Over the course of history, different forms of payment systems have been in existence. Initially, trade by barter was common. However, the problems of barter necessitated the introduction of various forms of money. This era became the cash based economy, which most countries are gradually phasing out, modified or integrating into a new cash-less system involving POS terminals and digital economy.
Recent development in technology for financial transaction has increasingly fueled the use of electronic-based payment instruments globally. In advanced economy like the United States, France etc. the use of cash for purchasing consumption goods has declined since 1980. Electronic payments have made substantial inroads among consumers in these countries accounting for ~ 60% of all consumer transactions.
Meanwhile, in most countries the cashless journey has only just begun. Majority of the Developing countries have a negligible share of consumer transactions being done via cashless means.
Electronic payments have proven to boost economic growth while advancing financial inclusion and for those reasons, countries are working to make payment systems less dependent on cash. Governments across the globe are pushing for a paradigm shift in economic policies to push cashless transactions.
One of the major instruments facilitating this transition in developing economies is the Handheld Point of Sale Terminals.
Point of Sale (PoS) Terminals
A point of sale terminal (PoS terminal) is an electronic device used to process card payments at retail locations. A PoS terminal generally does the following:
- Reads the information off a customer’s credit, debit card or prepaid
- Checks whether the funds in a customer’s bank account are sufficient
- Transfers the funds from the customer’s account to the seller’s account (or at least, accounts for the transfer with the credit card network)
- Records the transaction and prints a receipt
Apart from Payment Sector these terminals are also being used to revolutionizing the Banking & Public Distribution worlds by providing accessibility to electronic banking service in Rural & Urban Districts. Particularly in India we see such examples in the form of:
- Aadhaar Enabled Payment System (AEPS)
AEPS is a bank led model which allows online interoperable financial inclusion transaction at PoS (MicroATM) through the Business correspondent of any bank using the Aadhaar authentication. Aadhaar enables four basic types of banking transactions i.e. Balance Enquiry, Cash Withdrawal, Cash Deposit & Aadhaar to Aadhaar Funds Transfer.
- RuPay
A new card payment scheme launched by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI), to fulfill RBI’s vision to offer a domestic, open-loop, multilateral system allowing all Indian banks and financial institutions to participate in electronic payments.
- Aadhaar eKYC
Aadhaar ekyc is a paperless Know Your Customer (KYC) process, wherein the Identity and Address of the subscriber are verified electronically through Aadhaar Authentication.
Types of PoS Terminals
Businesses have a range of PoS options available to them from simple mobile payment processors to those capable of managing large multi-location businesses. The different types of POS Terminals are described below:
- POS Fixed:Commonly used & often sold in all-in-one solutions including barcode scanners & cash drawers. While they are hardware/software-based (PC based), most still require access to the internet (via LAN) and might even use cloud-based software. They are generally employed in restaurants, grocery & Electronic stores etc.
- Mobile POS:Enables payment by Mobile (smartphone or tablet) via Bluetooth, Wi-Fi or NFC. The client device must have the required app installed for the access.
- Pocket/Handheld POS: For exhibitors requiring terminal displacement, this POS allows to receive payments by bringing it directly to the customer. It is most commonly used in retail counters, restaurants, taxis and fuel stations. Wireless Technologies like Bluetooth, GSM/GPRS or UMTS, Wi-Fi & NFC are used here for transmission of data.
Security & Certification Requirements
POS Terminals handle customer sensitive financial information therefore the requirement of Security and Anti-tamper features (Hardware & Software) is paramount for these devices. Most payment POS devices usually adhere to Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards (PCI DSS) & EMV Standards, ensuring your company will be safe from data leaks, fraud and other harmful intrusions.
The PCI DSS is a proprietary information security standard for organizations handling branded credit cards from the major card schemes including Visa, MasterCard, American Express, Discover, and JCB.
Whereas, EMV is a standard for smart payment cards and payment terminals/ATMs to provide protection against counterfeit card frauds. EMV cards are smart cards that store the data on integrated circuits in addition to magnetic stripes and can be read using magnetic/ SAM Card readers or RFID/ NFC technology.
Handheld PoS: Typical Specifications & Requirements
The core of a POS terminal is an application processor with an OS that is used to drive the end application. The POS terminal is generally powered through AC mains using an adapter and often has a provision of a rechargeable battery that powers the terminal in case of mains power outage. The POS terminal may interact with external environment through wired or wireless means. The wired communication is typically through USB or Ethernet interface. The wireless communication is generally achieved through Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, GSM etc. User interaction with the terminal is achieved through keypad, LCD or Bio-metric interfaces. A typical block diagram of a POS terminal is shown below.
