AI can now run fast on small devices, use less memory, and still work well. Can this new method change everyday tech? Read more!
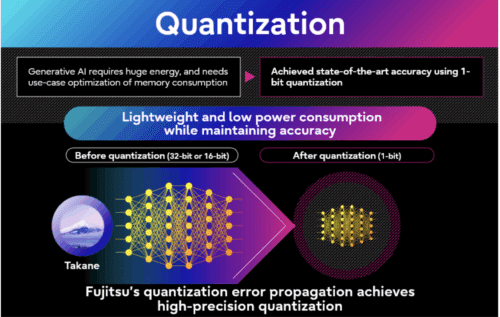
Fujitsu has developed a generative AI reconstruction technology that allows large AI models to run on a single low-end GPU. The method combines 1-bit quantization and AI distillation, achieving a 94% reduction in memory use, 89% accuracy retention, and three times faster inference speed, exceeding conventional methods like GPTQ. This allows AI deployment on edge devices such as smartphones and factory machines, improving performance, data security, and reducing power use. Fujitsu plans global trials for Takane with this technology in the second half of fiscal year 2025 and is releasing quantized versions of Cohere’s open-weight Command A models via Hugging Face immediately.
The technology is inspired by the brain’s ability to reorganize neural circuits and specialize in skills. It extracts only the knowledge needed for specific tasks, producing efficient AI models. Quantization compresses neural connections, reduces power use, and prevents error accumulation in multi-layer networks. Specialized distillation mirrors brain processes, removes unnecessary knowledge, and uses Neural Architecture Search to select the best model. Knowledge distillation transfers expertise from larger models like Takane into smaller, task-specific models that can perform better than the original.
Tests show improvements across multiple applications. In sales negotiation prediction, inference became 11 times faster, accuracy increased by 43%, a student model with 1/100th of the parameters performed better than the teacher model, and GPU memory and operational costs dropped by 70%. In image recognition, unseen object detection accuracy improved by 10% compared to existing distillation methods, achieving over three times better accuracy over two years.
The company plans to continue enhancing Takane to create specialized AI for finance, manufacturing, healthcare, and retail. The company aims to reduce model memory up to 1/1000 while maintaining accuracy, allowing AI across devices. Over time, these models are expected to evolve into AI agents capable of understanding the world and solving problems.