LDR (Light Dependent Resistor) as the name states is a special type of resistor that works on the photoconductivity principle means that resistance changes according to the intensity of light. Its resistance decreases with an increase in the intensity of light.
It is often used as a light sensor, light meter, Automatic street light, and in areas where we need to have light sensitivity. LDR is also known as a Light Sensor. LDR are usually available in 5mm, 8mm, 12mm, and 25mm dimensions.
How are LDRs Made?

The Light-dependent resistors made with photosensitive semiconductor materials like Cadmium Sulphides (CdS), lead sulfide, lead selenide, indium antimonide, or cadmium selenide and they are placed in a Zig-Zag shape as you can see in the pic below.
Two metal contacts are placed on both ends of the Zig-Zag shape these metal contacts help in creating a connection with the LDRs.
Now, a transparent coating is applied on the top so that the zig-zag-shaped photosensitive material gets protected and as the coating is transparent the LDR will be able to capture light from the outer environment for its working.
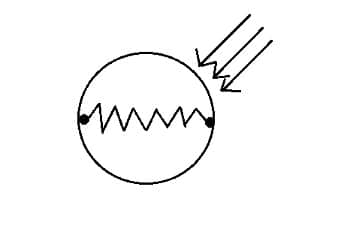
LDR Working Principle
It works on the principle of photoconductivity whenever the light falls on its photoconductive material, it absorbs its energy and the electrons of that photoconductive material in the valence band get excited and go to the conduction band and thus increasing the conductivity as per the increase in light intensity.
Also, the energy in incident light should be greater than the bandgap gap energy so that the electrons from the valence band got excited and go to the conduction band.
We have a detailed article on working, circuit, and construction of LDR.
The LDR has the highest resistance in dark around 1012 Ohm and this resistance decreases with the increase in Light.
Latency in Light Dependent Resistors for Circuit Design
Latency in LDRs manifests as a delay from the moment light levels change to when the resistor attains its stable resistance value for the new light condition. This delay can vary depending on the specific characteristics of the LDR and is a crucial factor in applications where light intensity changes rapidly.
For scenarios involving quick light transitions, LDRs might not be the optimal choice due to their slower response time. However, in environments where light changes occur more gradually, LDRs perform adequately.
Another related concept is the resistance recovery rate, which refers to the speed at which the LDR’s resistance returns to normal after a change in light exposure. Typically, an LDR will respond within tens of milliseconds to light after being in complete darkness, but it may take up to a second for the resistance to stabilize once the light is removed.
This behavior is often detailed in the component’s datasheet, where specifications such as dark resistance after specified time intervals—commonly one second and five seconds—are provided. These metrics offer insights into the latency of the resistor, helping designers understand how quickly the component reacts to changes in lighting conditions.
The implications of LDR latency are significant in circuit design. While the slow adjustment to light changes can be a drawback in fast-paced applications, this property can be advantageous in devices where a smoother response to light is beneficial, such as in audio compressors and other control equipment that benefit from gradual adjustments.
Moreover, understanding the latency characteristics of LDRs can aid in selecting the right type of photoresistor for specific applications. By considering both the latency and the light wavelength sensitivity, engineers can optimize electronic designs to better suit the operational demands of their projects.
LDRs are indispensable in electronic applications for their ability to change resistance based on light intensity and wavelength. The sensitivity of LDRs varies with different wavelengths, and their responsiveness diminishes when the wavelength is outside a specific range.
Additionally, the latency of LDRs—the time taken to adjust resistance in response to changing light levels—is a critical factor in circuit design, affecting how quickly devices can react to fluctuating light conditions.
By understanding both the wavelength-dependent sensitivity and latency characteristics, engineers can effectively select and utilize LDRs for optimized performance in specialized applications, paving the way for innovative and efficient electronic designs.
Difference Between Photodiode and LDR
Photodiodes give quick responses and are used where needed to detect quick responses on and off like in optical communication, and optoisolators. The photodiodes are semiconductor devices and work on PN junctions.
The photodiode works on the principle of converting the light energy into electric energy while the LDR is resistance, and its resistance decreases with the increase in light intensity. They are generally used in automatic security lights.
Whereas the LDR, Photocell, a photoelectric, photovoltaic effect, or photoconductivity is used to generate a current or a voltage when exposed to light or other electromagnetic radiation. They are generally used in burglar alarms.
For a detailed comparison, check the Difference Between Photodiode and LDR.
Types of LDR or Photoresistors
1. Intrinsic Photoresistor
This type of photoresistor is made with pure semiconductors without any doping. This kind of photoresistor uses pure semiconductors like silicon and germanium. when the incident light with an adequate amount of energy falls on this, electrons gain that energy and get excited, and a few of them go to the conduction band.
