On November 8, 2016, at 20:15, Prime Minister of India Narendra Modi addressed the nation through an unscheduled television speech. He declared that from November 9, 2016, the government of India would cease the usage of all 500- and 1000-rupee notes as legal tender, and instead new 500- and 2000-rupee notes would be available for exchange. The government claimed that this was being done to stop terrorism funding, crack down on black money, and reduce corruption and smuggling in India. However, after the announcement, banks and ATMs in the whole country faced severe shortages of currency.
The government of India is now trying to implement a cashless society. After the demonetisation move, several initiatives were taken to further encourage cashless transactions. Almost 300 per cent increase in digital payment activities has been observed since early November 2016.
In this article we present some of the many digital alternatives for making payments.
Debit and credit cards
A debit card is used to withdraw money from ATMs and to make purchases online and offline. The money is debited directly from your bank account. The card has a black magnetic strip on the back or a chip on one side, in which your account information and other details are embedded.
For making payments using a debit card, the merchant uses a point of sale (POS) machine to swipe or insert the card. Steps to be followed in this method are as follows:
1. While accepting a payment, the merchant submits the details after swiping or inserting the debit card on the POS machine.
2. You provide your personal identification number (PIN) though the machine.
3. After submission, the device communicates with your bank and deducts the amount from your account.
4. Two receipts are printed, one for you and the other for the merchant on the POS machine after successful payment.
5. An SMS from the bank confirming the transaction is sent to your registered mobile number.
In case of a credit card, the payment amount is not deducted while using the card; the payment is made later by the user.
Most online shopping websites support the use of debit and credit cards. Here, shopping venders direct you to the selected bank payment portals, where you enter your debit or credit card details like card number (16-digit number provided on the card), validity date and CVV number (last three digits provided on the back of the card next to your signature).
Then, you have to provide a one-time password sent by your bank to your phone or your Internet password for netbanking. A successful transaction message page is displayed after the payment is done.
RuPay is an Indian domestic card launched by National Payment Corp. of India. It facilitates electronic payments from all Indian banks. The procedure for using RuPay is the same as that of other debit cards.
Mobile/digital wallets
A mobile wallet is a virtual wallet where you can preload a certain amount of money from your bank account, and use this amount as cash. For example, if you go to a coffee shop and the coffee shop supports, say, PayTM wallet, you can pay your bill using the same.
There are four types of mobile wallets in India, namely, open, semi-open, closed and semi-closed. Open wallets allow you to buy goods and services, withdraw cash at ATMs or banks and transfer funds. These services can only be jointly launched with a bank; for example, M-Pesa by Vodafone and ICICI.

Airtel Money is an example of a semi-open wallet. To transact, the merchant must have a contract with Airtel. You have to spend what you add in the wallet, and would not be able to withdraw cash or get it back.
In a closed wallet, there is a certain amount in your account that will be locked with the merchant in case of cancellations or returns.
Semi-closed wallets do not permit any cash withdrawals or returns, but allow you to make purchases that support the wallet. The best example here is PayTM.
Steps to use a mobile wallet are:
1. Download the mobile wallet app on your mobile.
2. In the application, go to wallet section and add money to the wallet using the payment procedure.
3. After checkout from merchants who participate in the particular mobile wallet model, choose the mobile wallet option and pay. There are different types of verifications available in wallets like one-time password, PIN, scan code and so on.
NEFT, IMPS and RTGS
National Electronic Fund Transfer (NEFT), Immediate Payment Service (IMPS) and Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) allow fund transfer from bank to bank for individuals as well as companies. This can be done through the Internet banking facility, and it is possible to transfer money within the country only. To use these, you need to first add the beneficiaries to your account.
Please note that minimum amount for transferring through RTGS is ` 200,000. NEFT is settled in batches at the time defined by RBI, while RTGS and IMPS are settled immediately.
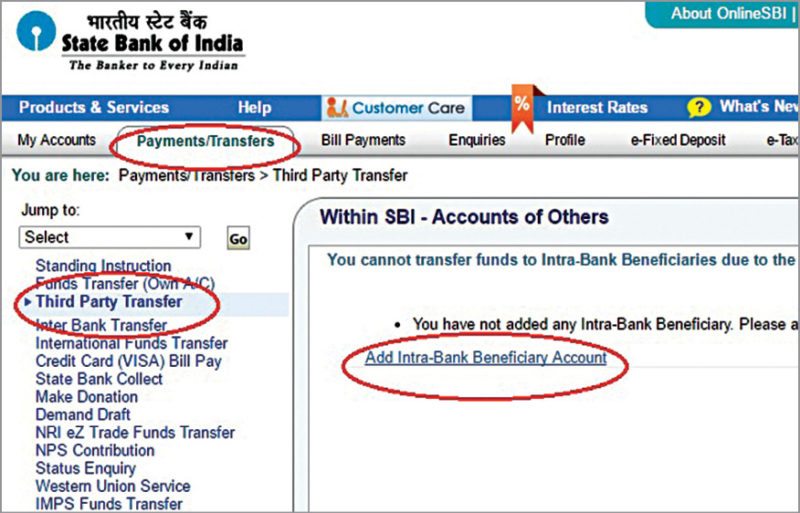
Steps for using NEFT/RTGS for State Bank of India Internet banking are:
1. Login to the Internet banking account.
2. On the account page, choose Third-Party Transfer option in the drop-down list. You will be directed to Add Beneficiary link; click on it (Fig. 2). You might have to provide your security password for that.
