
Choosing the right digital multimeter (DMM) requires thinking about what you will be using it for. Evaluate your basic measurement needs and job requirements and then take a look at special features/functions built into many DMMs. Think about whether you need it for basic measurements or for more advanced troubleshooting options.
Aspects to consider
Resolution and accuracy. Resolution of a DMM is expressed in the number of digits the unit can display. For example, a 4½ DMM has four full digits that display values from 0 to 9 and the fractional digit, which is the most significant digit in the display. Fractional digit is either 0 or 1. Such a meter shows positive or negative values from 0 to 19,999.
Accuracy of a DMM is different from display resolution. It is the maximum allowable limit of error in readings. All DMM manufacturers express accuracy specifications as ±(% of reading+number of least significant digit).
Working environment.
Measurements types. Almost all DMMs make voltage, current and resistance measurements. Most make accurate AC measurements with sinusoidal signals, but when such signals are not simple sine waves, their accuracy suffers. If you need to make AC measurements of signals that have a lot of harmonic distortion, you may want to purchase a DMM that makes true-rms AC measurements. These cost more but will make more accurate measurements.
Many DMMs are designed to solve complex problems in electronics, plant automation, power distribution and electromechanical equipment. With the ability to log data and review it graphically onscreen, you can solve problems faster and help minimise downtime. When selecting a digital multimeter (DMM) for data logging, important specifications include the speed at which the DMM can make measurements and the amount of memory it requires.
To work safely near electrical panels while wearing less personal protective equipment, or to avoid the risk of being bogged down while chasing interrelated events, one has to adapt to wireless DMM.
True-rms versus average-responding DMMs. Basically there are two types of DMMs: average responding and true-rms. The latter is a consistent and standard way to measure and compare dynamic signals of all shapes and sizes, whereas the former is calibrated for sine-wave inputs only.
Average-responding meters normally work well for linear loads (standard induction motors, resistance heating, incandescent lights and more), but if non-linear loads (electronic/electric-discharge lighting, adjustable-speed drive systems and so on) are present, errors occur, which could make the readings lower than expected. If you want to measure non-linear loads such as those found at electronic controls, you should choose true-rms.
DMM input impedance. It is especially important to select a DMM with high impedance for applications requiring measurement of sensitive electronics or control circuits to ensure accuracy of the readings.
Basic aspects. A basic DMM measures AC/DC voltage, AC/DC current and resistance, checks continuity and diodes, and includes auto-ranging feature. More expensive DMMs also measure capacitance, frequency, temperature and pressure. Before purchasing one, you should first identify the type of testing you need to perform, establish which features are important and determine the required tolerance range for those tests.
Specialty aspects/functions. Besides basic DMM measurement functions, consider looking for a DMM that offers avant-garde capabilities to befit your application needs. These avant-garde DMM functions save time when performing troubleshooting tasks. Here are some of the advanced capabilities designed to soothe the job of engineers and technicians.
Vsense. Voltage sense detector (Vsense) is a non-contact voltage detector in insulated wires, wall receptacles, fuses, junction boxes, switches and more that detects the presence of AC voltages nearby. If the presence of AC voltage is sensed, the multimeter’s beeper sounds and the LED turns on.
Smart ohm. This (offset compensation) is another feature designed to remove unexpected DC voltages within the instrument at the input or at the circuit being measured, where resistance measurement errors are introduced.
Data logging. This feature makes it easy for factory maintenance personnel to generate a range of troubleshooting, monitoring and process documentation. The personnel can also collect data over an extended duration to support installation or repair of factory systems such as heating, ventilation and air-conditioning.
LPF. A regular true-rms DMM cannot measure output from a motor drive because the variable frequency drive applies pulse-width-modulated, non-sinusoidal voltage to the motor terminals. The low-pass filter is designed to help block unwanted voltages above 1kHz when measuring AC voltage or AC frequency.
Harmonic ratio. This feature can help technicians quickly check for the presence of harmonics in the electrical power system. A pure sinusoidal waveform without harmonics has a harmonic ratio of zero per cent.
ZLOW (low impedance mode). With dual-impedance meters, technicians can safely troubleshoot sensitive electronic or control circuits as well as circuits that may contain ghost voltages. They can more reliably determine whether voltage is present on a circuit.
With low-impedance input to the circuit under test reduces the possibility of false readings due to ghost voltages and improves accuracy when testing to determine absence or presence of voltage.
Safety consideration. Many people do not give much thought to safety when buying a DMM. However, there are large differences in how good DMMs are protected against common electrical hazards. It is very important to consider the environment and applications you will use in order to choose an appropriate device. With these safety criteria in mind, there would be no physical damage to the device or life-threatening contact to electric energy while you hold it in your hand.
Voltage rating. It is important to identify the maximum voltage at which the circuit is designed to work. Choose a digital multimeter (DMM) rated to measure voltage that is expected to be present on the circuit.
