Such technologies as artificial intelligence, Big Data, machine learning and robotics,
if implemented properly, can make the Indian waste management sector much more efficient
Waste management is the generation, prevention, monitoring, treatment, handling, reuse, etc of solid waste. There are various types of solid waste including municipal, agricultural, hazardous, household and so on.
Waste is created by various human activities, and recycling processes are generally undertaken to reduce its effects on health, the environment or aesthetics. In 1971, the first municipal waste management effort was carried out in North America.
India produces 62 million tonnes of solid waste per year, but only 75 to 80 per cent of that waste gets collected and 22 to 28 per cent is processed and treated, according to Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate change.
Rapid industrialisation and population explosion in India have led to the migration of people from villages to cities. This generates thousands of tonnes of municipal solid waste (MSW). MSW is expected to increase significantly in the near future.
Automation and waste management
In critical areas like solid waste management, electronics and automation sectors acquire a whole new level of importance. The primary reason for increasing waste accumulation in Indian cities is the growing population of India. An effective and smart waste management system can deliver a sustainable, comfortable and healthy living environment.
Automatic waste segregation and deployment of sensors are two approaches for maintaining municipal solid waste. An automatic waste segregator can sort the waste into three main categories, namely, metallic, organic and plastic. Ultrasonic sensors are added to monitor the waste-collection process. Sensors are placed in all garbage bins, and when the garbage in these bins reaches the set level, indications are given to microcontrollers (MCUs). These MCUs then send notifications via SMS using GSM technology to the drivers of garbage-collection trucks.
In India, public dustbins are over-flowing. This creates unhygienic conditions for people. A smart waste management and monitoring system with automatic uploading feature can be effectively used to take care of this problem.
There are several electronic techniques that can help with the management of garbage or solid waste. Electronic hardware components include PLC MCU, LCD display, infrared (IR) and ultrasonic sensors, GSM modem, driver circuit, relays, robots and DC motors.
Some possible waste management options are waste minimisation, material recycling, waste processing, waste transformation and sanitary landfilling.
A waste processing treatment should:
- Be technically sound
- Be financially viable
- Be eco-friendly/environment-friendly
- Allow robust operation
- Allow maintenance to be controlled by the local community
- Have long-term sustainability
Evidently, India is lacking behind other countries when it comes to deploying an automated waste management system.
Startups in waste management
Today, several startups are coming up for waste management in India. Some of these are discussed below:
Timarpur Okhla Waste Management Co. Ltd.
This is the first commercial waste-to-energy project in India. It aims to convert one-third of Delhi’s garbage into much needed electricity—enough to serve 600,000 homes.
RVM Recycle Pvt Ltd.
This company has been conceptualised by three Indian School of Business alumini. It aims to revolutionise solid plastic waste management in India. The company has created a product that is based on reverse vending technology. Its automatic waste collection and segregation machine can process plastic, steel and aluminium bottles or cans, and reward people for their contribution towards Swachh Bharat Abhiyan through discounts, gift coupons, cashbacks and free Wi-Fi access.
Machines installed by RVM have a sensor-based mechanism that indicates when capacity of the machine is reached. It also calculates the time taken to fill the machines. Cost of transportation in waste management has reduced greatly by using these machines.
The concept of smart cities is resulting in better waste management. Effective waste management results in the reduction of carbon footprint, improved health and lifestyle of people, among other benefits. The concept of smart cities was started in India in 2015. Since then, a good number of smart products have entered the market to reduce waste. From smart bins to robotic road cleaners, smart cities are deploying interesting technologies to keep cities clean.
Another key area of focus in waste management is recycling of sewage water. Surat is one of the cleanest cities in India. It treats 57 million litres of sewage daily, which gets converted to 40 million litres of usable water. Jamshedpur in Jharkhand has set up bio-gas stations where waste is converted into reusable bio-gas.
Use of robots in waste management
Applying robots for public waste management and recycling can be challenging. Once such robots are developed, the next step is to create awareness among people and then to make the robots commercial. As far as waste management is concerned, robotics is still at an awareness phase.
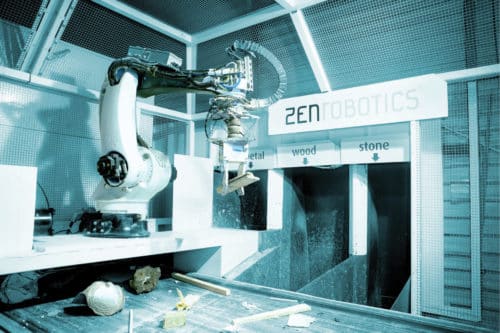
In 2011, Finland-based company Zenrobotics became the first commercial supplier of robots for waste sorting. The company has distributors in China, Singapore, the US and other countries, but it still does not have any distributor or branch in India.
A Spain-based company has developed robots powered by artificial intelligence (AI) for garbage sorting. The company provides robots smaller than those provided by Zenrobotics. Sadako robots can use proprietary algorithms that connect them to multi-layered neural network systems, which live in the cloud.
In 2016, Carton Council along with AMP Robotics and Alphine Waste and Recycling introduced Clarke robot. It can grab nearly 60 cartons per minute with near-perfect accuracy.

With the help of public awareness and global support, after crossing several hurdles, trash robots (trash-bots) are slowly becoming popular. These bots provide effective solutions for waste management. Their market is expected to witness a CAGR of 21.5 per cent by 2024. Reasons for such an alarming growth are:
- Robotics continuously reducing the cost of trash-bots
- Increased use of the Internet of Thing (IoT) technology, consumer electronics and connected devices
- Need for efficient waste-management systems
- Concept of smart cities
Trash-bots can easily sort the garbage, and increase productivity and efficiency. Visual sensors, metal detectors, weight-measurement sensors, spectrometers, 3D laser scanners and touch sensors are important components of trash-bots. These components can collect huge amounts of valuable data needed for recycling industries and act accordingly.
Connecting e-waste to waste management
Less than five per cent of India’s total electronic waste, or e-waste, gets recycled due to the absence of proper infrastructure, legislation and framework for disposing of electronic gadgets and products that have reached their end of life. According to Associated Chambers of Commerce and Industry of India (ASSOCHAM), India generates over 440,000 tonnes of e-waste annually (based on a 2012 survey). This is growing at a rate of about 20 per cent annually. About half of all unused and end-of-life electronic products lies in landfills, junkyards and warehouses.
Over 90 per cent of the e-waste generated in India is managed by the unorganised sector, and scrap dealers in this market dismantle the disposed-of products instead of recycling them. A number of startups have entered into e-waste management since the concept of smart cities and Make in India started. Some startups engaged in e-waste management are mentioned below.
- Altero Electronics Asset Management Co., which is mainly concerned with e-waste mining.
- Shivalic Solid Waste Management is an offshoot of UPL Group of Companies, Mumbai. It provides several waste-management services, including environmental monitoring, and e-waste, CFL and used lead-acid batteries recycling, among others.
- Namo eWaste Management Ltd was started by Akshay Jain, a 28-year-old entrepreneur from New Delhi. The company processes up to 20 tonnes of e-waste daily. With collection centres across 12 states and union territories across the country, the startup is building strategic partnerships with leading electronic companies.
The road ahead
In recent years, a large number of startups have ventured into the field of waste management. This number is expected to grow further. Such technologies as AI, Big Data, machine learning and robotics, if implemented properly, can make the Indian waste management sector much more efficient.
Vinayak Ramachandra Adkoli is BE in industrial production. He has been a lecturer in mechanical department for ten years, in three different polytechnics. He is also a freelance writer and cartoonist.






