The weather has a profound impact on a person’s mood. Research shows that higher temperatures raise a person’s mood, while weather encompassing wind or little sun tends to make a person feel depressed. As temperature rises, intergroup conflicts and interpersonal violence are known to increase, even though only marginally. These findings hold well not only for higher temperatures but also for rainfall.
Global warming is being caused by an increase in the average temperature of Earth’s surface. For life to exist on Earth, an average temperature of 15°C is maintained by the natural greenhouse effect. Without this effect, the average temperature would be -18°C. This average temperature rose by about 0.9°C during the last century. Scientific studies indicate that average temperature will rise further by 1.1°C to 4.5°C during the 21st century, depending upon an increase in greenhouse gases emissions. As an result, net cereal production in South Asian countries is projected to decline by four per cent to ten percent by the end of this century.

Melting glaciers could seriously affect five billion people in Himalaya-Hindu-Kush region. There could be more intense rainfall resulting in floods and more dry days in a year, causing drought. Deaths due to heat waves, water-borne and vector-borne diseases like dengue are also expected to increase. The tsunami that occurred in 2004 took millions of lives and caused destruction worth billions of dollars.
This is merely a glimpse into the repercussions of climatic changes and it makes us realise how important it is to be able to predict the weather. Powerful computers are playing a key role in making accurate weather and meteorological forecasts. However, Earth’s atmosphere follows complex non-linear rules of fluid dynamics. Despite meteorologists having comprehensive knowledge of the current weather, it is actually challenging to calculate a forecast before the next change in the weather actually happens.
Therefore there is need for more sophisticated information technology (IT) in the form of supercomputers and advanced software to handle complex weather equations. For example, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Association (NOAA) uses a supercomputer called Theia, which can make as many as quadrillion calculations per second and has 28,000 computer cores.
Computer cores enable very-high-speed calculations. Each computer chip has multiple cores, so the chip can do multiple calculations simultaneously. In a supercomputer, the chips are interconnected. Hence a task like predicting the weather of New Delhi a week from now is split among thousands of chips and tens of thousands of computer cores.
Historical role played by IT
Back in 1916, World War I ambulance driver, Lewis Fry Richardson, imagined a worldwide system of weather prediction in which Earth was divided into 64,000 cells. Each cell was to report its weather conditions into a single central control area, wherein a computer would calculate the weather forecast for that cell. On completion of all calculations, cell-wise data would be posted and the process would restart.
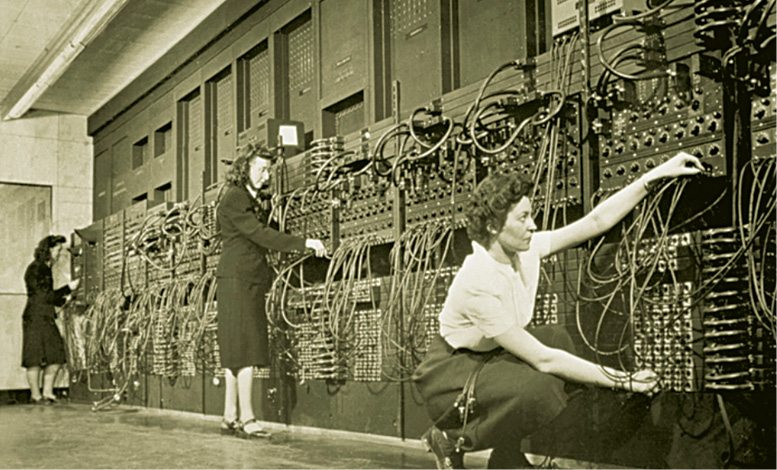

In this way, 64,000 people processing a constantly-evolving set of numbers would be able to arrive at non-linear equations essential to forecast the planet’s weather.
This method gave birth to two technologies that are currently in use, namely, 64,000-microprocessor supercomputers used by the government and large enterprises and computer-controlled mobile communication grids similar to those used in mobile phone networks.
It was John Mauchly, a computer scientist, who pioneered the usage of Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer, or ENIAC, the first electronic general-purpose computer, as a tool to facilitate long-term weather prediction.
