In the world of electricity, two primary types of current dominate: Alternating Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC). These currents, with their distinct characteristics and applications, play a vital role in powering our modern world. But what sets them apart? How do they behave, and where do they find their respective uses? What is the difference between AC and DC?
Table of Contents
This comprehensive article aims to shed light on the fundamental differences between AC and DC currents. We will explore their behaviours, generation methods, transmission capabilities, and applications across various industries. Whether you’re an electronics enthusiast, a student, or simply curious about the inner workings of electricity, this guide will provide you with a solid understanding of AC and DC currents.
What is AC Current?
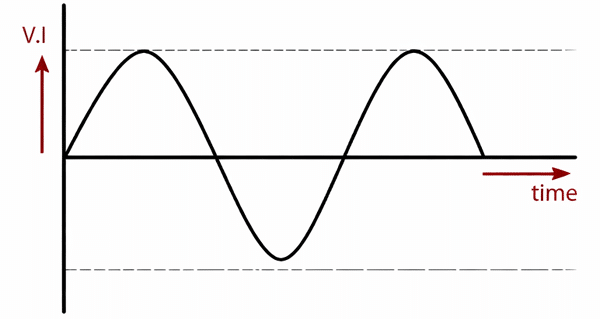
The AC current, also known as Alternating Current, changes its polarity and magnitude periodically and continuously with respect to time. The Ac current can be produced with an alternator that produces the alternating current.
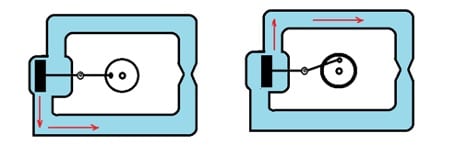
Let’s understand the Ac current with the water analogy-
Consider a scenario where a piston is placed inside a pipe and connected to a rotating rod, as shown in the provided diagram.
In this setup, the piston undergoes two distinct strokes: an upward stroke and a backward stroke.
During the upward stroke, the water within the pipe moves in a clockwise direction. Conversely, during the backward stroke, the water displaces in an anticlockwise direction. Consequently, the direction of water flow changes periodically as the piston oscillates back and forth.
Alternating Current Characteristics
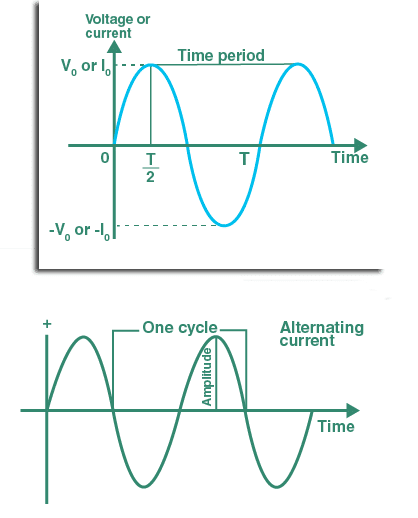
Time Period (T)
The total amount of time taken by a waveform to repeat itself or to repeat its one cycle is called the time period. You can also say the total amount of time taken by the waveform to complete one complete cycle is called the time period.
Frequency(f)
The rate at which the waveform repeats itself is called frequency, or you can say the number of times the waveform repeats in one second is called frequency. Its Si unit is Hertz.
f=1/T
Amplitude: The magnitude of the signal is called amplitude.
Waveform of AC Current
Every Ac waveform has a divider line, also called the zero voltage line, that divides the waveform into two halves as the Ac current changes the magnitude and direction periodically, so on every complete cycle, it reaches zero volts.
