The switches raise sensitivity while slashing current draw, enabling smarter, battery-efficient sensing for compact electronics, wearables, and always-on devices.
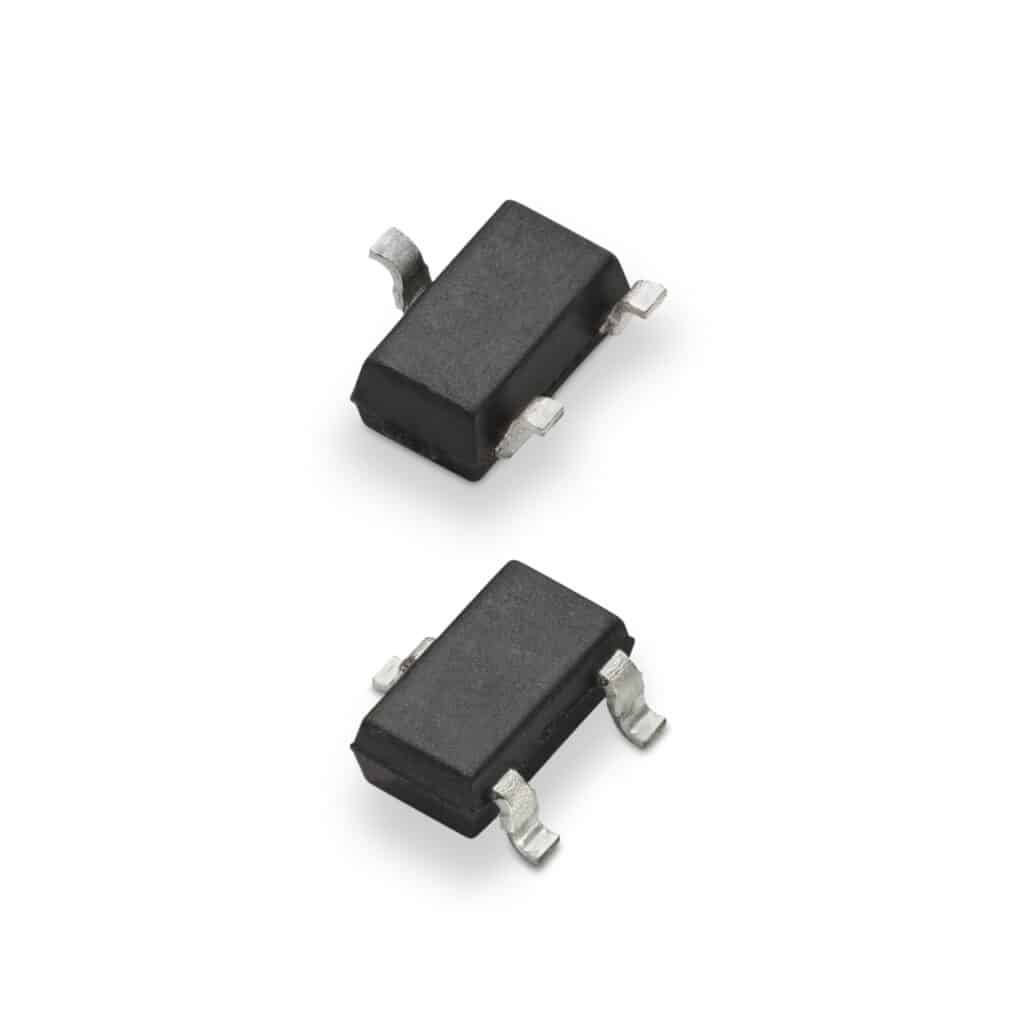

Littelfuse has expanded its magnetic-sensing portfolio with two new tunnel magnetoresistance (TMR) switches designed for always-on, battery-powered and space-constrained electronics. The devices bring a step-change in sensitivity and energy efficiency compared with traditional Hall-effect and legacy magnetic switches, aiming squarely at smart meters, wearables, home-automation gear, and compact industrial systems where every microamp matters.
The two new switches include an omnipolar device that detects either magnetic pole for simplified alignment, and a bipolar variant engineered for directional and rotational sensing. Both are built on a combination of TMR structures and ultra-low-power CMOS, a pairing that significantly cuts current consumption while improving thermal stability—two increasingly critical metrics for long-life devices operating in varied environmental conditions.
The key tech features are:
- Ultra-low current consumption suitable for long-life, battery-powered systems
- High magnetic sensitivity enabled by advanced TMR structures
- Omnipolar and bipolar options for flexible or directional sensing needs
- Push-pull CMOS outputs with Schmitt triggering for clean, noise-immune switching
- Wide 1.8–5 V operating range in compact SOT23-3 packaging
At the top of the lineup is an omnipolar switch with a typical draw of just 200 nA, enabling continuous monitoring in ultra-low-energy designs. By responding to both North and South poles, it removes strict magnet-placement constraints and helps reduce mechanical complexity in compact enclosures. For engineers needing polarity-specific detection, the bipolar model consumes only 1.5 μA while delivering high sensitivity suited for tamper detection, position sensing, and directional inputs in appliances, power tools, and automation systems.
Both devices come in compact SOT23-3 packages and integrate a push-pull CMOS output for clean digital transitions, along with Schmitt triggering to maintain signal integrity amid noise and mechanical vibration. High magnetic immunity and a wide 1.8–5 V operating range further support drop-in adoption in existing system architectures, including Hall-effect replacement scenarios.
Target applications span smart utility meters, wearables, wireless IoT sensors, lid-open detection in consumer appliances, and linear or rotary position sensing in light-industrial equipment and robotics. With sensitivity tuned for small magnets and limited space envelopes, the switches are positioned as power-efficient upgrades for designers looking to extend battery life without sacrificing response accuracy.
By combining directional flexibility, robust thermal behavior, and some of the lowest power figures in their class, the new TMR switches bring a strong option for next-generation designs moving toward smarter, smaller, and more energy-aware architectures.