As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, the demand for efficient and secure communication between devices grows ever more critical. Thin edge computing, with its ability to perform computation at the edge of the network, has emerged as a key enabler of the Internet of Things (IoT). In this article, we explore the fascinating intersection of thin edge and IoT, and examine how this powerful combination is driving innovation and transforming industries.
As we all know, the Internet of Things (IoT) and cloud computing have been revolutionising all kinds of industries and have introduced so many business models as well. They are allowing developers to introduce new ideas.
Today, manufacturing is going through a fundamental transition. Gone are the days where post facto analysis of defects would happen; today it is more about precision manufacturing, more importantly predictive defect analysis. Most of the time the technology that lets you do that is either on the device side, edge side, or the cloud side.
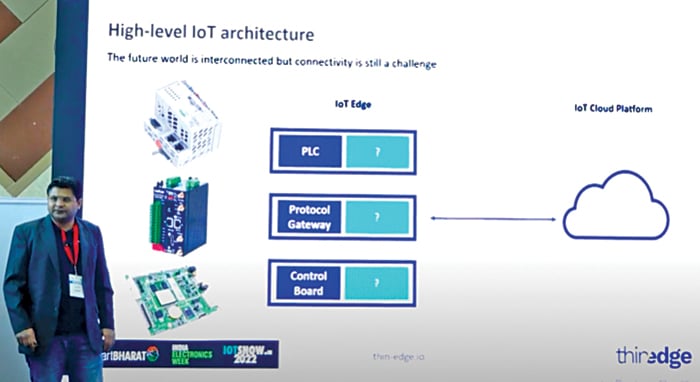
India is now making big moves in smart metering. Also, India is making investments to make changes in our consumption pattern of energy, such as oil and electricity. All of which is being done to improve the efficiency in consumption. And they are being driven by edge computing semantics.