The reference design converts AC to 54.5V DC for 48V servers, using MOSFET bridge, interleaved PFC, and 3-phase LLC for efficiency.
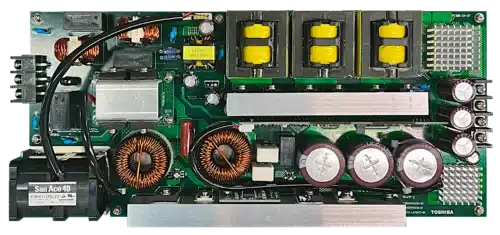
To support the growing adoption of 48V architectures in data centers, Toshiba has developed a reference AC-DC converter design that takes a 100V/200V AC input and delivers a stable 54.5V DC output for 48V server systems. This design includes an active bridge circuit using MOSFETs instead of conventional diodes, an interleaved power factor correction (PFC) circuit, and a 3-phase LLC resonant DC-DC converter.
The LLC converter uses three half-bridge converters arranged in parallel on the primary side. The secondary-side transformer terminals are connected in a Y configuration, enabling a 1U-sized system to deliver up to 1.6kW using a standard transformer. Each of the three LLC phases operates with a 120-degree phase shift, resulting in a current waveform on the primary side that mimics 3-phase AC behavior.
Toshiba’s TMPM372FWUG microcontroller generates the control signals for the 3-phase LLC converter. The complete system consists of a main board and three separate boards for the active bridge, PFC control, and LLC control, all mounted together. Each board has a distinct appearance when viewed individually or from different assembly angles.
By using MOSFETs in the active bridge circuit, the design significantly reduces conduction losses compared to traditional diode-based designs. The interleaved PFC circuit further improves performance by minimizing input current ripple and maintaining a high power factor under load.
The 3-phase LLC converter structure offers balanced power processing across all phases. The Y-connection on the secondary side helps evenly distribute the current and simplifies transformer design. The modular board structure enhances heat management and provides clear separation for control and power sections, making maintenance and design upgrades easier.
The system’s control strategy, driven by Toshiba’s microcontroller, ensures accurate timing and stable performance across all phases. This level of integration and control contributes to overall system reliability, even in demanding data center environments.
With this highly efficient AC-DC conversion system, data centers can significantly reduce energy losses during power conversion. The design exceeds the Titanium level of the 80 PLUS efficiency standard at 230V input, meaning lower electricity bills and reduced cooling requirements.
The support for 48V server power architectures aligns with current trends in scalable, high-density computing. The modular and compact nature of the design supports easy integration into 1U rack systems, allowing data centers to optimize space while maintaining high power delivery.
Ultimately, this design helps operators meet sustainability goals, lower total cost of ownership, and support the expanding global demand for data processing with improved energy efficiency.
Toshiba has tested this reference design. It comes with a bill of materials (BOM), schematics, assembly drawing, printed circuit board (PCB) layout, and more. The company’s website has additional data about the reference design. To read more about this reference design, click here.