How weather maps are created
Using various gadgets, instruments and tools, meteorologists state the present conditions of the atmosphere. These are then plotted on weather maps by computers to showcase the complete condition of the atmosphere around the globe. Quality control is achieved by computers, which rectify possible errors in the data related to weather. This leads to higher accuracy and reliability in reports.
To begin with, advanced computing systems are fed data to draw independent weather maps for the seven levels of the atmosphere used in forecasting. Once data has been analysed in the form of maps, IT is used to provide inputs by way of drawn maps, to determine the weather in each of the seven-layer grid. Thereafter, processing is carried out, that is, the various number crunching and tracking of the dynamic weather conditions. Final output encompasses the different types of weather maps based on a number of data points that have been collected and analysed.
Numerical forecasting is a term that refers to the usage of mathematical equations to forecast the weather and is based on a large number of very-high-speed calculations that only supercomputers are capable of performing. It is inferred that these equations are more multifaceted than those used in aerospace engineering.
On an average, National Weather Service (NWS) receives as high as 100 million weather observations every day. Data on a number of different variables such as wind speed, air temperature, barometric pressure and humidity is collected from many sources including land based observation points and ships moving around in the ocean. This information is then fed into a supercomputer, which usually has two sets of several fast processors capable of parallel processing. The first set performs weather-related calculations used in forecasting, while the other set is continuously looking for ways to improve the supercomputer’s software, thereby making weather predictions more accurate and meticulous.
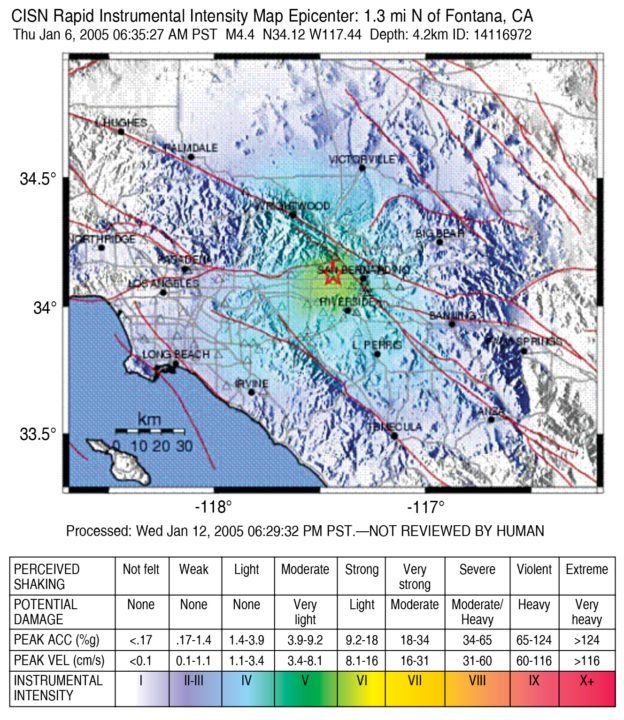
TriNet is a five-year-old collaborative project focused on producing a better, more effective, real-time earthquake-information system for southern California, USA. A high-tech system developed by TriNet has the capability to provide instantaneous damage reports for emergency relief in certain areas of greater Los Angeles area (USA). At its core, Tri-Net system consists of a broad array of earthquake sensors linked to computers. When an earthquake occurs, seismographs automatically record and transmit data to a computer at California Institute of Technology. The computer synthesises a shake map from the entire ground-motion data, which immediately informs emergency managers about the worst-shaken location. Emergency relief can then first be provided to the most severely affected areas. The shake map also indicates where the ground did not shake, thus enabling emergency crews to establish relief shelters and hospitals in areas near destruction points.
IBM’s Deep Thunder
Deep Thunder is a research project by IBM that aspires to develop short-term local weather forecasting using high-performance computing. The project belongs to the same family as Deep Blue system that beat world chess champion Garry Kasparov in May 1997. It uses information gathered by NWS but focuses on much smaller geographic areas than NWS and that too in greater detail.

