Electronic devices have not only transformed the lifestyle of common people by providing comfort, security and entertainment, but have proved a boon for people with injuries or physical disabilities. This type of electronics is generally called assistive electronics.
There are many people using assistive electronic devices. Stephen Hawking is an important example with the best use of these. In 1963, he contracted motor neurone disease and was given two years to live.
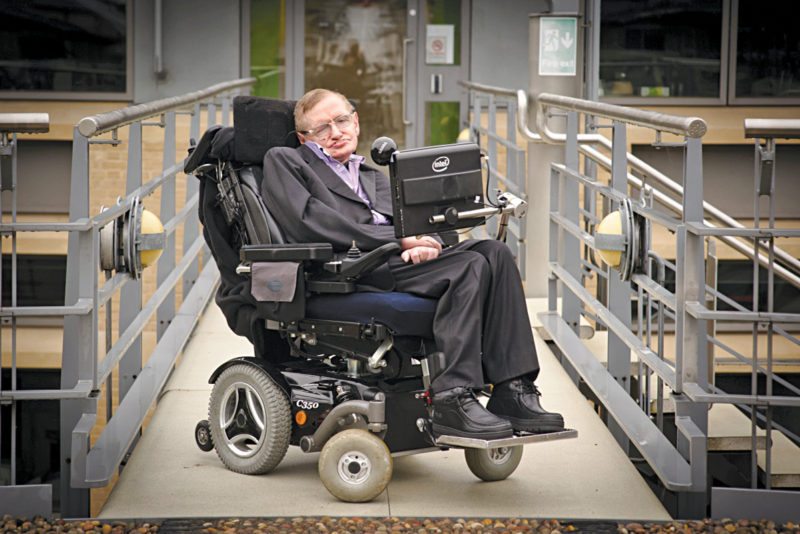

Hawking suffers from a rare early-onset, slow-progressing form of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neuron disease or Lou Gehrig’s disease, which has gradually paralysed him over the decades. He communicates using a single cheek muscle attached to a speech-generating device.
Yet, he went on to become a brilliant researcher and professorial fellow at Gonville and Caius College. From 1979 to 2009 he held the post of Lucasian professor at Cambridge, the chair held by Isaac Newton in 1663.
Hawking has more than a dozen honorary degrees and was made Commander of the Order of the British Empire (CBE) in 1982. He is a fellow of The Royal Society and a member of the US National Academy of Science. He is regarded as one of the most brilliant theoretical physicists since Albert Einstein. He is the former Lucasian professor of mathematics at University of Cambridge and author of A Brief History of Time, which was an international bestseller. His other books for the general reader include the essay collection Black Holes and Baby Universe and The Universe in a Nutshell.
At present, Hawking is at Dennis Stanton Avery and Sally Tsui Wong Avery, as director of research at Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics and founder of Centre for Theoretical Cosmology at Cambridge.
For his communication, he initially raised his eyebrows to choose letters on a spelling card, but in 1986 he received a computer program called Equaliser, which is used to help people suffering from ALS who have lost the ability to speak and write. Hawking could simply press a switch to select phrases, words or letters from a bank of 2500-3000 that are scanned.
The program was originally run on a desktop computer, but later a small computer was attached to his wheelchair. Released from the need to use somebody to interpret his speech, he commented that, “I can communicate better now than before I lost my voice.”
Hawking gradually lost the use of his hand and, in 2005, began to control his communication device with movements of his cheek muscles. With this decline, there is a risk of him developing locked-in syndrome, so he is collaborating with researchers on systems that could translate his brain patterns or facial expressions into switch activations.
Assistive electronic devices
There are a number of assistive electronic devices or rehabilitation equipment to aid people with injuries or physical disabilities. These are tools, products or types of equipment that help people with disabilities or injuries, or the elderly perform daily tasks and activities. These devices may help to move around, see, communicate, eat or get dressed/undressed, and help a person improve the quality of life and maintain a sense of independence.
Well-designed high-quality assistive devices promote greater independence by enabling people to perform tasks that they were formerly unable to accomplish or had great difficulty accomplishing, by providing enhancements to or changed methods of interacting with the technology needed to accomplish such tasks.
An assistive device could be a wheelchair, smartcane for the blind, hearing aid, Braille smartphone, smartbelt, smartring or a disability product (like a bionic organ). Certain devices like eyeglasses and hearing aids require an expert’s assessment, but devices like wheelchairs, walkers, bath seats and grab bars are easily obtainable.