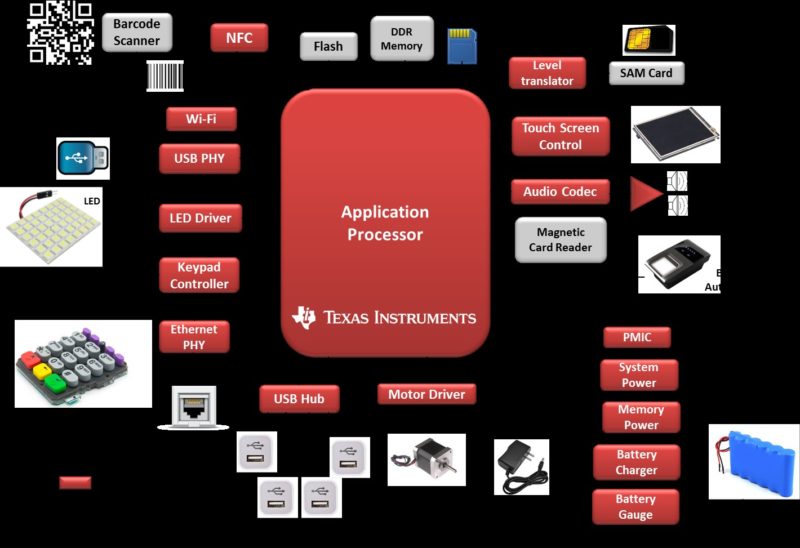
PoS Terminals: Hardware Components
Embedded Processor is the heart of any POS system and its core features determine its usability in POS ecosystem. ARM processors based on Cortex-A8 & A9 CPUs with Graphics Accelerator are generally employed for these applications. These ARM and graphics processors with advanced security features like secure boot & high strength encryption are optimized for performance while delivering low-power consumption. The balance of performance, Power & Security make the devices ideal for Point of Sale equipment.
-
Connectivity
POS terminals require full duplex wireless communication with remote servers and data storage facilities. Most systems require IEEE 802.11abgn wireless LAN as well as 2G/3G/4G cellular modems to allow for true mobility.
Wi-Fi & BT/BLE modules are also used as connectivity options in modern POS terminals. These modules are designed to offer high throughput and extended range along with a power-optimized design. Some modules available today also offer dual-band coexistence flexibility i.e. 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz with dual antennas. Additionally, modules today are being offered with multiple certifications like FCC, IC, ETSI/CE, and TELEC for expediting time to market.
With the advent of NFC enabled smart cards and new mobile payment systems like Apple Pay, Android Pay etc., there is an increased demand for NFC enabled POS terminals. Multiple NFC & RFID Solutions available today include Readers/ Writers, Transceivers, Static & Dynamic Tags and Integrated data framing systems.
-
Signal Chain & Motor Drives
For POS terminals requiring audio output, audio codecs can be used in conjunction with speakers. Audio codecs support external microphone connection and often include features such as integrated microphone bias, digitally controlled stereo microphone preamplifier, automatic gain control, integrated signal processing etc.
In applications that include a LCD and require a tactile interaction, a touch screen controller (TSC) may be used. TSC contains a low-power analog-to-digital resistive touch screen converter along with drivers and the control logic to measure touch pressure.
POS terminals often use stepper motors in applications that require paper slip printing. Motor drivers required to drive the stepper motors in such applications need to consume low power. These also offer protection features like under voltage, over current and over temperature protections.
-
Interfaces
Ethernet PHY transceivers help enable 10/100 Mbps Ethernet communication in POS terminals. These transceivers typically offer integrated cable diagnostic tools, low latency, and low power consumption making it suitable for battery operated applications.
To enable USB2.0 and USB3.0 communication in POS terminals, physical layer transceivers and controllers are required. USB hubs enable POS terminals to connect with multiple devices simultaneously and can be of various types, namely Full-speed (USB1.1), High-Speed (USB2.0) and Super-Speed (USB3.0).
-
Power
POS terminals derive power from either AC mains or rechargeable battery (single-cell/ multi-cell Li+/ Li Pol) that in turn are charged using either linear or switch-mode chargers. Linear chargers offer advantages like simplified design, better EMI and smaller solution size. Whereas, switch-mode chargers offer higher efficiency and support higher charge currents.
In applications requiring continuous & accurate battery monitoring, battery gauges are used. Different gas gauge techniques include – Coulomb Counting, EDV (End-of Discharge Voltage), CEDV (Compensated End-of Discharge Voltage) & Impedance Track™. Impedance Track™ technique uses a highly accurate algorithm that calculates changes in impedance caused by battery age, temperature and cycle patterns to predict remaining run-time within 1% accuracy throughout the entire life of the battery.
Additionally, the input power needs to be scaled to different voltage levels for powering various components. This is achieved using low quiescent current LDOs & DC-DC Converters. LCD used in POS terminals need an array of back-lit LEDs for illumination that can be achieved using LED drivers.
More cool stuff available here.





