FEBRUARY 2012: Electronic devices are increasingly being seen in the field of medicine for diagnosis, therapy and rehabilitation. Medical electronics and electromechanical equipment have become indispensable for the better service of patients not only in hospitals but also outside the hospitals. The service quality of hospitals is often judged by the state of the equipment they have at their disposal.
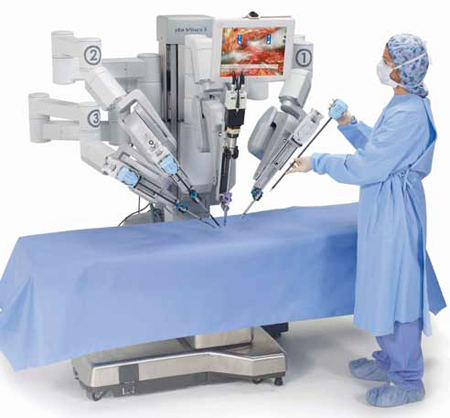
Consider a few cases to understand the reach and impact of medical electronics on patient care. Surgeons use three-dimensional (3D) body registration systems and high-resolution imaging for cutting into invisible areas. Also, implanted insulin pumps with a closed loop-feedback are capable of automatic fine-tuning of drug delivery, thus cut-ting down the need for diabetics to opt for regular self-tests. Unlike oral psychiatric drugs, implanted stimulators and drug delivery devices focus only on affected parts reducing the risk of collateral damages and side effects.
Today, electronic therapeutic and diagnostic instruments and techniques are blended innovatively for overall improvement in healthcare and devising potential cure for a large number of hitherto incurable diseases. With growing popularity of medical electronics, there is now a growing concern about quality, safety, reliability, cost, liability and regulatory issues.
Design, repair and maintenance
Medical electronics engineering ranges from model-driven embedded software design to PCB design and manufacture, and a large number of inter-related sub-sectors too. It covers a very wide range of technologies including radio frequency, analogue semiconductors, digital and microprocessor chips, digital signal processors, sensors, actuators, electromagnetics, optoelectronics and photonics, displays, embedded software, power supplies and antennae.
The rapid advancement in information technology and healthcare consciousness has accelerated the scope for medical electronics. Fast growth in medical electronics is further influencing various demographic trends like consumers’ expectations of more household medical electronic equipment, enhanced portability of complex imaging and monitoring systems, further miniaturisation of implantable equipment with lower energy consumption, and functional integration of equipment and applications in wireless and network technology.

A large number of hospitals are equipped with high-tech medical equipment but lack trained manpower. This results in long down-time and early classification of equipment as defunct. Rou-tine preventive maintenance is required to ensure proper working condition of equipment and applications. The need for special skills to repair and maintain these equipment is realised as hospital technicians normally do not have the expertise and in many cases require special technical skill for rectification.
Quality, safety and reliability
Designing and manufacturing medical electronics equipment for compliance with product safety standards is no easy task. The best way to ascertain a product’s compliance with its governing standard is to get type testing done on sample products by a third-party test house or recognised test lab after the design phase and before the product is launched in the market.
Once a newly designed product has undergone proper compliance testing, the dielectric withstand or hipot test is one of the primary safety tests routinely performed as part of the final production process. This test has long been required on medical electronics products as well as most other electrical devices and appliances before these exit the manufacturer’s production floor. The intention of the test is to stress a product’s insulation beyond what it would encounter in normal use. The end goal is to ensure that patients or caregivers never serve as a current path to ground due to faulty insulation or faulty grounding within the product.
Medical device manufacturers’ concerns are changing due to tighter governmental quality requirements, regulations of agencies worldwide and current legal climates. When designing semiconductor products for medical original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), quality and reliability considerations are paramount and the stakes are high. Enhanced product flows to catalogue processes bring extended product lifetimes as well as well-defined and improved change-control processes.
To meet the demands of the medical market, dedicated and controlled manufacturing lines effectively eliminate facility-to-facility variations, extend qualification practices, improve product traceability, and enhance production testing rigours. Enhanced product flows can also save manufacturers cost and time-to-market by offering an alternative to upscreening, which is commonplace in high-reliability markets. Another way to address these concerns is to adopt portions of ISO13485 (a quality management system) for medical devices as they apply to the semiconductor industry.
Expanding applications
With advancement in technology, new medical electronics devices are emerging in all healthcare segments. In hospitals these devices include handheld smart phone-sized ultrasound systems, digital stethoscopes and digital X-ray systems. Outside hospitals there are medical devices that ensure seamless vital sign monitoring with wireless connectivity between the hospital and home. In homes, available today are healthcare systems for daily activity monitoring, blood coagulation test, continuous glucose measurement and insulin delivery.
The latest medical systems deliver faster and more accurate diagnostic information, thus improving quality of life and reducing healthcare costs. A common requirement for all these devices is operation from a battery, small form factor, and a portable and lightweight design with intuitive user interface.
With devices like injectors or inhalers, the pharmaceutical sector is now looking for more electronics integration. This integration can allow it to develop new ways of administering drugs. Injected drugs can be inhaled and delivered through the lungs for improved efficiency, thanks to electronics-assisted devices.