3. On this page, add beneficiary account details in relevent fields.
4. After successful addition of beneficiary details, the bank will take 24 hours to approve payment to the beneficiary account.
5. Once approved, go to Inter Bank Transfer option under Payment/Transfer tab. Opt for RTGS, NEFT or State Bank Group.
6. On the next page provide the amount and remarks, and select the beneficiary account. Transfer can also be scheduled for a later time. After giving the required details, you can transfer the money.
7. A successful transaction message will appear if the process is successful.
State Bank of India also provides quick fund transfer option, where adding the beneficiary is not needed. You can directly provide account details and amount to transfer, and send the money. A small service charge based on a slab may be applicable while transferring money through NEFT/RTGS.
IMPS facility is provided in banks to transfer amounts up to ` 200,000 immediately, after proper registration of the beneficiary.
UPI
Unified Payment Interface (UPI) is a system that helps combine multiple bank accounts into a single mobile application. It merges all bank features and other activities in one place. UPI helps you to pay directly from a bank account to another in online and offline modes. You do not have to add any beneficiary or insert any card details or IFSC code, etc. UPI applications are available for different banks. Since you only need to share the virtual address and not any sensitive bank information, UPI is much safer and faster.
After downloading and installing the application on your smartphone, follow the steps given below:
1. Set up application login information. Your mobile phone number must be the registered number in your account.
2. In UPI registration, you have to give a unique virtual address for the account. This account address will be in the bank domain according to the installed app. You can select the bank in which you have the account.
3. Enter other details and submit after accepting the terms and conditions.
4. After registration, create a password to login to the application.
5. Set up a UPI PIN. For this, select your options, and a one-time password will be sent to your registered mobile number. Using this password, you can create your UPI PIN (MPIN). After necessary setups, you can transfer money using this method to any bank account.
6. In UPI app (for example, SBI Pay) it is possible to pay through UPI or bank account method. If you choose UPI, you need to enter your UPI virtual address and details. For bank account transfer, you need to enter account number, IFSC code, payee name, etc.
7. While transferring using UPI, once you enter the virtual address, all other details will get automatically filled in various fields. You will be guided to security MPIN entry, and the transaction will be complete.
Note that, to transfer money through UPI, your bank must support UPI. Most major banks support it, including State Bank of India, Canara Bank, ICICI, UCO Bank, Federal Bank and Punjab National Bank.
BHIM app
Bharat Interface for Money or BHIM (Fig. 3), is a common application for all banks and financial institutions. The app does not require an Internet connection, so it can also work on feature phones. An Aadhaar based payment system will be added soon. After that, for transactions, BHIM will not even need a mobile phone or the Internet; thumb impression would be enough.
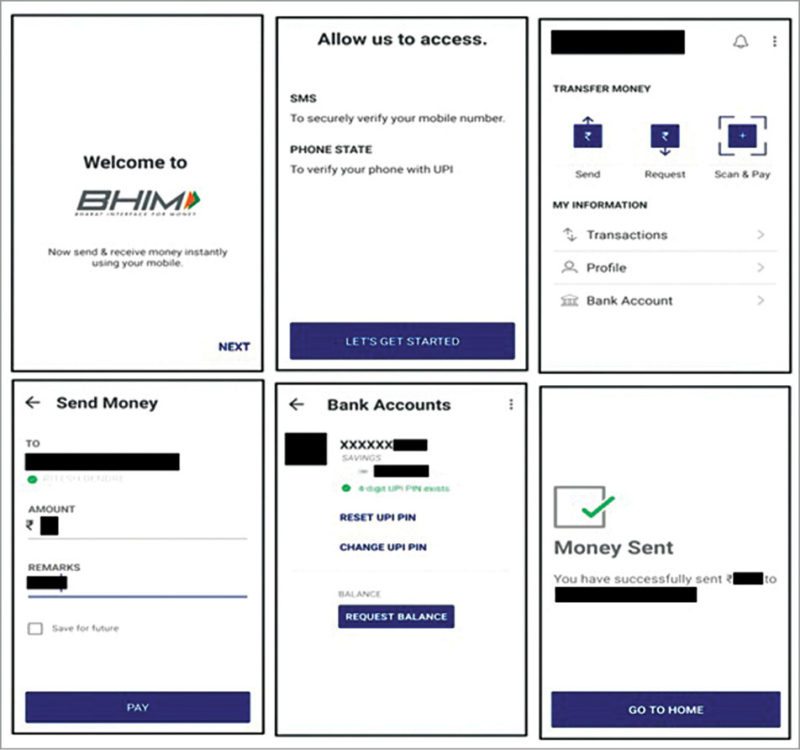
BHIM has features like linking bank accounts, sending and receiving money, profile saving, adding beneficiaries, changing languages and balance enquiry. Banks supporting UPI are already supporting BHIM app, and there will be more banks supporting it soon.
