This research demonstrates a stable, lead free photodetector architecture that supports scalable fabrication and environmentally responsible electronic systems.
Photodetectors are essential components in modern electronics, converting light into electrical signals for use in cameras, environmental sensors, smart wearables, security systems, and biomedical imaging. Many high performance photodetectors today rely on lead based perovskite materials, which raise environmental and health concerns and often show poor durability in real world conditions. As electronics move toward more sustainable solutions, safer and more reliable alternatives are needed.
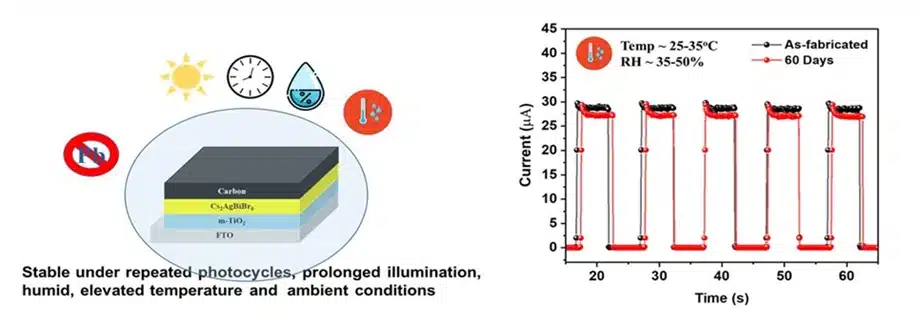
Addressing this challenge, researchers at the International Advanced Research Centre for Powder Metallurgy and New Materials in Hyderabad, in collaboration with IIT Hyderabad, have developed a lead free and eco friendly photodetector. The device is based on the double perovskite material Cs₂AgBiBr₆, offering strong optoelectronic performance along with improved environmental safety and long term stability. The work marks a step forward in the use of sustainable materials for next generation electronics.
The photodetector also stands out for its simple and low cost fabrication. Unlike conventional designs that depend on expensive metal electrodes, additional hole transport layers, and complex processing environments, the new device is hole transport material free, uses carbon electrodes, and is fabricated at room temperature using a one step coating process. This significantly reduces manufacturing complexity and improves scalability.
The device architecture supports efficient charge separation, enabling self powered operation without any external voltage. Tests show a stable response to visible light, clear on off switching, and over 90 percent performance retention after 60 days under ambient conditions, highlighting its improved durability compared to existing perovskite based photodetectors.
Key features of the research include:
- Lead free Cs₂AgBiBr₆ double perovskite photodetector material
- Self powered operation without external bias
- Room temperature, one step fabrication process
- Low cost carbon electrodes with no hole transport layer
- More than 90% performance retention after 60 days under ambient conditions
The research, supported by the Department of Science and Technology, Government of India, has been published in the international journal Solar Energy, aligning closely with national priorities on green manufacturing, sustainable materials, and self-reliance in advanced electronic technologies.