PXI Express Platforms For Semiconductor Testing
As semiconductor testing grows more complex, PXI Express platforms can bring changes at both the measurement channel and system architecture levels.
ADLINK Technology has introduced...
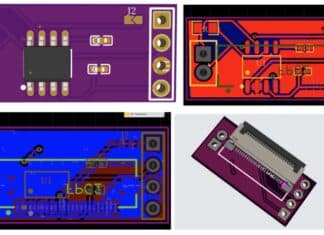
AI Tool For Faster PCB Part Creation
An AI tool converts component datasheets into symbols, footprints, and 3D models in minutes, saving time, reducing errors, and avoiding library work.
PCBPartz is live...
30 Rupees CAN Bus Transceiver Design
Transreceiver plays a crucial role in CAN bus communication, transmitting data from the MCU to the CAN network. While most MCUs, such as the...
Electronics Drive Stable Humanoid Walking
A real-time control system that sharply improves humanoid robot balance, accelerating reliable deployment in industrial and electronics-driven environments.
Researchers at the Georgia Institute of Technology...
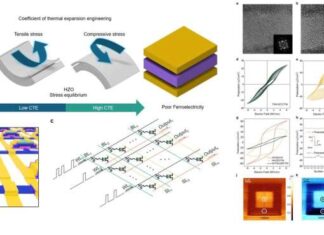
Thermal Design Reshapes AI Chips
Thermal constraining technique stabilizes ferroelectric transistors, boosting efficiency and endurance for next-gen electronics.
A team led by Professor Taesung Kim at Sungkyunkwan University has unveiled...
Honouring Engineering Breakthroughs At EFY’s Pune Auto R&D Awards 2026
From contactless EV charging and indigenous fast chargers to AI-driven design platforms and secure vehicle software systems, the Pune Auto R&D Awards 2026 by...
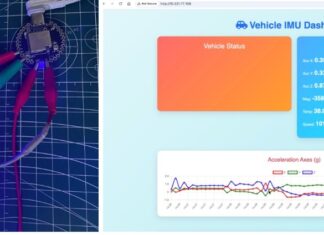
IoT-enabled CAN Bus Vehicle Monitoring System
This project demonstrates how to build an IoT-enabled CAN bus monitoring system using the Indusboard Coin. While the CAN bus is widely used in...
JOB: Hardware Test Engineer At BorgWarner In Bengaluru
APPLY HERE
Location: Bengaluru
Company: BorgWarner
Educational Qualifications: B.E. / B Tech /M Tech with Electrical / Electronics / Instrumentation.
Experience: Minimum 7 - 9 years of experience...
JOB: Member Technical Staff At Siemens In Noida
APPLY HERE
Location: Noida
Company: Siemens
This role involves developing and implementing emulation test plans to validate sophisticated semiconductor products. The engineer will leverage hardware description languages...
JOB: Electronics And Embedded System Engineer At IIT Bombay In Mumbai
APPLY HERE
Location: Mumbai
Institute: IIT Bombay
Qualification And Key Skills Required
PhD with relevant experience OR
MTech / ME or equivalent with relevant experience OR
BTech / BE or...