Liquid cooling is no longer optional for AI infrastructure, but reliability at connection points is emerging as the next bottleneck.
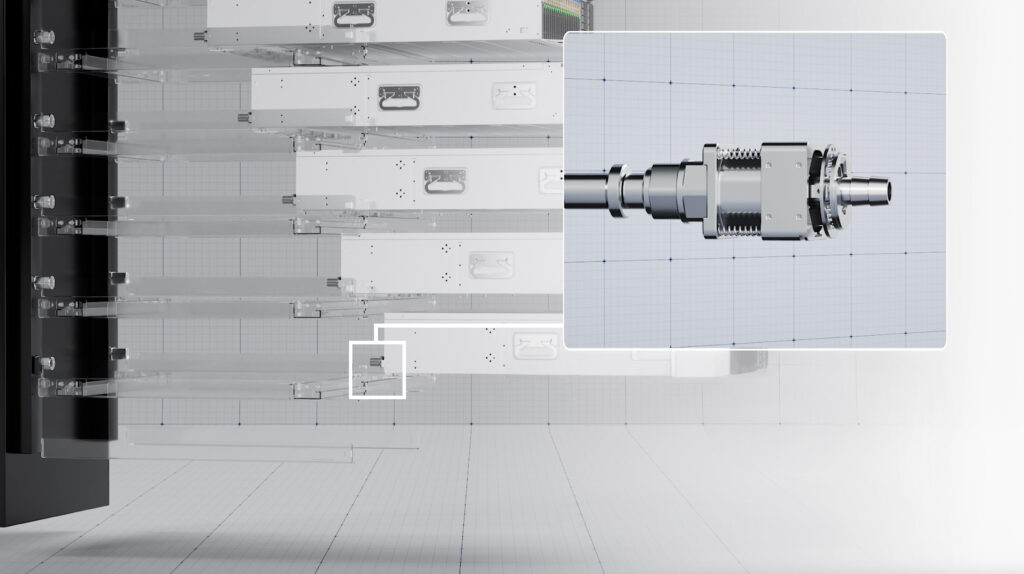
As AI workloads and high performance computing continue to drive chip power densities higher, traditional air cooling methods are approaching their physical limits. Liquid cooling has rapidly moved from an experimental option to a core requirement for next generation data centres due to its vastly superior thermal efficiency. However, as adoption scales, mechanical reliability at liquid cooling connection points has emerged as a critical challenge impacting energy efficiency, uptime, and long term operational costs.
Even small mechanical misalignments at liquid cooling interfaces can have outsized consequences. Industry data shows that a deviation as small as one millimetre can significantly increase flow resistance, driving higher pump energy consumption across thousands of connections in hyperscale environments. Installation tolerances, vibration during transport and operation, and thermal expansion of materials compound the issue, exposing the limitations of traditional rigid connection designs that cannot adapt to dynamic real world conditions.
To address this growing bottleneck, Southco has introduced its Blind Mate Floating Mechanism, a liquid cooling connection solution designed to accommodate multi dimensional movement without compromising sealing performance. Built on Southco’s precision engineering expertise, the mechanism enables reliable blind mating in complex rack environments, allowing liquid cooled systems to operate efficiently while supporting rapid deployment, maintenance, and future scalability.
Key features of the solution include:
- Three dimensional dynamic tolerance compensation supporting radial and axial movement
- Self centring floating design to maintain alignment during repeated connections
- High pressure sealing performance tested for long term data centre operation
- Blind mate quick disconnect interface for faster maintenance and reduced downtime
By directly addressing real world alignment, vibration and thermal expansion challenges, the solution enables stable, low resistance cooling at large scale. The result is infrastructure that supports higher compute densities while reducing energy loss, maintenance effort and operational risk as data centres evolve for AI driven workloads.






