Capacitor design enabling slimmer PCB layouts, automated assembly, and improved reliability for critical EV systems like chargers, inverters, and battery management units.
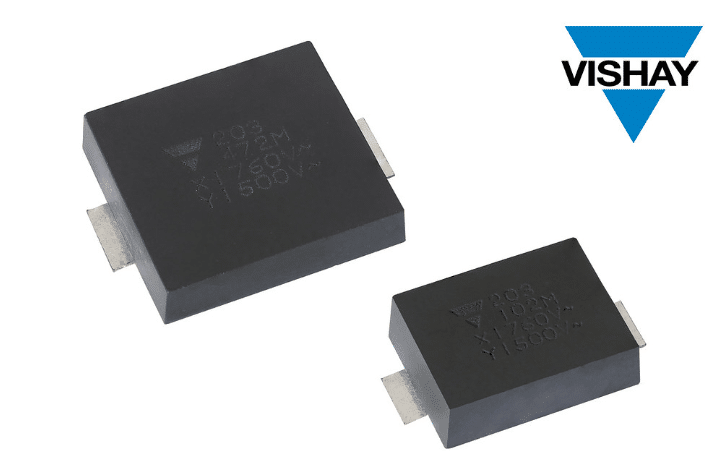
Vishay Intertechnology has launched the industry’s first automotive-grade ceramic capacitors with a Y1 safety rating in a surface-mount device (SMD) casing—marking a shift in how EMI/RFI suppression components are integrated into electric and hybrid vehicles.
The key specifications include:
- Dielectric: Y5U, Ceramic Class 2
- Capacitance range: 470 pF to 4700 pF (±20% tolerance)
- X1 rating: 760 VAC
- RoHS-compliant and halogen-free construction
The new capacitors are rated at 500 VAC (Y1) and 1500 VDC, offering capacitance values up to 4.7 nF. Designed for high-reliability automotive electronics, they target critical functions such as on-board chargers, traction inverters, battery management systems, e-compressors, and AC/DC converters in EVs, HEVs, and PHEVs.
One of the key advantages is their ability to combine Y1 safety certification—typically found only in bulky through-hole capacitors—with a compact surface-mount format. This enables flat, low-profile PCB layouts, supports reflow soldering for automated assembly, and reduces overall production costs. Manufacturers can also leverage backside PCB mounting, eliminating the clearance constraints of traditional leaded capacitors.
The series is AEC-Q200 qualified with PPAP support, making it suitable for automotive-grade compliance. Vishay highlights its robust humidity resistance, with Class IIB certification under IEC60384-14 Annex I. Devices withstand the rigorous 85/85 test (85°C, 85% RH, 1000 hours), ensuring reliability in harsh, moisture-prone environments.
Structurally, the capacitors are built around a copper-plated ceramic disc encapsulated in UL 94 V-0 flame-retardant epoxy resin, offering both mechanical durability and safety. Two case options are available: C case with a 10 mm creepage distance and D case with 14.5 mm, meeting stringent insulation and spacing requirements for automotive power electronics.
For more information, click here.







