Uncover the four unique modelling iterations and the pivotal role of the SHapely Additive Explanation (SHAP) method in interpreting the ML model’s insights.
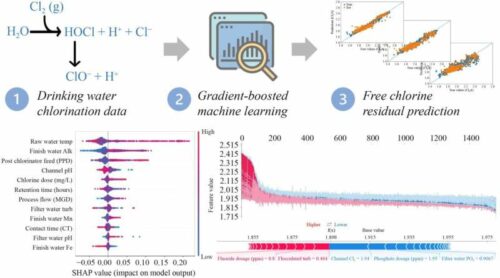
In the realm of small, rural drinking water treatment (DWT) plants, ensuring effective disinfection is of paramount importance. These plants typically rely on chlorine as their primary disinfectant, and the concentration of free chlorine residual (FCR) in the treated water is a crucial indicator of disinfection effectiveness. FCR represents the amount of free chlorine remaining in the water after it has reacted with contaminants, making it a vital performance measure. In practice, DWT plant operators determine FCR levels based on their experience, often requiring estimations of chlorine requirements. The challenge lies in accurately predicting FCR, which has prompted the exploration of advanced techniques, including machine learning (ML) algorithms.
A recent study published in Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering presents a novel approach to predicting FCR using a gradient boosting (GB) ML model, specifically employing the CatBoost technique. GB algorithms, such as CatBoost, leverage decision trees to formulate prediction functions. The study sourced input data from a DWT plant in Georgia, USA, encompassing a wide range of DWT monitoring records and operational parameters.
Four modelling iterations were developed, each with distinct characteristics:
- Base case,
- Rolling average,
- Parameter consolidation
- Intuitive parameters.
To enhance model interpretability, the research team applied the SHapely Additive Explanation (SHAP) method, an open-source software for interpreting ML models with numerous input parameters. SHAP enables users to visualise the impact of each parameter on the prediction function. For instance, the analysis revealed that the Cl2 channel was the most influential parameter in predicting FCR. The study’s key findings highlighted several critical insights: (1) ML models, when provided with an adequate number of relevant input parameters, can yield accurate predictions; (2) ML models may identify correlations that lack a direct physical basis; (3) ML models can emulate the decision-making process of experienced operators.
Looking ahead, the research team advocates for expanding the applicability domain in future studies. While the current dataset covered only one full year, more significant data availability is expected to enhance the model’s scope and predictive capabilities, further advancing the science of disinfection in small DWT plants.





