NOVEMBER 2011: Agri-electronics is an emerging and multidisciplinary frontier of advanced research that takes convergent and holistic look at all the related areas in the agricultural sector. It ensures optimal induction of IT and electronics for improvement in crop productivity, quality and value.
R&D in agri-electronics is a potential vehicle for digitisation of green revolution. It promises a catalytic role in national agricultural development in terms of diversification, enhancing productivity, adding value, capturing markets, mixing farm and off farm income, entering and creating marketing chains, improving food quality and safety, and balancing ecological interests.
Scope and challenges of agri-electronics
The latest practice adopted worldwide is precision agriculture. It implies knowledge based agriculture employing the latest techniques of science and technology bringing together diverse fields agronomy, plant science, soil science, entomology, metrology, weed science, plant pathology, ecology, water technology, environment and economics to deal with complex issues of production, distribution, pricing, marketing, etc.
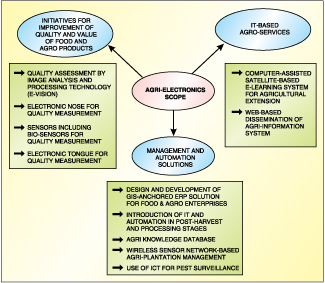
Fig. 1 shows the scope of agri-electronics. To deal with cross-disciplinary complexities, multitudes of technologies like bio-electronics, sensors, software, embedded systems and soft computing need to be harnessed to develop efficient agri-electronics solutions. Management of new technologies for agri-electronics research is one of the stiffest challenges. Agri-electronics research must be carefully planned and modulated to take account of present and future trends in agriculture, bio-technology, and information and communication technology (ICT).
Partnerships and networking are essential for a multidisciplinary field like agri-electronics. It is imperative that agri-electronics research be conducted through alliances. Stakeholders and researchers from different organisations need to collaborate to identify the needs for specific kinds of knowledge, to implement research projects, and to disseminate results.
Bringing different interest groups together (such as policy-makers, scientists, traders, farmers, producers, governments, industries and consumers) is the key to increasing the contribution of ICT research in agricultural development.
National status
Agri-electronics activities at the national level may be divided into two major categories: Electronics and instrumentation for agriculture, and ICT for agriculture.
While very few national R&D laboratories are involved in the field of electronics and instrumentation, government agencies, NGOs and ICT companies in the private sector are involved in developing and deploying e-solutions mainly focused on information dissemination services. Such ICT services include advisory information provision over the Internet or mobile devices to the farmers on weather forecasts, price information, etc.
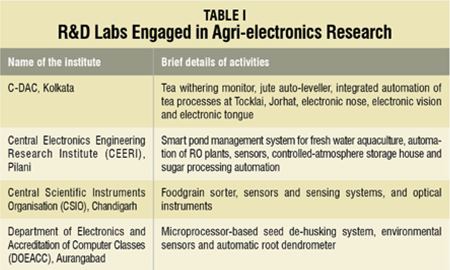
IT and electronics in agriculture. Table I shows the R&D labs in India that are engaged in agri-electronics research to develop novel and smart instruments.
Agri information dissemination systems. In India, there are 46 Web portals and 39 IT based Web enabled applications already operational. All these portals and applications provide information transaction services to the government departments, agro marketers at all levels, farmers and all the stakeholders in agricultural domain.
Though a number of these Web based portals have very friendly user interfaces and presentations in vernacular languages, these are not yet used regularly by the small and medium farmers due to a number of reasons including lack of infrastructure, lack of IT literacy and inadequate content. Of course, the portals find good use in government to government transactions.
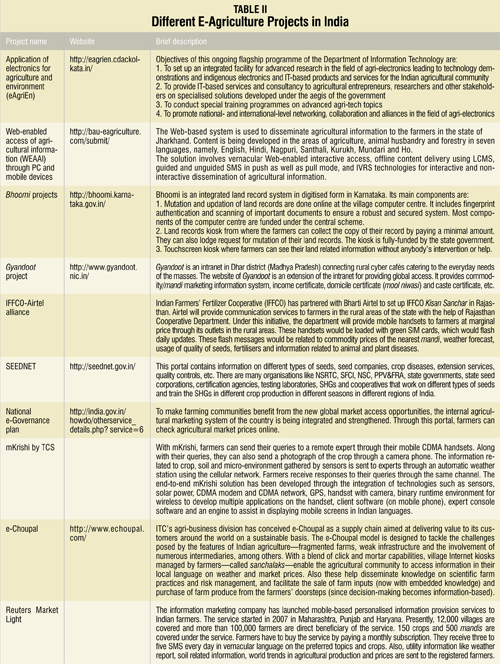
A comprehensive farmers’ portal is under development by the Ministry of Agriculture & Cooperation, government of India. Mobile governance is also making its way to the e-governance arena, and a number of solutions using mobile-based agro advisory services are being developed by a number of companies. A brief synopsis of such e-agriculture initiatives is given in Table II.
The following conclusions can be drawn from the above discussion:
1. In India, more stress is in deploying eagriculture solutions over the Internet or mobile devices by multiutility Web portals.
2. No focus is directed towards development of smarter electronics and instrumentation systems in India.
3. Even the deployed ICT projects in India provide very few success stories, and there is no widespread outcome and impact at the grassroot level.
In view of the above, there exists an emergent need for focused and integrated endeavour towards development of smart devices for the agricultural sector and coupling of the smart devices to the intelligent software through advanced telecommunication (Internet or mobile devices).
A few innovative solutions have been developed for quality measurement, monitoring and management of Indian crops. These innovations are detailed in the box.
[stextbox id=”info” caption=”INNOVATIONS”]
1. Electronic nose (e-nose) for aroma characterisation of black tea
An emergent need for some physical, fast and lowcost methodology for measurement of physical quality attributes like smell has been felt by the food processing industries, especially black tea manufacturing industries in India. The e-nose system proposes a pragmatic methodology for measuring the aroma of black tea by fusion of advanced sensor technologies backed up with intelligent self-learning-type software algorithms.