There are two most important things that you should consider whilst setting up a rework station. The first is that you must take all precautionary measures for electrostatic discharge (ESD)-sensitive components at the station. The second is that you should have all the correct tools for different jobs to make your rework more efficient.
ESD safety measures
Electronics is becoming smaller and faster but it is also becoming more sensitive towards ESD. The rework station needs to be specifically designed to minimise the effect of ESD, especially when various studies around the world have revealed that 60-90 per cent of defective devices are damaged due to ESD, and 70 per cent of these failures can be attributed to damage caused by ungrounded workers. So it becomes really important that you take ESD-control systems seriously, or otherwise, the losses can be astonishingly high.

A basic ESD control rule is to ground all conductors including workers at the rework station. Grounding works very efficiently in ESD-control systems and reliably removes ESD to ground. For such a grounding system, it is important that the electrical wiring system of your lab is correct. All electrical outlets in your lab need to be evaluated for correct wiring of live, neutral and ground wires.
A wrist strap is an effective method for grounding the workers. The Electrostatic Discharge Association’s standard ANSI/ESD S1.1-2006 defines a wrist strap as an assembled device consisting of a wrist cuff and ground cord that provides electrical connection of a person’s skin to the ground. The standard document completely describes the parameters for evaluation, acceptance and functional testing of wrist straps. Whilst the document describes the whole set of mechanical and electrical parameters over which a wrist strap needs to be evaluated and accepted, the most important parameter amongst all is the wrist strap continuity and resistance, which should be 1 mega-ohm ±20 per cent, for acceptance. The document also suggests the testing procedure for the same. Whilst you are buying grounding materials, do check if they comply with the above-mentioned standard and specifications.

Now to ground rest of the conductors, including equipment lying on the workstations, ESD mats should be used which cover the complete bench top. Best practice is to use metal grounding hardware snaps and ground wires connecting the work surface mat to the common point ground. ANSI/ESD S4.1 standard defines test methods for evaluating and selecting work surface materials, new work surface installations and previously installed work surfaces.
The defined guidelines for work surface in the document are mentioned below:
1. Resistance-to-groundable point 1×106 to 1×109 ohms
2. Resistance from point to point ≥1 mega-ohm
These guidelines represent a range of resistances that have been proven to provide protection in the manufacturing environment. If the mat’s resistance is too low, static transfers to the mat will be so fast that a spark is created. This spark is an ESD and will damage electronic devices. If the mat’s resistance is too high, static transfers to the mat will be so slow that the items placed on the mat will not lose their charge. When the item is removed from the mat, it will still have a static charge and be capable of discharging to other items. Vinyl and rubber are the materials that are widely used in making these types of mats. Vinyl is used in most cases. Rubber is used in situations where required resistance to heat and chemicals is high.
When you are working with sensitive electronic components, you should consider buying all the equipment for your workstation that is tagged as anti-static or ESD-safe. The materials mentioned below are optional but can be used for better electrostatic protected area (EPA):
1. ESD tables, chairs and stools
2. ESD-safe toolkit (cutter, plier, desoldering pump, etc)
3. ESD-safe equipment like soldering iron
4. ESD-safe brush
5. ESD-safe trays, bins and cabinets
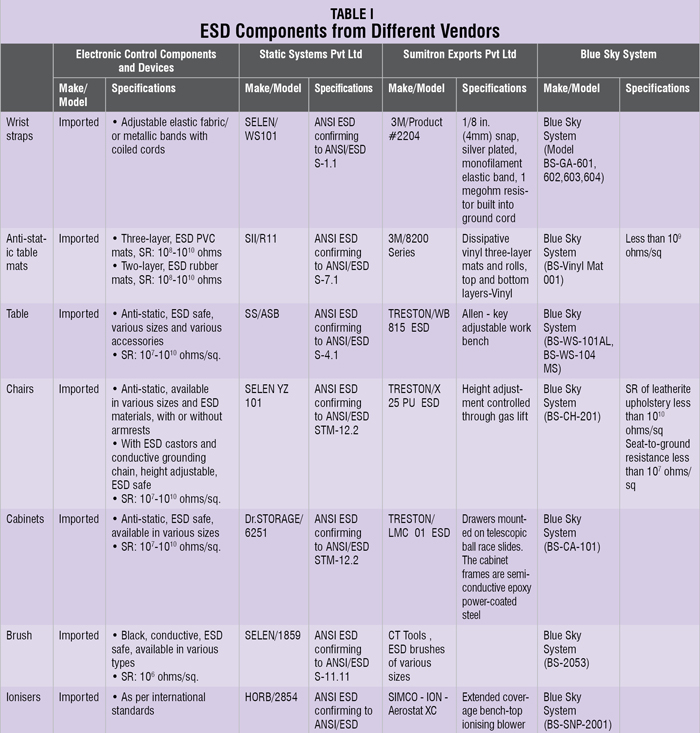
A bench-top ioniser can be used to neutralise ESDs at the workstation. This is the only ESD-control method available to neutralise ESDs on essential insulators or isolated conductors that may be at the workstation. The required limit according to ANSI/ESD S20.20 is less than ±50V offset voltage (balance). In addition to that, the discharge time to reduce +1000V to +100V and to reduce -1000V to -100V should also be measured. Faster the static elimination time, the better it is. Do look for one that strictly complies with the ANSI/ESD S20.20 standard. Refer Table I for anti-static components available from different vendors.
Correct and good-quality tools
It is easy to get away with cheap tools available in the market, but they may reduce the efficiency and quality of the job. Select each tool very carefully, considering your requirement in detail, to effectively set up the rework station. It is best if you can use all ESD-safe equipment and tools.








