In this project, I show how to control a robotic arm servo using real-time hand tracking powered by AI image processing. We use MediaPipe for fast hand detection, a web browser for processing camera input, and an IndusBoard Coin to translate hand movement into servo motion. The result is a simple but powerful human-machine interface that connects hand gestures directly to robot movement.
AI image processing has become one of the most practical tools in modern robotics. From factory automation to human-machine interfaces, vision-based control systems are now replacing traditional input devices.
In this project, I combine real-time hand tracking with robotic control to demonstrate how natural hand movements can directly control a servo motor. The idea is simple. Your hand becomes the controller, and the robot responds instantly.
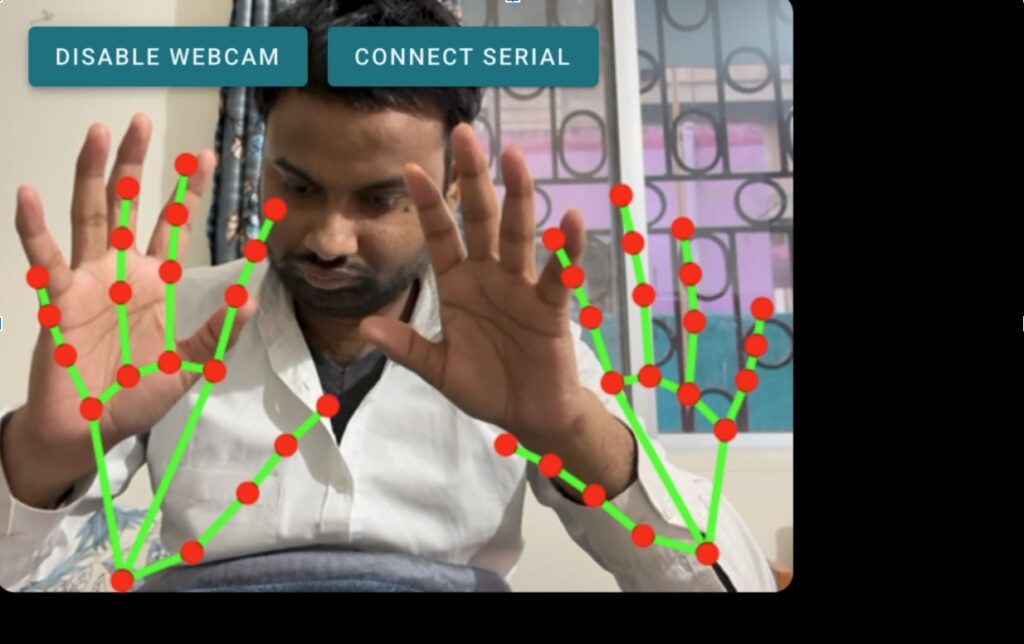
This approach is especially useful in industrial environments where touchless control is preferred, such as welding stations, assembly lines, soldering setups, and training simulators.
Why MediaPipe Is Used for Hand Tracking
For hand detection and tracking, I use the MediaPipe hand tracking model. It is fast, lightweight, and works efficiently inside a web browser. MediaPipe detects key hand landmarks and provides accurate x, y, and z coordinates in real time.
These coordinates are exactly what we need to translate human hand movement into robotic motion without adding extra sensors or hardware.
How the Hand Tracking Robot Control System Works
The complete system works in three simple stages:
- A webcam captures live video of your hand.
- MediaPipe processes the video and extracts hand movement coordinates.
- These coordinates are sent to the IndusBoard Coin through the WebSerial API.
- The IndusBoard Coin maps the received values to a servo motor using PWM.
This makes the browser act as the AI brain, while the controller board handles motor control.
Bill of Materials
You only need a few components to build this project:
- IndusBoard Coin: 1
- Microgear Servo Motor: 1
- USB Type-C Cable: 1
This minimal setup makes the project easy to replicate and scale.
Circuit Connections
For the servo motor, you can use any free PWM-compatible pin on the IndusBoard Coin. All standard servo motors work with PWM signals, so pin selection is flexible.
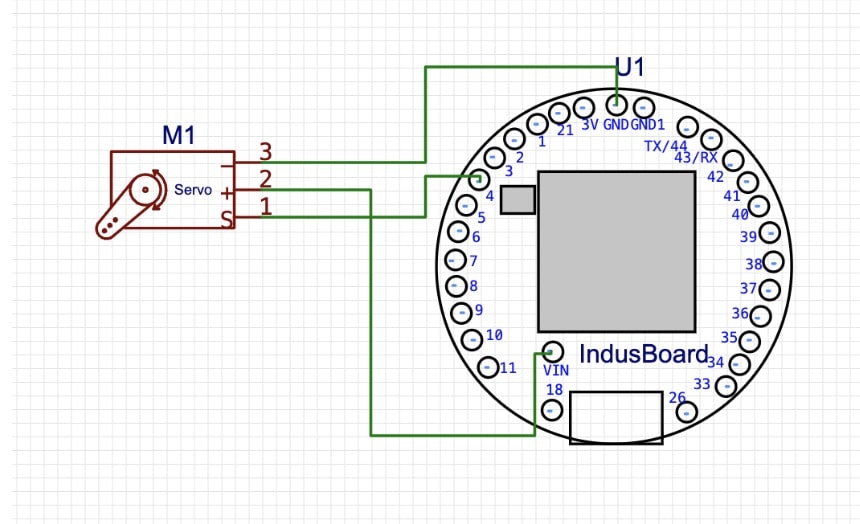
In this demo, I use only one servo motor to control movement along different axes using mapped hand coordinates. If you want to expand the system, you can modify the code to control multiple servo motors for full robotic arm motion.