2. Extrinsic Photoresistor
This type of photoresistor uses a doped semiconductor; this means some impurities are mixed with the semiconductor such as phosphorus to make this photoresistor.
Extrinsic light-dependent resistors are generally designed for longer wavelengths of light, with a tendency towards infrared (IR).
In another article, we explained in detail different types of LDRs.
How to Test LDRs?
- Take a multimeter and set it up in Ohm’s mode.
- Now connect the positive terminal and negative terminal wires to the two sections of the LDR
- Place a glowing torch light or any medium of light onto the surface of the LDR and check the reading.
- Now place a hand over the LDR or place the LDR in the dark and check the multimeter reading.
- You can see that in 1st case the value of Ω would be lower than in the 2nd case. In the dark, LDR’s resistance is high as several megaohms, while in the light, it can get reduced to 100Ω also.
LDR Applications
- The photoresistor is generally used to detect the presence and intensity of light
- Used in automatic lights that switch on and off according to the light
- Simple Smoke Detector Alarm, Clock with automatic light
- Optical circuit design
- Photo proximity switch
- Laser-based security systems
- Solar Street Lamps
- Camera light meters
- Clock radios
- Can be used in Dynamic Compressors; some compressors use LDR and LED connected to the signal source to create changes in signal gain.
By understanding the specifications and applications, engineers and designers can better harness the potential of LDRs
Advantages and Disadvantages
LDRs are highly valued for several reasons, making them a go-to choice for projects ranging from simple DIY setups to complex professional systems.
Despite the numerous advantages of Light Dependent Resistors (LDRs), they also come with a set of limitations that can impact their effectiveness in certain applications.
Check the detailed analysis of advantages and limitations of LDRs.
Understanding both the strengths and weaknesses of LDRs is crucial for selecting the appropriate sensor for your specific needs, ensuring optimal performance and reliability in your applications.
Explore the Top 10 LDR-based Electronics Projects to try out.
People Also Ask
Below are the answers to each frequently asked question about Light Dependent Resistors (LDRs):
What is the difference between LDR and a phototransistor?
An LDR (Light Dependent Resistor) is a passive component that changes its resistance with the intensity of light. It decreases resistance as light intensity increases.
On the other hand, a phototransistor is an active semiconductor device that acts like a transistor but is controlled by light instead of electrical current. Phototransistors are faster and more sensitive, providing amplified output, while LDRs are slower and typically used in applications where gradual response is sufficient.
How does temperature affect the performance of an LDR?
Temperature changes can influence the resistance of an LDR. Generally, an increase in temperature causes a decrease in resistance due to enhanced electron activity in the photoconductive material.
This means that in high-temperature environments, an LDR may show lower resistance even without changes in light intensity, potentially affecting its accuracy in light detection.
Can an LDR detect infrared light?
Standard LDRs are designed to be sensitive to visible light, typically in the wavelength range of 400 nm to 700 nm. They are not effective at detecting infrared (IR) light because their photoconductive material does not respond well to IR wavelengths.
For detecting infrared light, devices like photodiodes or phototransistors designed for IR sensitivity are more appropriate.
Why do LDRs have a slow response time?
LDRs have a slow response time because the change in resistance relies on the movement of charge carriers within the photoconductive material. This process takes time, especially when switching from dark to light conditions or vice versa.
The delay is due to the time required for electrons to transition between the valence and conduction bands, making LDRs unsuitable for applications requiring rapid light detection.
How do you choose the right LDR for your project?
To choose the right LDR, consider the following factors:
Resistance Range: Select an LDR with an appropriate dark and light resistance range for your application.
Spectral Response: Ensure the LDR’s sensitivity matches the light source wavelength you plan to use.
Size: Larger LDRs generally offer more stability, while smaller ones are more responsive.
Response Time: Choose based on the required response speed. For applications requiring fast response, an LDR may not be ideal.
What precautions should be taken while soldering an LDR?
When soldering an LDR, use a soldering iron set to a low temperature and limit the soldering time to avoid damaging the photoconductive material. Excessive heat can alter the characteristics of the LDR, affecting its performance. It is advisable to use a heat sink or a clip to dissipate heat away from the LDR during the soldering process.
Can an LDR work in complete darkness?
In complete darkness, an LDR exhibits its maximum resistance, often in the range of several megaohms. While it cannot detect light in darkness, its high resistance level can be used to indicate the absence of light. This characteristic makes LDRs useful in circuits designed to activate when it is dark, such as night switches or light alarms.
Are there any safety concerns when using LDRs?
Some LDRs are made using cadmium sulfide (CdS), which contains cadmium—a toxic heavy metal. Handling these components requires caution, and proper disposal is necessary to prevent environmental contamination. Avoid breaking the LDR and dispose of it according to local electronic waste regulations.