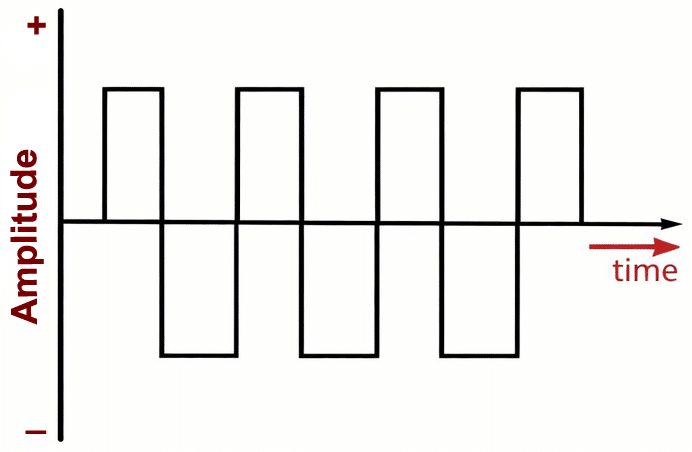
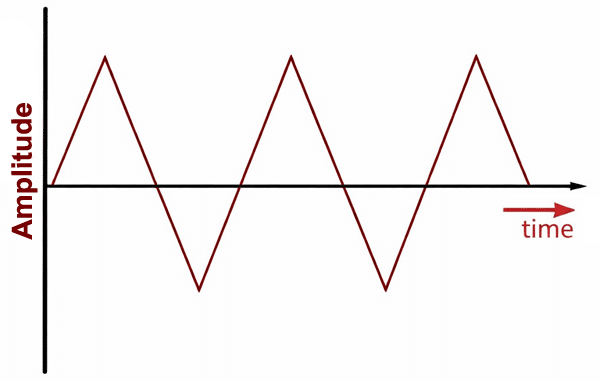
Types of AC Waveforms
Sine Wave

Square Wave
Triangle Wave
Applications of AC
- AC is used for long-distance transmission for Offices and Homes
- Energy Loss in AC is less, so widely used in transmission
- The AC current can be converted into a high voltage to low voltage and low to high voltage efficiently using the transformer
- AC power is used in larger applications and appliances like Freezers, AC, Dishwashers, washing machines, Fans, and Bulbs.
What is DC Current?
The DC, also known as Direct Current, is a unidirectional flow of current or electric charge; unlike AC, it does not change the magnitude and polarity with time. The DC current has constant magnitude and direction, and as the direction and magnitude do not change, the frequency of the DC current is zero. The electrons in DC current flow from high electron density to low electron density.
We can get DC from Ac current using the process called rectification, and the device that does this is called a rectifier.
Applications of DC Current
- DC current is widely used in small electronic devices and gadgets
- DC current is not suitable for long-distance transmission, but the storage of dc current is easy in the form of a battery.
- DC power is used in Cell phones, laptops, radios, and other electronic gadgets
- DC Current are used in flashlights
- DC current is used in EVs and hybrid cars and automobiles
Also read: Which is more dangerous, AC or DC?
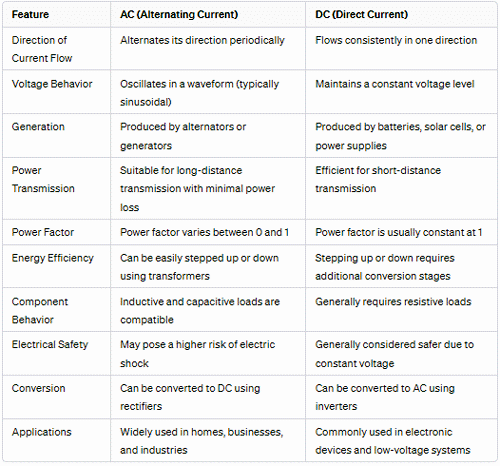
Difference Between AC and DC
- Ac current changes its direction during flow, while DC current does not change its direction during flow and remains constant.
- The AC current has a frequency that shows how many times the direction of current flow changes during flow, while the frequency of the direct current is zero, as it does not change the direction of flow.
- The power factor of AC is between 0 and 1, while that of DC is Constant at 0.
- The alternator generates the AC current, while the Photovoltaic cells, generators, and batteries generate DC current.
- The AC load can be capacitive, inductive, or resistive, but the load on DC is always resistive.
- The DC current graph has a constant line showing magnitude and direction are constant, while the AC current can be a sinusoidal wave, square wave, or triangular wave.
- The AC is converted into DC using a device named a rectifier, while the DC is converted into AC using an inverter.
- AC is widely used in industrial equipment and consumer electronics like AC, Freezer, Cooler, washing machines, lights, and fans; While DC is used in electronic gadgets and small devices like clocks, laptops, cell phones, and Sensors.
- Ac can be transmitted over long distances with some loss, while DC can be transmitted over very long distances with very low loss using HVDC








Very helpful I’m grateful for this special information, i have a better understanding on the difference between A.C and D.C
Thank you for your feedback.
Thanks alot, this is helpful
You are most welcome.
Thanks
Straight to the point, thank you
You are most welcome.
Difference between points plz mention on serial ways with separate. Thanks a lot for helping in study
Sir, Thank you for explaining AC and DC with simple analogy and illustration.
“Amplitude:-The magnitude of the signal is called amplitude”
It’s better to mention RMS, Peak, Average, Form Factor, etc.
“The power factor of AC is 0 to 1 While DC is Constant Zero.”
Power factor = cos ϕ
ϕ is the angle between the voltage and the current.
For a purely resistive (DC) circuit, the angle between the voltage and current is 0°. ∴ The power factor for a purely resistive circuit is:
P.F. = cos 0°
P.F. = 1 (unity)