Software Architecture and Code Overview
The project uses two separate programs working together.
Web-Based Hand Tracking Code
The first part is an HTML-based web page that runs the MediaPipe hand tracking model. This page accesses your webcam, detects hand landmarks, and extracts finger coordinates.
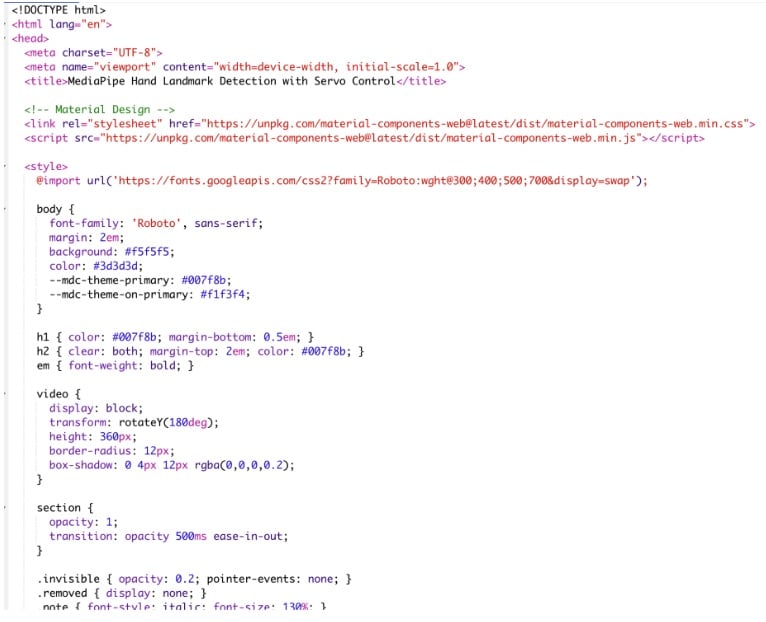
Using the WebSerial API, the browser sends these coordinates directly to the IndusBoard Coin over USB.
IndusBoard Coin Arduino Code
The second part runs on the IndusBoard Coin using the Arduino IDE. Here, I use the esp32servo library to generate PWM signals for the servo motor.
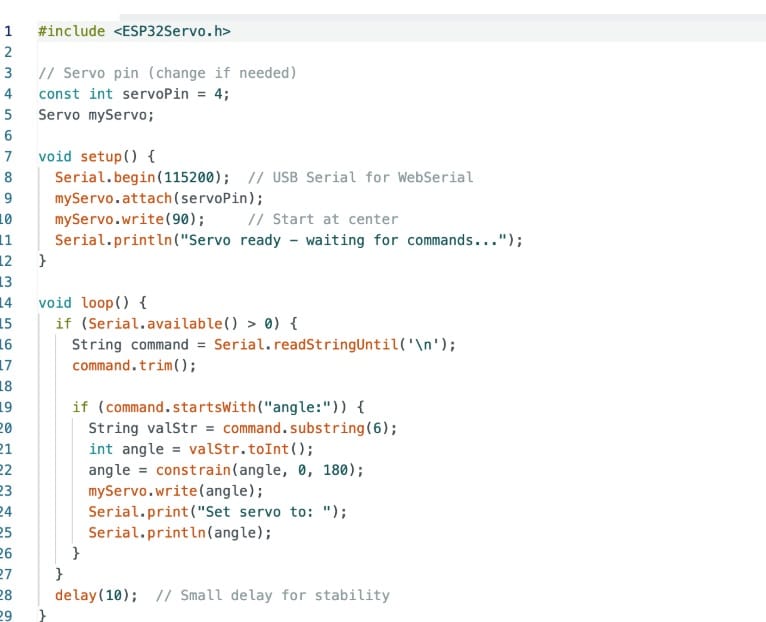
The board continuously listens for serial data from the browser. Once coordinate values are received, they are mapped to servo angles, allowing smooth and responsive motor movement.
Note: You can download the complete code, given at the end of the article.
Testing the Hand Tracking Robot Control System
Once the code is uploaded and everything is connected, testing is straightforward.
Open the HTML file in a supported browser and click the Connect Serial button. Select the IndusBoard Coin from the device list. After the connection is established, enable the webcam.
At this point, the system starts tracking your hand in real time. As you move your hand, the servo motor responds instantly, mimicking your motion.
This is where AI image processing truly feels alive.

Applications of AI Hand Tracking in Robotics
This project is not just a demo. It can be extended to real-world applications such as:
- Human-machine interfaces for industrial robots
- Touchless control panels in factories
- Educational robotics and AI learning kits
- Gesture-based robotic arms
- Research prototypes for collaborative robots
Final Thoughts
What I like most about this project is how accessible AI-powered robotics has become. With just a browser, a camera, and a small controller board, you can build an intuitive robot control system that feels natural and futuristic.
If you are exploring AI image processing, robotics, or human-machine interfaces, this project is a great place to start.