A new GaN-based motor-drive inverter designed for tight robotic joints is pushing the limits of power density, thermal efficiency, and fast dynamic control aimed squarely at next-generation humanoid mobility systems.
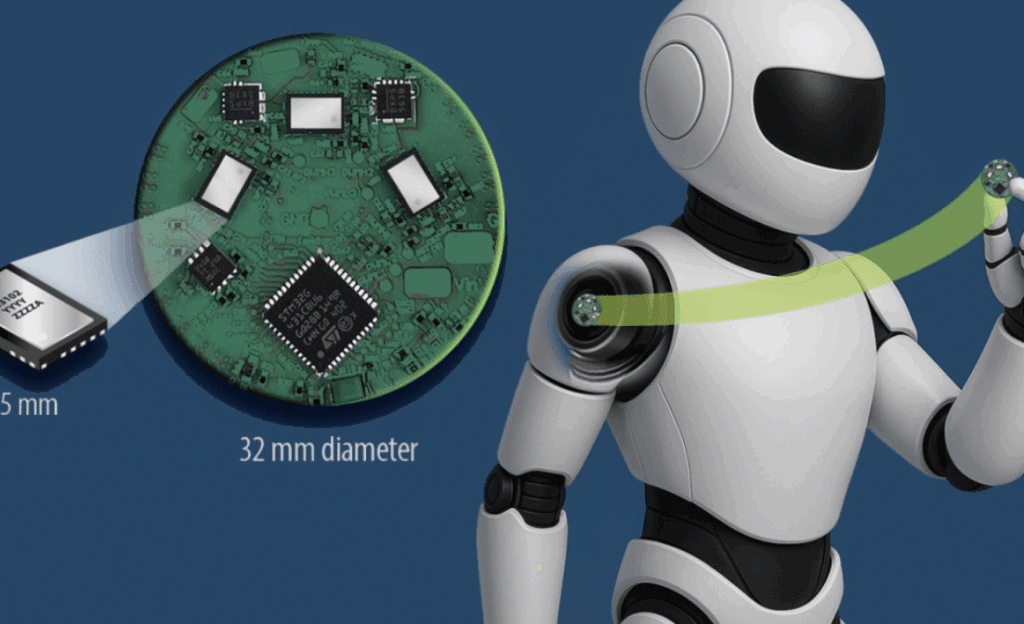
Efficient Power Conversion Corporation (EPC) has launched a highly compact GaN-based motor drive inverter, the EPC91120, specifically developed for humanoid-robot joint actuators. Built on the company’s EPC23102 ePower Stage IC, the 32 mm-diameter board integrates power, control, and sensing elements to deliver high performance in tight, weight-sensitive spaces.
Unlike external inverters, the drive packs three EPC23102 monolithic GaN half-bridge ICs, a microcontroller, current and voltage sensing blocks, a magnetic rotor-encoder interface, and RS-485 communications. It supports a wide input range (15 V–55 V DC), making it suitable for compact robotic power systems.
The key features are:
- 32 mm ultra-compact, joint-mountable inverter board
- Wide 15–55 V DC input range for robotic power systems
- Supports up to 15 A RMS continuous (42 A peak pulses)
- High-speed 100 kHz switching with 50 ns dead time
- Integrated sensing, MCU control, and RS-485 communication
In terms of output, the design can sustain up to 15 A RMS continuously (21 A peak) and pulses up to 30 A RMS (42 A peak). Its switching logic runs at 100 kHz with just 50 ns dead time, enabling fast dynamic response and high efficiency, a key requirement for precise, high-bandwidth humanoid motion.
Thermal tests show that under natural convection at 26 °C, the board handles about 7 A RMS per phase without a heatsink. But when embedded inside a robot joint using the motor housing as a heatsink it can go up to 15 A RMS. The system’s overall efficiency, measured from DC input to mechanical output, exceeds 80%, validating its design for torque-dense, yet lightweight robotic joints.
Mechanically, the board is dimensioned to align with the Unitree A1 robot’s motor architecture, enabling easier integration and evaluation in existing platforms. This underscores the growing role of GaN ICs in robotics: by embedding the inverter within the joint, the company reduces system size, improves power density, and enhances motion control all while cutting thermal and efficiency trade-offs.