Deep Thunder takes data and puts it through a numerical model, which predicts the weather. It works on software called Local Analysis and Prediction System (LAPS) that can process up to a million separate pieces of information each day. This entire system consists of several hardware and software components in an integrated environment, namely, a high-performance computer system (IBM RS/6000 SP), a forecasting model (such as RAMS, MM5 or WRF), a data-assimilation package (like LAPS), visualisation software (Data Explorer) and associated peripherals.
LAPS software developed by Forecast Systems Laboratory (FSL) of NOAA is a data assimilation and analysis package, which takes in local, national as well as global data from various sources such as satellite, radar and aircraft. LAPS functions as a pre-processing assimilation step, therefore resultant grid data from LAPS is used as initial conditions for the model. It executes serially on a single processor and does more than just model initialisation.
LAPS provides a high-resolution view of the atmosphere in its current state and derived products (like icing, visibility and clouds) and variables (like heat index and buoyancy), which prove useful for a wide array of real-time applications. It produces surface analysis and three-dimensional (3D) wind, temperature, cloud and moisture analyses, and also incorporates facilities to assess data quality.
Deep Thunder’s power can be gauged by the fact that it can produce highly-accurate weather predictions within the narrow ranges of a single city. The system was used during 1996 Atlanta Olympics to successfully schedule weather-affected events like sailing and the closing ceremony. It is also proposed to be used for 2016 Summer Olympics in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
How India forecasts its weather
Param was the first mission taken up by C-DAC for the development of a high-performance parallel computer and was completed in July 1991. Later, Param Yuva II was launched in 2013, which was capable of performing at a peak of 524 teraflop per second and was used for research in weather forecasting and seismic data analysis.
In 2015, India achieved another milestone with the release of supercomputer Bhaskara. This supercomputer assists meteorologists in research and predicts the weather, which includes effective forecast of tropical cyclones, heavy rainfall and cloud-burst events. Bhaskara enables Earth System Science Organisation-National Centre for Medium Range Weather Forecasting (ESSO-NCMRWF) to make very high-resolution 10-day deterministic weather forecasts and probabilistic forecasts from a 44-member ensemble prediction system. This is within the generally accepted time window of about five hours from the standard observation time with a horizontal resolution of 1.5km and probabilistic forecasts using an ensemble prediction system.
Bhaskara is powered with IBM iDataPlex supercomputer that has a peak computing power of 350 teraflops with 67 terabytes of aggregate memory. This takes the total ESSO high-performance computing facility to a peak computing power of 1.14 petaflops.
Conclusion
The tsunami disaster that devastated the world a few years ago could have been less lethal had better tsunami-warning systems been in place. Scientists studying tsunamis have their computers working as fast as possible, but they still cannot quite figure out how the killer waves behave or predict when and where these will strike next.
Computer modelling of tsunamis is very complex as it involves solving the full 3D motion of water. However, by using computer models of wave motions based on the known terrain of the undersea floor, scientists have managed to generate tentative maps that display the havoc a big tsunami could cause.
The IT industry needs to take up tsunamis forecasting based on effective computer modelling as an opportunity. In 2010, the storm and mudslides in Rio de Janeiro killed more than 200 people and rendered thousands homeless. This calamity made the city embrace IBM Deep Thunder weather-forecasting system in order to be better geared up for such future disasters.
Apart from saving lives, weather forecasting has a number of applications and uses. For example, public utility companies that provide, say, electricity can benefit vastly from forecasts. This can help identify areas where incoming storms are likely to damage poles, transformers and power lines. Hence, the required number of maintenance staff can be quickly transported to areas near disaster sites to carry out repair work and radically decreasing downtime.
In the area of agriculture, sophisticated weather-forecasting supercomputing systems can decide the best times to plant, irrigate and harvest crops, based on dynamic weather conditions of the various farm locations. This is likely to result in better crop prices, less water and manpower wastage for farmers.
Deepak Halan is associate professor at School of Management Sciences, Apeejay Stya University