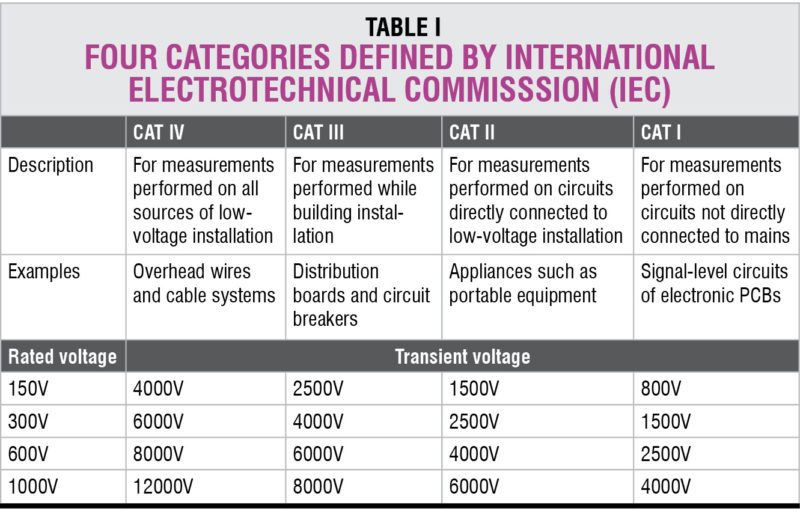
Transient voltage rating. Such voltage comes from two main sources: natural causes such as lightning outside the building or by switching operations on the power-distribution system. Switching events in power distribution include switching of transformer taps, motors, inductances, sudden variation of load or disconnection of circuit breakers. Amplitudes of these voltages vary from a few hundred volts peak to about 6000 volts peak. These randomly-occurring high-voltage spikes tend to last from 50 microseconds to 200 microseconds.
Energy capacity. To protect yourself you should also know the energy capacity of the circuit before you start taking measurements. Circuits with higher energy capacity can deliver more current and energy into faults than low-energy circuits.
There are four categories (Table I) defined by International Electrotechnical Commisssion (IEC) that all manufacturers of DMMs are required to mark their products with. These are CAT I, CAT II, CAT III and CAT IV. With these markings one can easily identify what the maximum transient voltage is that the meter can safely withstand.
Safety indicators. Responsible manufacturers of DMMs obtain safety certifications from independent third-party testing agencies. These marks can usually be found at the back of the devices.
Digital multimeter (DMM) probes should also be marked with a logo of a third-party safety-testing agency. You can check out some such marks in Fig. 2.
Other important features. Large displays, clear backlight to read comfortably in dark areas, ergonomic design for good grip while working, rugged body design with high-grade drop-proof material to ensure no break/damage even when dropped from a height, availability of warranty, service and affordable service parts are other important features to look for.

Standards and certifications in Digital Multimeter
IEC 1010 standard is the safety standard for low-voltage test and measurement equipment. Look out for CE, UL, CSA and other symbols, safety categories (CAT certification) and EMC certification that would certify that the meter will work in inductive areas and so on. The digital multimeter (DMM) should have ingress protection (IP) certifications, which protect it against dust, water or any liquid and guarantees uninterrupted performance in harsh conditions. Look for IP ratings such as IP42, IP30, IP54, IP67, etc.
Calibration to standards of ISO or NIST is particularly important to companies that hold related certifications. These certifications indicate products that are made to very rigorous standards, so obtaining DMMs with correct certificates is important in these cases.
Wireless DMMs
 Fluke 233 remote display digital multimeter (DMM) comes with an innovative wireless display. It allows observation 9.1m (30-feet) away from the measurement point.
Fluke 233 remote display digital multimeter (DMM) comes with an innovative wireless display. It allows observation 9.1m (30-feet) away from the measurement point.
Fluke CNX 3000 wireless digital multimeter (DMM) is the captain of Fluke wireless team. It displays meter measurement plus readings from up to three wireless modules, as far as 20 metres away. If more than three readings are required from more modules, you can add an optional PC adaptor to your laptop for real-time viewing of up to ten modules.
EXTECH EX540 and EX542 are twelve-function wireless true-rms industrial DMM/dataloggers (up to 9999 readings) with a wireless PC interface.
Smart DMMs
The new range of DMMs offers a new way to perform measurements much more accurately and comfortably with additional features like measurements through mobile applications. Using an app, the user can control any data remotely in real-time using a mobile phone or another mobile device with Android OS.
PROMAX PD-350, PD-351, PD-352 are DMMs with rms and Bluetooth control via an Android app. These also feature smart power-off function, which extends battery life.
OWON DMM – 35 category maintains features like voice warning supported to assure measurement safety, smart voice-reading, smart power-off option extending battery life, supports mobile device with Android 4.3 or above/iOS 7.0 or above and is equipped with BLE 4.0 module.
Keysight meter logger for Android smartphones and tablets improves productivity and safety by allowing the user to stream measurements in real-time from up to three Keysight DMMs and clamp meters wirelessly.
What Future Holds For Digital Multimeters
For the most part, the future of digital multimeter (DMM) will evolve slowly as these are well-establish, general-purpose test equipment that do not need to conform to rapidly-changing applications are. For such applications or those that need to address certain parameters, there will be more specific meters. They will address the needs of each application requirement and the resulting instrument would not be called a DMM.
Where you will see some changes to digital multimeter (DMM) in future will be inclusion of more memory for logging and graphing of data, along with wireless transmission of said data.
Love reading this article? Explore similar articles
Biswajit Das is manager-R&D, EFY Labs









The article seems mostly about general electrical applications.
Electronics field requires micro and milli range of voltages and currents, among other things.
The ability to select a wide range of voltages, currents and ohms are important.
You would realise the problem only when you cannot measure small signals (milli volt/current) of a BJT or JFET or sensor.
Also, test leads/probes along with saftey ratings should be flexible and strong.
These points have not been covered.