Given below are some high-tech assistive electronic devices that are helping those with disabilities lead full and fulfilling lives.
Assistive devices for mobility/ambulation can also be referred to as ambulatory aids. Such aids like canes, crutches and walkers provide an extension of the upper extremities to help transmit body weight and provide support for the user.
A combination of electronics and computer devices gives individuals suffering from paralysis, cerebral palsy and stroke the ability to participate in spoken communication using only their eyes. Using a sophisticated eye-tracking system, they can interact with an onscreen keyboard, allowing them to enter words and phrases, which are then translated into spoken text via the device’s text-to-speech mechanism.
SmartCane is an electronic travel aid that fits on the top-fold of the white cane. It serves as an enhancement to a regular white cane and overcomes its limitations by detecting knee-above and hanging obstacles. For safe mobility, it is important that such obstacles are detected early.
The cane has other uses as well. As a spatial-awareness device, it can detect the presence of objects in its surroundings. Also, as compared to the white cane, the detection distance is increased from 0.5 meters to three meters. It informs about the presence of objects before actually touching these with the cane and thus helps in preventing unwanted contact. This avoids socially-awkward situations like collision with people while walking or unsafe collision with animals or into trash.
SmartCane uses ultrasonic range to detect objects in its path and generates tactile output in the form of different vibratory patterns. These vibrations convey the distance information and thus enable the user to negotiate obstacles from a safe distance. With simple orientation and training, any visually-impaired person who is a regular user of the white cane for mobility can benefit from this device.
Travelling alone can be a challenge for the visually impaired, whether it is across the country or down the street. There is always the possibility of taking a wrong turn or getting disoriented in the shuffle of busy pedestrians. That is where a personal navigation device, which is a very small GPS locator, plays an important role.
As the user walks down the street, the device speaks directions and locations, so the user always knows where he or she is and where he or she is headed. In addition, the user can plan and store routes and tag locations for later reference.
Designed as an affordable GPS accessory (and not a replacement) to the cane or guide dog, the device offers an incredible amount of security, confidence and a wealth of useful information, allowing blind people to travel independently without the fear of getting lost or wandering in the wrong direction.
Speaking of mobility for the blind, engineers are developing a car that can actually be driven by the blind. The aim is to integrate several computer systems, sensors and cameras to observe the environment around the vehicle and provide alternate forms of sensory input, including sound and vibration. This may include seat vibrations of various strengths and locations, pulsing vibration signals in gloves worn by the driver, auditory alerts from a headset and a sort of screen that paints a virtual picture of the surroundings using compressed air.

The technology is extremely promising, and even if the vehicle never makes it to the street as a legal, safe and affordable car, the sensors and innovations coming out of the project are sure to help in other areas. Not only could this serve as a means of independent, safe transportation for the visually impaired, but also for many individuals with physical and mental handicaps that prevent them from operating a motor vehicle. Whether it is further study of brain re-mapping and alternate sensory input, practical implications of better sensors and safety devices that can be applied to all motor vehicles or an all-out safe and practical means of driving blind, this technology excites many.
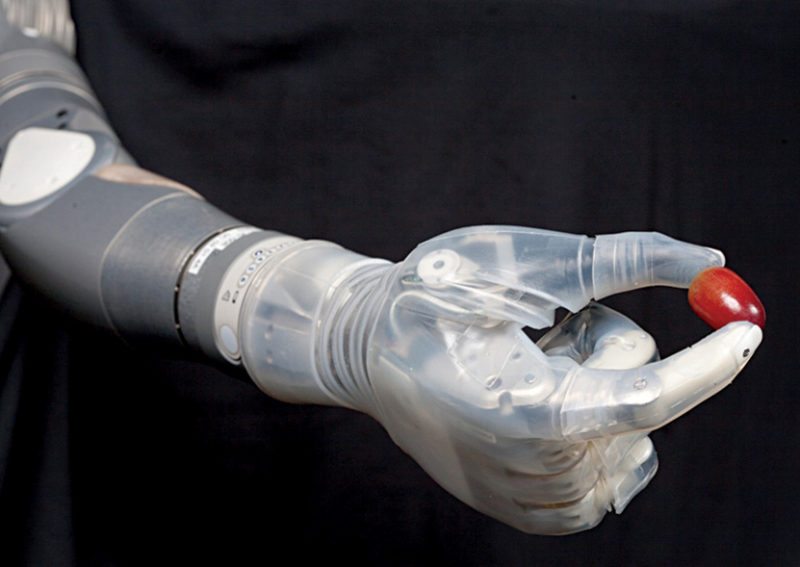
A group of researchers have developed a highly-sophisticated, highly-functional prosthetic arm and the results are amazing—a less-than-3.6kg prosthetic arm with such precision and control that it can peel a grape. The arm supports a number of customisable controls and modular components, making it easy to tailor to the wearer’s individual needs, whether he or she requires only a hand or an entire arm and shoulder socket.
