And more the number of people, more is the number of such required foldable furniture (which seems to be quite a hassle, both from cost and storage perspectives).
Interestingly, shape-shifting structures could be deployed to create dynamic furniture. But creating them is not easy because of fabrication complexity. Now, a group of computer scientists from the University of Colorado Boulder, who aim to alleviate that, have created “LiftTiles” – modular blocks that gradually rise to the desired height (between 15 and 150 centimetres) via air pressure and when needed, gradually collapse to their original state with the help of a spring force.
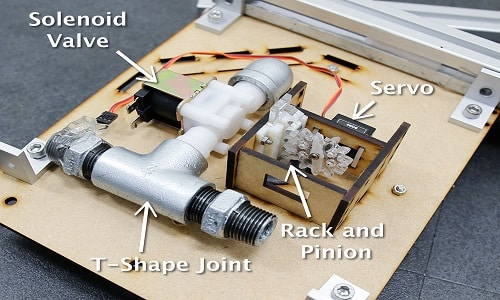
What makes it even more interesting is that the entire mechanism is based on an Arduino Mega 2560 board, along with an SR300 depth camera to measure the height of each section and software running on a control computer.
Lightweight and sturdy
LiftTiles, consists of an array of retractable and inflatable actuator that is compact and light (for example, 1.8kg), while at the same time, robust enough to support objects weighing up to several kilograms (Each tile can support up to 10 kg).

Pneumatic supply connections
Each actuator enables large-scale shape transformations. These actuators are modular and are connected using a T-shaped plumbing joint to an air-intake valve. Adjoining actuators are pneumatically connected via a silicon tube between the T-shape joints, enabling them to share pressurised supply line. Thus, the tiles extend when inflated and retract by spring force when deflated.
Other applications
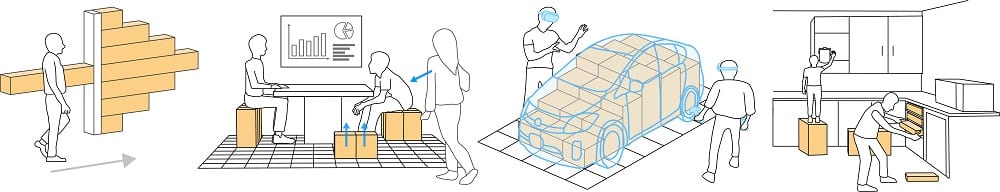
Besides serving as a piece of shape-shifting, adaptive furniture, LiftTiles can also find the following applications:
- Shape-changing wall: User can easily construct a horizontal shape-changing wall that can act as a separator, or boundary to make a temporary meeting space.
- Innovative public signboard: Thanks to its shape-shifting ability, the expansion and contraction of the tiles can function as public signage by displaying arrow, or any other similar shape to guide a passerby.
- Temporary pop-up structures: Be it any event or a relief/rescue operation, the flexible and retractable tiles (powered by several actuators) can easily transform into any designer structure or a temporary arrangement.
- Interactive haptics for VR: While hand-shaped VR displays continue to amaze people by providing a real-time sensation of virtual objects and features, LiftTile can take it further by presenting a 4-D VR experience in which users can walk, run, climb and feel various other actions – in real-time.
Further enhancements
In summary, the creation is clearly a unique way of facilitating services across multiple fields. In order to make LiftTile even more applicable across other sectors, scientists are aiming to enhance it by making the overall structure withstand even more heavier weights, creating even more powerful actuators and making the interconnection between the tiles wireless by replacing the several connecting wires with Wi-Fi.
Read the research paper in detail here.