IR-guided missile systems
Some of the better known IR-guided missile systems are briefly described in the following paragraphs. These missile systems have been grouped into three categories, namely, anti-tank-guided missiles (ATGMs), surface-to-air missiles (SAMs) and air-to-air missiles (AAMs).
Anti-tank-guided missiles. ATGMs, also known as anti-armour missiles or anti-tank missiles, are designed to precisely hit and destroy heavily-armoured military vehicles including all combat and transportation vehicles. Different variants of anti-tank missile systems include shoulder-fired weapons, large-tripod-mounted weapons, vehicle-mounted weapons and systems launched from airborne launchers. American Javelin, German PARS-3 LR, Israeli Spike and Indian Nag are some examples.
American FGM-148 Javelin (Fig. 12) is a man-portable third-generation fire-and-forget anti-tank-guide missile jointly developed by Raytheon and Lockheed Martin. It has an effective firing range of 75m to 2500m, with 4750m being the maximum range. It uses a tandem-shaped charge warhead that can penetrate reactive armour. The missile can be used in both top attack mode to hit usually thin-top armour of the target vehicle and direct mode to hit buildings and airborne targets. It uses an IIR seeker and on-board tracker to make it a fire-and-forget missile. It was introduced into service in 1996 and is in service till date. It was successfully used in Operation Enduring Freedom (war in Afghanistan) and Operation Iraqi Freedom.
PARS 3 LR (Fig. 13) is an autonomous fire-and-forget missile intended for long-range

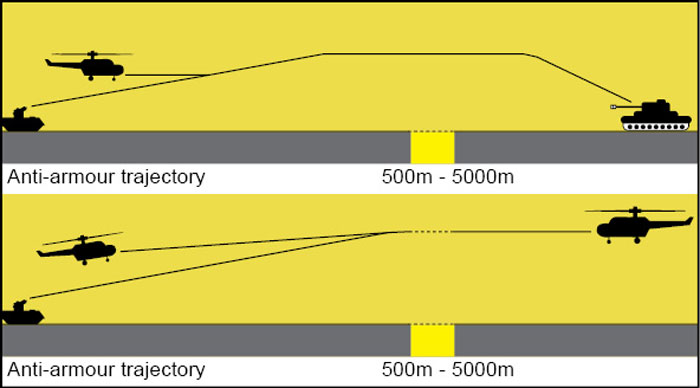
applications and designed to destroy ground (tanks and armoured vehicles), air (helicopters) and other individual targets. Manufactured by Parsys GmbH, MBDA Deutschland GmbH and Diehl BGT Defence, PARS 3 LR is also known as TRIGAT-LR and AC-3G. The missile can be launched from a ground vehicle or a helicopter and can be fired in salvos of up to four missiles in eight seconds. The missile has a specified operational range of 500m to 5000m, which is extendible up to 7000m. It can be used in both top (terminal dive) mode as well as direct mode. Fig. 14 (top part) shows the flight trajectory for top-attack mode employed for anti-armour role with the missile launched from either a land vehicle or a helicopter.
It also shows the flight trajectory for direct-attack mode (bottom part) employed for an anti-helicopter role with the missile launched from either a land vehicle or a helicopter. The missile uses a passive IR seeker that locks on to the target before the missile is fired. It uses tandem-shaped charge for maximum lethality against modern reactive armour. German army has authorised series production of the missile system. The delivery began in mid-2013 and shall continue till 2016.
Spike is a fourth-generation man-portable fire-and-forget anti-tank and anti-personnel missile designed and developed by Rafael Advanced Defence Systems. The missile can be launched in fire-and-forget mode, destroying targets within the line-of-sight of the launcher and also in fire, observe and update guidance mode while following a top-attack flight trajectory.
In fire-and-forget mode, the tracker is locked on to the target. The missile is launched and it automatically propels itself towards the target. The missile uses a tandem-charged high explosive anti-tank (HEAT) warhead that can penetrate explosive reactive armour.

The guidance system of Spike comprises a charge-coupled device (CCD) and an IIR seeker. The IIR sensor, in addition to providing higher sensitivity, offers improved thermal background rejection characteristics for all-weather day and night operation.
Different variants of Spike missile system include Spike short range (Spike SR) with a maximum operational range of 800m, Spike medium range (Spike MR) with maximum operational range of 2500m, Spike long range (Spike LR) with maximum operational range of 4000m, Spike extended range (Spike ER) with maximum operational range of 8000m, Spike non line-of-sight (Spike NLOS) with maximum operational range of 25km and Mini Spike with engagement range of 1300m. Mini Spike is an anti-personnel-guided weapon.
The Spike missile system is currently in service with Dutch, Chilean, Colombian, Finnish, German, Polish, Italian, Peruvian, Spanish and Singaporean armed forces. The missile system has been successfully used during Lebanon war in 1982, Second Intifada beginning year 2000, Afghanistan war from 2001 till date and Iraq war in 2006.
Nag (Fig. 15) is a third-generation fire-and-forget ATGM from India, designed and developed by Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and manufactured by Bharat Dynamics Ltd. It has two variants employing an active IIR seeker and a millimetric wave seeker. The operational range for the land version is 500m to 4000m, and 7km to 10km for air-launched version. It is likely to be inducted into service in 2015.