New soft robots are mimicking the function of human muscle protein, myosin, that generate large, unrestricted moves through contractions.
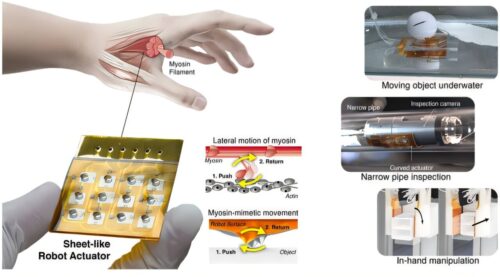
Developments in the robotics industry are continuously upping the game of application-based electronics. A research team from POSTECH (Pohang University of Science and Technology) has taken credit for creating a thin and flexible robotic actuator, mimicking human muscle protein behavior, the Myosin, responsible for contractions and movement.
Traditional robots have inbuilt rigid metal components giving them strength and durability, but at the same time limiting their motion ability to deal with tight spaces, perform high precision narrow tasks, or operate in confined environments.
This robotic intervention is as thin as paper and capable of generating strong grip forces, giving robots an option to maneuver through tight-knit spaces, deal with narrow and highly precise tasks.
The look of an actuator is similar to an ordinary flat sheet, but inside it lies a complex system of multiple air chambers and layered multi-channel pneumatic pathways.
When air is injected in sequence, tiny surface protrusions move in multiple directions, combining to create powerful motion. Even when bent, the actuator can crawl supporting six-axis movement—up, down, left, right, rotation, and diagonal—with adjustable speed and range.
The research is backed by positive experimental outcomes. Applications include tasks like cleaning narrow pipelines, assisting precision surgeries, industrial use involves inspecting confined spaces, home cleaning, and helping with all those tasks that were impossible due to location, space, or other obstacles.
Professor Keehoon Kim quoted “successfully integrating a complex three-dimensional pneumatic network within a thin and flexible structure, enabling multi-directional movements through a bio-inspired approach. We hope this technology will be applied in various fields, including surgical robots, collaborative robots in industrial settings, and exploration environments.”






