A new lifecycle-focused software platform aims to close critical gaps in validating, explaining, and monitoring AI systems used in safety-critical applications such as automotive and industrial automation.
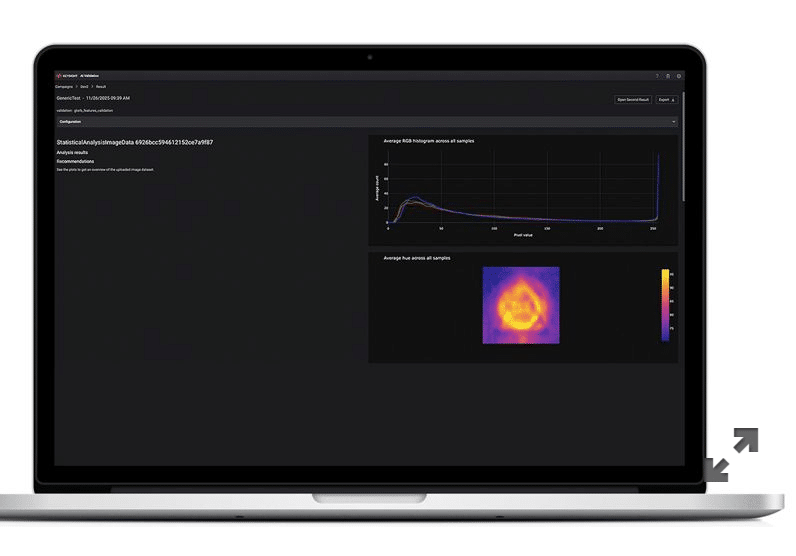
As AI adoption accelerates in safety-critical domains, ensuring that intelligent systems behave predictably and remain compliant over time has become a major engineering challenge. A newly launched software solution by Keysight Technologies addresses this issue by offering an end-to-end framework for validating, deploying, and continuously monitoring AI systems in regulated environments.
Unlike conventional AI testing tools that focus on isolated stages of development, the platform follows a lifecycle approach spanning dataset preparation, model validation, real-world inference testing, and post-deployment monitoring. The goal is to help engineering teams answer a fundamental question increasingly raised by regulators and system integrators alike: what exactly is happening inside an AI system, and can its behavior be trusted once deployed?
The key features are:
- Dataset quality and bias analysis using statistical methods
- Model explainability to uncover hidden correlations and limits
- Real-world inference testing beyond training conditions
- Continuous monitoring for data drift and performance changes
- Unified workflow supporting regulatory evidence and audits
The need for such tools is growing as regulations such as ISO/PAS 8800 for automotive AI and the EU AI Act demand explainability, traceability, and evidence-based validation. While these frameworks define what must be achieved, they provide little guidance on how to demonstrate compliance. As a result, developers often rely on fragmented toolchains that leave blind spots between training and real-world operation.
The new software platform aims to bridge this gap by combining data analytics, model explainability, and inference testing in a single workflow. It enables teams to identify dataset bias or gaps early, understand how models reach decisions, and verify whether performance in the field aligns with expectations set during training. Continuous monitoring further allows engineers to detect data drift and performance degradation after deployment an increasingly critical requirement for AI systems that evolve alongside their operating environments.
By unifying AI validation and assurance activities, the solution supports more transparent, auditable, and maintainable AI deployments. This is particularly relevant for high-risk applications such as advanced driver assistance systems, autonomous functions, and other embedded AI use cases where failures can have serious safety implications.
As AI systems become more complex and regulatory oversight tightens, lifecycle-based AI assurance tools like this are likely to play a central role in moving intelligent systems from experimental deployments to trusted, production-grade infrastructure.