This solution helps design engineers reduce development risk while delivering reliable biometric monitoring and seamless wireless data transmission.
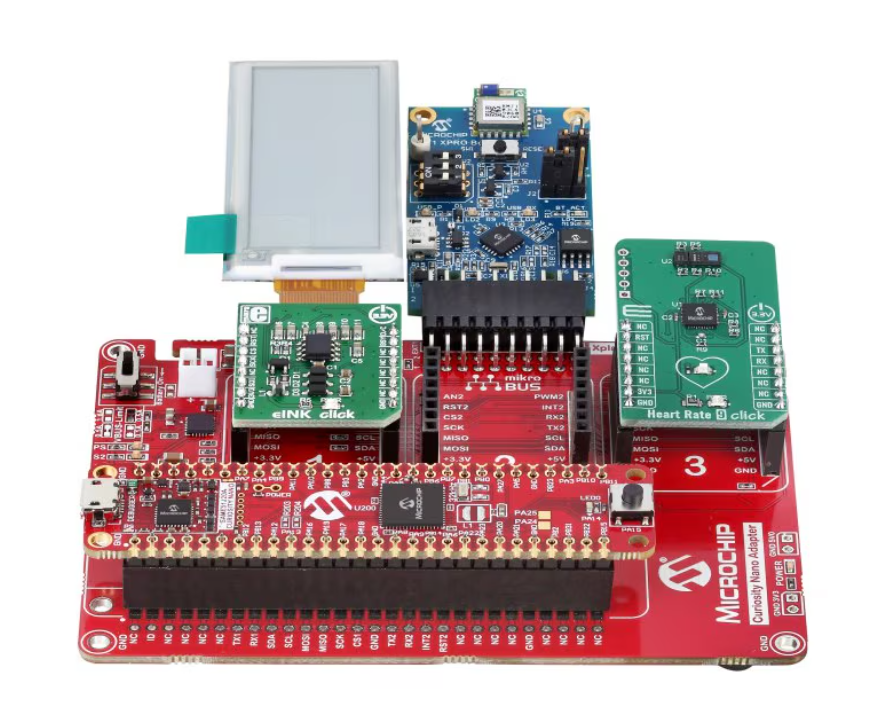
Design engineers working on next-generation health and activity monitoring wearables often face challenges such as ultra-low power consumption, compact form factor, reliable biometric sensing, and seamless wireless connectivity. To accelerate development cycles and reduce integration risk, Microchip Technology offers a comprehensive Fitness Tracker Wearables Reference Design that provides a proven hardware and software foundation for wearable products in healthcare and fitness markets.
At its core, the reference design demonstrates how a 32-bit microcontroller (MCU) can be integrated with sensors, a display, and wireless communication to build a versatile fitness tracker platform. This modular design lets engineers quickly move from concept to prototype while providing flexibility to expand or adapt the platform for various wearable use cases.
The design showcases real-time heart rate monitoring, displayed on a low-power e-ink screen, and optionally transmitted via Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) to a mobile application. It supports multiple MCU variants, such as SAM D21, SAM E51 or SAM L21, allowing developers to choose the performance or ultra-low-power profile that suits their product requirements.
In the reference platform, the chosen MCU communicates with external sensor and display modules over standard interfaces:A heart rate sensor module connected via I²C measures beats per minute when the user places a finger over the sensor.A low-power e-ink display connected over SPI shows biometric data while consuming minimal energy and retaining information without a continuous power source.In BLE-enabled configurations, a dedicated Bluetooth module transmits the heart rate readings to a smartphone or tablet for logging or analysis.
This architecture demonstrates how signal acquisition, processing, display, and wireless communication can be combined in a power-efficient wearable product design.One of the biggest advantages of this reference design is the time saved in early development, as engineers don’t have to build the entire signal chain, wireless stack, and display interface from scratch. The modular nature also supports reuse across multiple projects, such as fitness bands, basic smartwatches, or even medical activity monitors.
The inclusion of BLE connectivity simplifies integration with companion mobile apps, enabling real-time data streaming and remote monitoring — critical features in modern wearable ecosystems. Engineers can leverage this capability to build products that feed data into cloud services or health platforms.Microchip provides a variety of compatible evaluation kits and boards that implement this reference design. These include MCU curiosity boards, BLE modules, and sensor click boards. A bill of materials (BOM), schematics, and design documentation are available to help developers analyze and customize the solution for their specific needs.
This reference design is a practical starting point for engineers building wearable products that demand low power operation, reliable biometric sensing, and wireless connectivity, helping accelerate design cycles and reduce development risk.To read more about this reference design, click here.







