In the present age of globalisation, businesses are spread all around the world. In order to operate the business smoothly, there is a strong need for a dedicated telecom link that can connect geographically spread out locations of several businesses. The telecom facility may be either shared such as dial-up lines or non-shared such as leased lines and managed leased line networks (MLLNs). Obviously, businesses prefer a highly secured dedicated non-shared communication facility that is available all the time.
A leased line is a dedicated link or telecommunication path provided between two fixed locations, which is made available round the clock for use by the designated user (an individual or a company). Leased lines are provided to users for internal communication between their different business centres/offices/factories at various locations within a city or different cities on a point-to-point basis or on a network basis.
These leased lines can carry voice, data and video and can be used for connecting telephone sets, computers, electronic private automatic branch exchange (EPABX) and for establishing a virtual private network (VPN). These lines are exclusive for the designated user and are particularly not shared in common amongst multiple users as dial-up lines.
Such ordinary leased lines are not very efficient and have lots of disadvantages such as limited range of services, bandwidth support only up to 64kbps (2.4kbps, 4.8kbps, 9.6kbps and 64kbps), no support for n×64kbps bandwidth provisioning, cumbersome operation and vendor-specific equipment.
Other disadvantages are first-generation network elements with minimal maintenance features, difficult fault isolation and rectification, no centralised alarm or performance statistics monitoring, no health diagnostics for the network, high lead time for new circuit installation, manual verification of resources needed, cross-connection of individual circuits done at the channel level, poor customer satisfaction, no proactive maintenance, high mean time to repair (MTTR), no guaranteed quality of service (QoS), no way to measure circuit quality or generate customised performance reports, poor network reliability and availability, non-redundant network elements, no alternate routing of circuits in case of failure and no centralised network management system (NMS).
Applications of MLLN
Managed leased line network (MLLN) is a system that can provide leased line connectivity, that is, a dedicated telecommunication path between two fixed points. It is an integrated, fully managed, multi-service digital network platform through which a service provider can offer a wide range of services at an optimal cost to business subscribers. MLLN allows the service provider to keep an end-to-end control and monitor over the leased line and hence provide guarantees of uptime of the circuit.
With the use of managed leased line circuits by various sectors such as banking and financial institutions, stock markets, news and print media industry, broadcasting houses and Internet service providers (ISPs), people of all the sections are benefitted by way of accessibility of bank accounts from anywhere, instant news coverage, faster Internet access, etc.
The applications/services offered by MLLN are
1. Speech circuits (hot line or P-wire). Dedicated telecom links for speech, say, hot line for voices between two different locations is established by local or long-distance circuits within a city or between two different cities. The terminating equipment at both ends is telephone set without dialling facility. In such a connection, both-way signalling and speech is possible.
2. Data circuits. Dedicated local or long-distance point-to-point or point-to-multipoint data circuits at different speeds, namely, n×64kbps and up to 2Mbps can be offered for different bandwidth needs of the customer. MLLN offers flexibility of providing leased circuits with speeds of n×64kbps and up to 2Mbps with differential time-dependent bandwidth provisioning.
3. Private data network. More than one local or long-distance leased circuits can be provided such that data from one leased circuit can be transferred automatically to another leased circuit for the same subscriber.
4. International leased circuits. International long-distance leased circuits can be offered for business across the globe, which are useful for Internet leased lines and international private leased circuits (IPLCs).
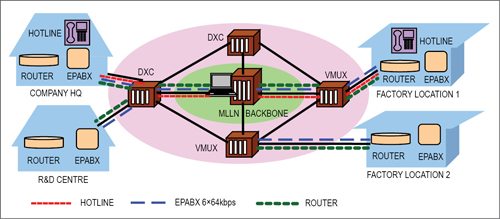
The MLLN also supports enhanced features such as corporate hi-speed Internet access, EPABX interconnection, EPABX remote extension (EPABX of one city can be connected to EPABX of another city), ISDN (integrated services digital network) line extension, virtual private network (VPN), local area network (LAN) interconnection (LAN of one city can be connected to LAN of another city) and extension of VPN to customer through MLLN. A typical MLLN system connecting various facilities of a customer is shown in Fig. 1.
Salient features of MLLN
Managed leased line network or MLLN service is specially designed for having effective control and monitoring on the leased line so that the downtime is minimised and the circuit efficiency is increased.
MLLN mainly deals with data circuits ranging from 64kbps to 2048kbps (n×64kbps). One of the major attractions of MLLN is its ability to provide differential time-dependent bandwidth on demand basis to the customers. For example, it is possible to provision 1024kbps MLLN circuit for 16 hours a day and 512kbps for remaining 8 hours of the day, as per the requirement of the customer.
Another great thing about MLLN is its very efficient NMS that can proactively maintain the circuit without waiting for customers to book a complaint. NMS provides features such as bandwidth management, alternate or back-up transmission routing, powerful diagnostics and maintenance tools and self-repair tools.
