Chinese researchers have developed fast-charging, durable lithium-ion batteries using innovative graphite-based anodes, promising significant advancements for electronics.
In recent years, engineers and material scientists have focused on developing advanced battery technologies that charge faster, have longer lifespans, and store more energy, which is essential for the progress of the electronics and energy sector. These batteries are vital for powering various portable devices and electric vehicles. Lithium-ion batteries (LiBs) are the most common worldwide, used in most everyday electronics. One of the main objectives in the energy field is to find scalable methods to increase the charging speed of these batteries, as this would improve performance without necessitating a switch to entirely new battery compositions.
Researchers at Huazhong University of Technology in China have developed a novel approach for creating fast-charging lithium-ion batteries (LiBs) using a graphite-based material. This innovative battery design has demonstrated the ability to reduce charging times for LiBs significantly. Furthermore, it enables the batteries to maintain a substantial portion of their capacity, even after undergoing thousands of charging cycles.
The team conducted various experiments to understand how the solid electrolyte interface (SEI) components influence the Li+ solvation structure. This understanding is crucial as it can reduce the time it takes for a battery to charge. They discovered a material combination that enhances the efficiency of the Li+ desolvation process, facilitating faster movement of Li+ ions across the SEI.
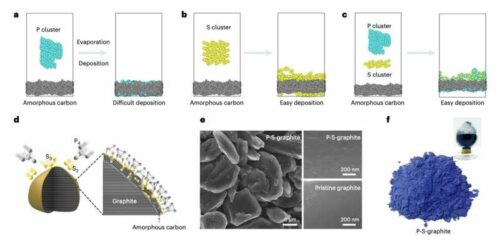
Following this discovery, the researchers focused on a promising anode material, P-S graphite. This material consists of an ultra-thin phosphorus layer on a graphite base. They manufactured anodes from P-S graphite and incorporated them into lithium-ion battery (LiB) cells to assess their performance in practical scenarios.
The methodology and encouraging experimental outcomes they presented could significantly advance the creation of LiBs that charge faster and last longer. This progress is vital for addressing the growing needs of the electronics industry.
Reference: Shuibin Tu et al, Fast-charging capability of graphite-based lithium-ion batteries enabled by Li3P-based crystalline solid–electrolyte interphase, Nature Energy (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41560-023-01387-5




