See how time-of-flight technology measures distance. Learn how data converters, optics, and signal processing are used in drones, LiDAR, and robotics.
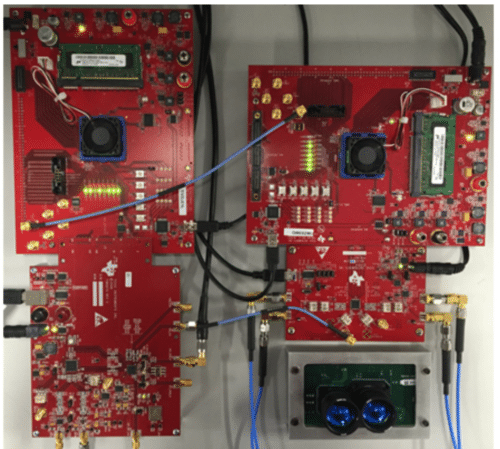
Time-of-flight (ToF) optical methods are used in various applications for precise distance measurement, including laser safety scanners, range finders, drones, guidance systems, and autonomous vehicles. TIDA-01187, LIDAR-pulsed time-of-flight reference design using high-speed data converters from Texas Instruments (TI), highlights the benefits of a high-speed data converter-based solution, such as improved target identification, reduced sample rate demands, and a simpler signal chain. It also covers optics, driver and receiver front-end circuits, ADCs, DACs, and signal processing.
Applications include architectural surveying equipment, automotive scanning LiDAR, drones, gas analysis, laser range finders (LiDAR), laser safety scanners, retinal imaging, and robotics.
The design supports a measurement range of up to 9 meters or more with additional optics and increased laser power. It achieves a range measurement mean error of less than ±6 mm and a standard deviation of less than 3 cm, ensuring high accuracy.
The system features a 5.75-W pulsed 905-nm near-infrared laser diode and driver with an average output power of less than 1 mW. It includes a near-infrared PIN photodiode with a high-speed trans-impedance amplifier front end. Laser collimation and photo receiver focusing optics are also incorporated for enhanced performance.
Key components include 14-bit, 125-MSPS ADCs, 16-bit, 500-MSPS DACs, high-speed amplifiers, and precise clocking. The system uses a pulsed ToF measurement method with DFT-based range estimation for improved efficiency. Additionally, automotive-grade versions are available for selected devices.
The coherent nature of laser light makes it ideal for distance measurement, as it can be easily collimated into a narrow beam with minimal divergence. By utilizing the constant speed of light, distance can be calculated by measuring the time it takes for laser light to travel to a target and return. Advances in small lasers and photodiodes have enabled the development of compact and portable systems, supporting applications such as laser safety scanners, drones, laser range finders, and guidance systems.
In this system, light emitted by the laser is collimated into a narrow beam using a lens. The beam travels to the target, reflects off it, and is then focused onto the detector by a second lens. The laser driver and stimulus subsystem can apply pulsed or amplitude modulation (AM) waveforms. While some lasers support frequency modulation (FM), which involves modulating the emitted wavelength, this feature is beyond the scope of this design.
To further optimize system range, the optical detector—a PIN or avalanche photodiode—generates a current proportional to the return signal. A very low-noise TIA is essential for amplifying the signal, as its amplitude decreases with the square of the distance. The amplified signal is then processed to produce accurate range measurements, making this design a comprehensive solution for distance measurement applications.
TI has tested this reference design. It comes with a bill of materials (BOM), schematics, assembly drawing, printed circuit board (PCB) layout, and more. The company’s website has additional data about the reference design. To read more about this reference design, click here.