MLLN-NMS also provides periodic performance report which is useful in providing high-speed leased lines with improved QoS, high availability and reliability to the business and good service to existing customers.
The network management system also supports service provisioning, network optimisation and planning and service monitoring. The system offers features such as end-to-end circuit creation and monitoring, software loop test to check connectivity of various network elements and fault isolation and software programmability of customer end equipment.
MLLNs offer great amount of security because media is not shared and is exclusively dedicated for a particular subscriber. With MLLN, lead time is very low for provisioning of a new leased line. Its modular system and new application can be implemented very fast by simply adding or plugging the units.
Managed leased line network architecture
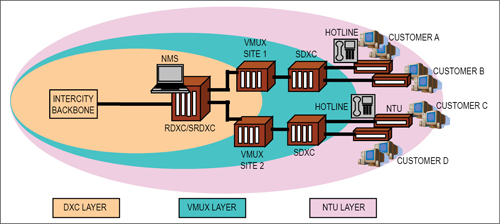
Managed leased line network (MLLN) is a three-tier structure and comprises network elements such as digital cross connects (DXC), versatile multiplexer (VMUX), network termination units (NTU) and NMS (Fig. 2).
Stage 1 comprises NMS, regional DXC (RDXC) and/or sub-regional DXC (SRDXC), billing servers, database servers, etc. At this stage, all the network management functions are done from the central location. This stage provides connectivity to second-stage nodes and provides traffic aggregation.
Second stage comprises SRDXC, SSDXC (secondary switching DXC) and VMUX, and is located in major cities where demand for leased line is high. This stage provides connectivity to third stage and performs leased line traffic aggregation.
Third stage comprises VMUX and NTU and is located in small cities/towns where leased line demand is lower (approximately 20). This stage provides leased line traffic aggregation.
The media for interconnecting various network elements and extending line up to customer end may be optical fibre, copper wire, radio, microwave transmission or a combination of these.
MLLN has to provide high reliability service and is supposed to obtain efficiency greater that 99.5 per cent. Therefore all the interconnections of different network elements are provided as rings, wherever available, so that an alternate circuit path can be automatically used for routing the traffic in case of main route failure. In long-distance network, links between the same stations can be split into alternate physical path of rings to the extent feasible. This also saves on-port capacity required for providing alternate path within MLLN.
With these network elements, the MLLN is able to provide functions such as fault, configuration, accounting, performance and security management.
Network management system (NMS)
It is built on open architecture and relational database system and manages all the network elements and their functions centrally. It is able to configure, provision, manage and monitor all aspects and parameters of the remote elements of the MLLN network centrally without the need of any local intervention.
On-demand bandwidth configuration is performed at NMS and priority can also be set for a particular leased line. This enables the high-priority customer lines to be routed first to the standby route in case of failure of the main route.
Any change of configuration of any network element is auto-recognised by the NMS. NMS is also capable of re-initialisation of the network element in the event of software/hardware failure. A predefined routing schedule is used by NMS to perform fast re-establishment of circuits within the network across alternative paths totally automatically, in the event of failure.
A detailed fault report is generated in order to identify the exact problem so that immediate corrective measures can be taken in order to restore the services.
The fault information provided by NMS contains type of faulty network element, the time at which fault occurred, time when it corrected, etc. The NMS keeps polling all the network elements after some predetermined interval and generates alarms so that proactive measures can be taken.
Digital cross connect (DXC)
It is a large-capacity cross-connect device that separates channels coming from other devices and rearranges them into new channels for output. A digital cross-connection allows lower-level time division multiplexing (TDM) bit streams to be rearranged and interconnected amongst higher-level TDM signals. The signal is first de-multiplexed into a lower level after which it is cross-connected and then multiplexed again.
Versatile multiplexer (VMUX)
It is a small capacity cross connect device with several channel interfaces which is installed at different sites for providing user connectivity. VMUX multiplexes all tributaries coming from other devices and forms a higher hierarchy level output at the specified port. The VMUX is provided with different types of interfaces to connect SDSL and HDSL product family modems. The number of interfaces (such as 64/128kbps, n x 64kbps, E1 or hotline) depends on the type of VMUX configuration (VMUX type I, VMUX type II, VMUX type III/DC operation and VMUX type III AC operation).
Network terminating unit (NTU)
It is simply a base band modem and which is located at the customer’s premises. The NTU works on normal AC supply. NTUs of various capacities (64/128kbps and n×64kbps) are available with several interfaces (V.35, G.703, Ethernet). NTU also allows for the use of existing telecom copper cables (twisted pair) for digital traffic with medium distances (~5 km) and high speeds.
Conclusion
In the changing economic environment, dependence of organisational and industrial activities on leased circuits is increasing. In such a scenario, high QoS, high efficiency, highly secured network, customer-oriented tariffs along with desired bandwidth, time-dependent bandwidth provisioning, no congestion, centralised control and monitoring, lower lead time for new installations and proactive fault maintenance prove MLLN to be a commercial boon for corporate and individual customers.
Feel interested in managed leased line networks? Check out other tech focus articles.