Another promising feature of the arm is its sensory feedback system. Hand sensors measure the strength of the hand grip, for instance, and provide feedback to the wearer in the form of vibrations that grow stronger as the strength of the grip increases. This enables the wearer to learn what level of grip strength is appropriate for specific tasks and how much pressure is being applied.
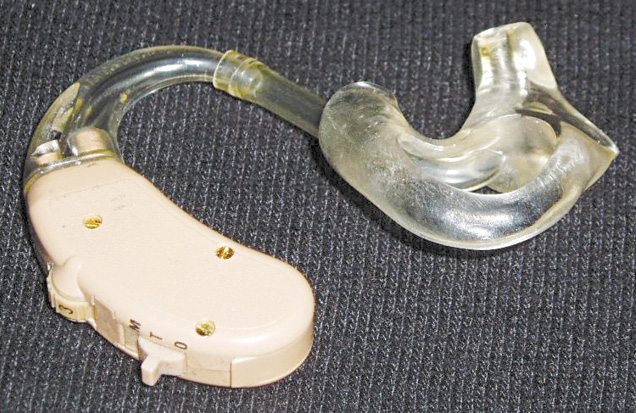
Development on the cochlear implant first began in the late 1950s, and the first commercial implant device received approval in 1984. However, cochlear implants have come a long way. Initially, the single-channel implant provided mostly static, while early commercial implants with five channels allowed for some indication of cadence and rhythm.
Today’s cochlear implants, however, have more than 20 sound channels, allowing wearers to hear with much better quality. The implants are still far from perfect, with background noise continually being a problem, but the technology has advanced to such a point now that voices can be heard with enough clarity to be readily understood and identified, making verbal communication possible and productive.
Cochlear implants are pretty amazing and only grow more so as the software and hardware continue to improve. More than just a hearing aid, these first pick up a sound via a microphone, which carries the signal to a small computer worn behind the ear, where it is transferred to a digital signal and transmitted to the implant itself. Once received by the implant, the device directly stimulates the auditory nerve, providing an entirely new means of auditory sensory input.
Stairs are nearly everywhere and navigating these in a traditional wheelchair is impossible. Enlisting the services of others to drag or carry the person up and down the stairs is dangerous, inconvenient and often embarrassing. iBot is a self-balancing, stair-climbing wheelchair for the physically disabled. Using self-balancing technology, it aims to give wheelchair-bound individuals the freedom to navigate any terrain.
Advancements in wearable technology enable people with disabilities to carry on with everyday functions. Winkymote is an infrared remote control hidden in make-up that helps quadriplegics change TV channels by blinking. This development has grown to include metalised false eyelashes that can activate various electronic devices and other cosmetics tech products.
People with epilepsy experience seizures at any time, often without warning. In May 2013, senior engineering students at Rice University in Texas developed Seizure Monitoring and Response Transducer (SMART) belt to detect signs of seizures. This belt can also wirelessly send messages to guardians or caretakers. It is meant for people aged six and above, and is still under development (at the time of this writing).
There are mobile phones with Braille number keys, but what about touchscreen smartphones? Researchers are developing a phone with a screen comprising a grid of pins. When the user receives a message, the pins form shapes and characters using shape memory alloy technology.
With Lucy 4 keyboard, people with limited or no use of their hands can operate a computer. The user mounts a battery-operated laser pointer on the glasses or headband and selects keys on the custom stand-up keyboard. A woman named Janine who has cerebral palsy created Lucy and even created a website and an introductory video using her invention. Lucy 4 keyboard allows people with disabilities to compute, while lessening fatigue.
