Researchers at the Tokyo University of Science catalyse a transformative shift in energy storage systems, guiding the world towards a more environmentally friendly and sustainable trajectory, edging closer to realising a carbon-neutral global society.
In recent years, Lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) have revolutionised the power storage landscape, becoming the preferred energy source for many electronic devices and vehicles. Their reliance on scarce lithium resources and environmental and safety challenges cannot be dismissed despite their impact. These issues have spurred global scientific communities to delve into alternative battery technologies, such as aqueous batteries, with potassium-ion batteries (KIBs) emerging as a contender. These batteries are crafted from readily available materials and are characterised by increased safety profiles compared to LIBs. Their compatibility with water-in-salt electrolytes (WISE) grants them superior thermal and chemical stability.
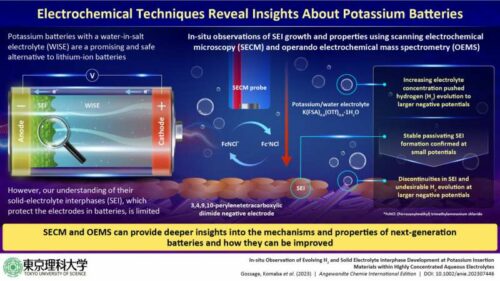
One hurdle with high-voltage aqueous batteries like KIBs is the suppression of hydrogen evolution at the negative electrode. Though SEIs have proven beneficial in stabilising electrodes in LIBs, less is known about their behaviour and effectiveness in the context of KIBs. To bridge this knowledge gap, a Tokyo University of Science (TUS) team conducted a study to understand SEI formations and characteristics in WISE-based KIBs.Enhancing SEI formation is critical to optimise forthcoming aqueous batteries’ functionality. The team suggests that this might be achieved through the evolution of novel electrolytes capable of fostering distinctive SEIs or introducing electrolyte additives and electrode surface treatments. Prof. Komaba also underscored the potential of SECM and OEMS techniques in augmenting the understanding of electrode-electrolyte interplays in next-gen batteries, encouraging peers to adopt these methodologies for deeper explorations.
The team, led by Professor Shinichi Komaba, leveraged technologies such as scanning electrochemical microscopy (SECM) and operando electrochemical mass spectrometry (OEMS) to scrutinise SEI dynamics in real-time. Their experiments indicated that solid-electrolyte interphases (SEIs) could form a protective layer in WISE, similar to LIBs, thereby mitigating hydrogen evolution and promising greater KIB longevity. They noted that SEI layer completeness waned at elevated voltages, inducing hydrogen release.
This investigation aims to advance aqueous batteries like KIBs, poised to replace the more hazardous and costly LIBs in applications such as electric vehicles and renewable energy systems. As we navigate towards carbon neutrality, developing accessible energy storage solutions, such as KIBs, will undoubtedly be critical in fostering a greener, sustainable future.