How can the resistance of an LDR be measured?
The resistance of an LDR can be measured using a digital multimeter or an analog ohmmeter. Connect the LDR leads to the multimeter’s probes, set it to the resistance (ohms) mode, and observe the reading. Keep in mind that the resistance varies with light intensity, so the measurement should be taken in consistent lighting conditions.
What is the dark resistance of an LDR?
The dark resistance of an LDR is its resistance when there is no light falling on it. This value can range from hundreds of kilohms to several megaohms, depending on the type and size of the LDR. It indicates the maximum resistance of the device in complete darkness.
Can exposure to bright light damage LDRs?
Yes, LDRs can be damaged by exposure to extremely bright light sources like direct sunlight or laser beams. Prolonged exposure can degrade the photoconductive material, causing a permanent decrease in resistance or even failure of the LDR.
What is the spectral sensitivity of an LDR?
The spectral sensitivity of an LDR refers to the range of light wavelengths it responds to. Most LDRs are sensitive to visible light, with peak sensitivity around 550 nm, which corresponds to green light. Some LDRs may also have limited sensitivity in the infrared range.
Can LDRs be used in high-temperature environments?
LDRs are sensitive to temperature changes, which can affect their resistance significantly. High temperatures can decrease their resistance, altering performance. It’s important to select LDRs rated for the operating temperature range of your application to ensure reliable performance.
Can Light Dependent Resistors be used in wet environments?
LDRs are typically not waterproof and can be damaged by moisture. They should be used in dry environments or enclosed in a waterproof housing to protect them from exposure to water.
Can a Light-dependent resistor be used for measuring light intensity?
Yes, LDRs can be used for measuring light intensity. By using a voltage divider circuit, the LDR’s resistance is converted to a voltage, which can be measured with a voltmeter or an ADC. This voltage corresponds to the light intensity, allowing for basic light level measurements.
Can LDRs be used for color sensing?
No, LDRs are not designed for color sensing. They only respond to changes in light intensity, not to specific colors or wavelengths. For color detection, RGB photodiodes or color sensors are typically used.
Can LDRs be used for detecting motion?
LDRs are generally not used for motion detection, as they only sense changes in light intensity and not actual movement. Motion detection is typically achieved using passive infrared (PIR) sensors, ultrasonic sensors, or radar sensors, which are better suited for this purpose.
Why does the resistance of an LDR decrease when light intensity increases?
Because more photons release charge carriers in the semiconductor, increasing conductivity.
What material is used in an LDR?
LDRs are made from photoconductive semiconductor materials such as cadmium sulfide (CdS) or cadmium selenide (CdSe).
What is the purpose of using an LDR in a circuit?
To detect light levels and convert them into a changing resistance used for control or measurement.
What is the resistance range of an LDR?
Typically 100–1,000 Ω in bright light and 100 kΩ–10 MΩ in darkness.
How does the resistance of an LDR vary with changing light intensity?
Resistance decreases with increasing light and increases with decreasing light.
Why is an LDR made in a zig-zag or snake shape?
To increase its effective surface area, improving sensitivity to light.
What type of sensor is an LDR?
An analog light sensor.
What principle does an LDR work on?
Photoconductivity.
What affects the resistance of an LDR most?
The intensity and wavelength of light falling on it.
How do you adjust LDR sensitivity in a circuit?
By changing the fixed resistor in the voltage divider or adjusting the threshold in the controller.
What is the approximate resistance of a photoresistor in complete darkness?
Often 1 MΩ to 10 MΩ, depending on the type.
What component is used with an LDR in a voltage divider circuit?
A fixed resistor.







thanks for knwoledge
You are welcome.
I have a circuit using LDRs to monitor lighting in a room with florescent fixtures throughout. When directly under a fixture, and the LDR is covered, a separate LED is lit. Got that, no prob.
BUT when the same LDR circuit is placed in a part of the room not directly under the florescent fixture, the LDR doesn’t “see” enough light (as if covered) and thus the LED is constantly lit – that is a problem!
So, how can I vary the LDR’s sensitivity to react to the uneven amount of florescent illumination (illuminance) as in a corner of the room, etc)?
Should I be using photodiodes instead of LDRs?
Application: I’m a model railroader. I have RR crossing signals located where roads cross or intersect RR tracks (just as in prototypical situations). I’ve used OR IC chips so that multiple LDRs can detect when they are covered by freight cars or engines as they roll over them. When that happens, light is blocked and the RR crossing signals begins alternating flashings until the cars are past the LDRs when light is, once again, detected and the flashing stops as default.
We have shared your query on our forum page. Our community members will surely help you out. To follow the discussion, click here
very good