Steps for using BHIM are the same as UPI. You can use the existing UPI account for BHIM app.
USSD based mobile banking
Until now you saw applications and methods, except in case of BHIM, that needed at least a smartphone and Internet connectivity. But there are times when you do not have access to the Internet or even a smartphone, and that is when USSD based mobile banking can come to your rescue.
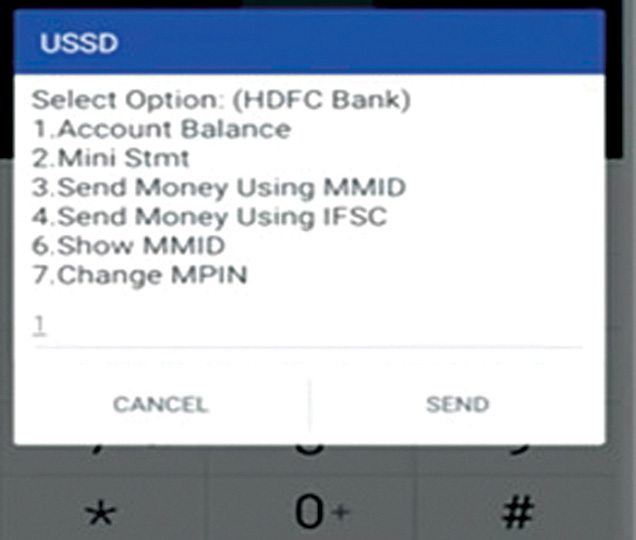
USSD is short for Unstructured Supplementary Service Data. Its platform is built by National Unified USSD Platform. Communication between telecom operators and banks is done through global system for mobile (GSM), since it works on phones with basic calling functions. This method aims to reach rural areas and non-English speaking people, and it supports up to 11 Indian languages. You can access your bank account and transactions using your registered mobile number. You also need a Mobile Money Identifier (MMID) and an MPIN, which will be sent to you by your bank.
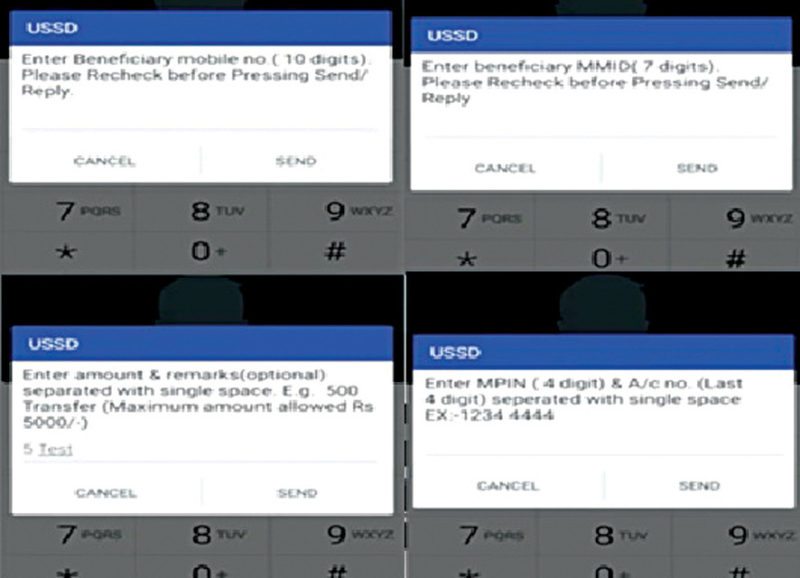
Steps for using this method are:
1. Dial *99# from our mobile number. You will get a greeting message asking for the first three letters of your bank’s name or its four-letter IFSC code. For example, for HDFC bank, type HFD (Fig. 4). If you are dialling for the first time, then you will get a welcome message asking you to register.
2. The second screen gives you options where you can type and send the option number and get the information of the bank. For example, if you want to know your account balance, type 1 and click on Send. You will receive the account balance.
Similarly, to transfer funds using MMID, type 3 in numeric and send. You will then have to enter the ten-digit beneficiary mobile number followed by the recipient’s MMID.
3. Enter the transaction amount, followed by space and transaction remarks. Then you will be asked to enter the four-digit MPIN and last four digits of your account number separated by space.
4. Once the transaction is authenticated, funds will be transferred to the beneficiary account.
As of now, there are limitations in options and some error message pops up from time to time. Also, transaction limit is ` 5000 per transaction.
Gift cards
A gift card is a pre-stored value money card issued by a merchant or bank. It can be used as an alternate to cash for purchasing in a store or from a retailer. It is similar to a debit/credit card, which has a specific number or code; sometimes, information is available on the magnetic strip at the back.
You can purchase a gift card directly from the merchant or bank, or can also get it online. The person you gift the card to can use it to buy something of his or her choice. The balance can be carried over to the next purchase(s).
Manu Prasad is M.Tech in VLSI and embedded systems, and is currently working as assistant professor at AWH Engineering College, Kerala. His interests include VLSI, EDA tools, MATLAB and Latex







