Handling cameras, radar, and sensors in one system can be very complex. Imagine sending data, power, and control over a single cable. Find out more!
Automotive and industrial systems increasingly rely on multiple sensors, including cameras, radar, and LIDAR, to support advanced driver assistance, surround view, and monitoring applications. Designing these systems poses several challenges. You must handle high-speed data from multiple sensors, provide synchronized clocks, deliver power reliably, and maintain bidirectional control communication. Complex cabling, limited space, and integration of diverse sensors can increase system cost and design time. Additionally, automotive electronics need protection against faults such as reverse polarity, without sacrificing efficiency. Ensuring all these requirements while maintaining robust performance is a significant challenge in multi-sensor system design.
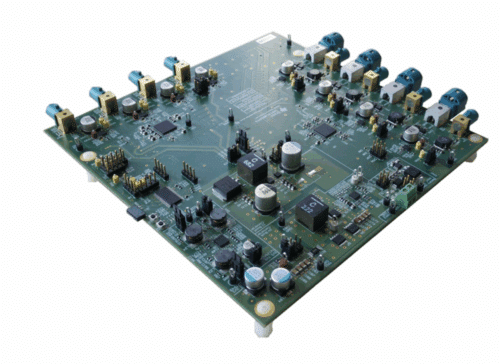
TIDA-01413, the reference design from Texas Instruments (TI) addresses these challenges by simplifying multi-sensor integration. It allows up to four 2-megapixel cameras and four radar modules to connect using a single coaxial cable per sensor. These cables deliver power, transmit sensor data, enable back-channel control, and synchronize clocks. By combining high-speed data and bidirectional control signals on one cable, the design reduces system complexity, lowers cabling costs, and improves reliability. Two high-speed deserializers provide dual digital output ports that connect directly to application processors or SoCs, supporting efficient data aggregation from multiple sensors.
At the core of the system, high-speed serializers at the sensors and a multi-channel deserializer at the hub manage data streams from cameras and radar modules. This setup supports multiple camera inputs at 2-megapixel resolution with 60 Hz frame rates, ensuring timely and accurate sensor data for advanced driver assistance or industrial applications. Bidirectional passive switches and high-speed multiplexers allow flexible signal routing between sensors and processors without adding extra cabling, providing engineers with adaptable design options for complex systems.
Power delivery and protection are integrated into the reference design to ease implementation. Step-down converters supply multiple regulated outputs from a wide input voltage range, while eFuse switches provide bidirectional current control and fault protection. Reverse polarity protection is implemented using MOSFET-based controllers that emulate ideal diode behavior, preventing voltage drop and improving system efficiency. Low-power microcontrollers offer fast wake-up times and control for battery-powered or portable modules, adding to the system’s versatility.
By consolidating high-speed data, control, and power over single coaxial cables, this reference design addresses the most pressing challenges in multi-sensor integration. Engineers can implement systems with simplified cabling, synchronized data, reliable power delivery, and robust protection features. The design also allows easy scaling to support additional sensors and advanced applications, such as camera monitoring, mirror replacement, surround view, or sensor fusion in ADAS domain controllers.
The design provides a practical solution for multi-sensor automotive and industrial systems, helping engineers reduce design complexity, cut development time, and achieve reliable operation while managing high-speed data, control, and power efficiently.
TI has tested this reference design. It comes with a bill of materials (BOM), schematics, assembly drawing, printed circuit board (PCB) layout, and more. The company’s website has additional data about the reference design. To read more about this reference design, click here.