DynaVox’s EyeMax uses eye-tracking technology for computing, watching television, reading books and speaking for people with limited mobility. EyeMax’s camera tracks the user’s eye movements, allowing him or her to use the device simply by blinking or gazing.
The form of home automation called assistive domotics focuses on making it possible for the elderly and disabled to remain at home, safe and comfortable. Home automation is becoming a viable option for the elderly and disabled who prefer to stay in the comfort of their homes rather than move to a healthcare facility. This field uses much of the same technology and equipment as home automation for security, entertainment and energy conservation but tailors it for the elderly and the disabled.
Home robots are helpful for people who cannot easily clean their homes with traditional equipment. These use localised navigation to clean their environments thoroughly.
Bionic devices are revolutionising prosthetics, giving users more control.
Google Glass is often seen as a gadget for tech-savvy geeks who want to remain connected at all times, but Catalin Voss is working to create face-tracking software for the augmented reality glasses. It is a tool for users with autism and related disorders. The face-tracking engine helps people better recognise and understand others’ facial expressions and, in turn, their emotions.

A Kerala based IT company has developed a smartring to control electronic gadgets such as mobile phones, car music systems, home appliances and more. It can be worn on a finger and used to switch on and off electronic gadgets including mobile phones without picking these up. The ring can also be used as a car key and enables users to attend phone calls or control the music system without taking their hands off the steering wheel.
It uses smart, low-energy technology such as Bluetooth for communication with connected devices. It can transmit natural gestures as commands to a Bluetooth-connected device such as a smartphone, music player, gaming console, digital interface inside a car or television set.
Further scope
Assistive electronics technology can be customised with the use of electronics to make life easier for a disabled person. The personal computer can be the backbone of independence for millions of individuals with sensory, physical and learning disabilities.
Many people with disabilities face a variety of challenges in terms of providing computer input, interpreting output and reading documentation. For such persons, the keyboard, mouse and monitor are of prime concern. Therefore adaptive hardware and software have been developed to provide alternatives.
Screen-reader programs are designed to allow even completely blind people use the computer. These convert text and icons to speech so they can use a computer without needing to look at the monitor.
Accessible computer equipment and compute-access aids can make it easier for users to use word-processing programs, surf the Internet and send emails, but these can also help non-computer users handle many non-computing tasks.
Any system that aids individuals who are not independent verbal communicators is known as an augmentative communication system. The system can include speech, gestures, sign language, symbols, synthesised speech, dedicated communication aids or microcomputers.
Voice-recognition and dictation systems are powerful assistive technologies that allow persons with disabilities control a computer and dictate documents verbally using spoken commands.
A number of companies as well as individual entrepreneurs are focussing on people living with disabilities. They are creating adaptive devices to help improve their customers’ lives. Legislation (Disabilities Discrimination Act) and social awareness and concern for persons with disabilities are also fostering development of assistive technology.
Incorporating assistive technology, these gadgets include anything that help people complete everyday tasks, and these cover all ranges of complexity. This is a very exciting time for new developments in assistive technology. Development programs are regularly updated so new and previously-unseen technology is en-route to improve accessibility for the disabled.
With the advent of e-book readers like Kindle, Sony E-reader and Nook, there could be another wave of new methods for people with learning disabilities and other conditions to access e-books and books. However, not all devices have text-to-speech capability, and if this proves useful, other producers of e-book readers will probably follow suit and adopt that utility in the near future.
Specialty computer stores often carry items like screen-reading software that include screen-enlargement features for persons with vision impairments. Voice-recognition systems, modified keyboards and computer mice are also available for people with mobility and dexterity limitations. By current estimates, more than 4000 assistive technologies have been designed for the disabled and seniors. These include everything from wheelchairs to a wide assortment of high-tech tools.
Many companies today are turning their research and development to assistive technologies. To benefit from using an assistive device, there is a need to consult a healthcare professional such as doctor, pharmacist or an occupational therapist to find out what is available to suit individual requirements. It is important to not let the disability or sensory loss infringe on the lifestyle, especially when tools and devices exist to help and overcome these obstacles.
Dr S.S. Verma is a professor at Department of Physics, Sant Longowal Institute of Engineering and Technology, Sangrur, Punjab







“At present, Hawking is at Dennis Stanton Avery and Sally Tsui Wong Avery, as director of research at Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics and founder of Centre for Theoretical Cosmology at Cambridge”.
I’m sorry to remind you that Hawkins died in 2018