
Bluetooth-based spying devices enable eavesdropping, much like those in James Bond films. However, Bluetooth and Wi-Fi have a limited range, restricting their effectiveness.
Now, imagine discreetly intercepting conversations, uncovering criminal intent, and taking timely action—an intriguing possibility.
A compact GSM-based surveillance device can enable monitoring across vast distances, even between countries. Its small size ensures easy concealment while maintaining an unlimited range.
Strictly intended for security and surveillance, it must not be used for unauthorised purposes. The series of articles beginning with this one covers various long-range spying technologies, starting with GSM-based communication, followed by FM and Wi-Fi-based methods.
POC Video Tutorial:
A compact board is required to construct this device. The IndusBoard Coin is an ideal choice, measuring only 3cm, with the SIM800L GSM module fitting perfectly within this small form factor. This combination allows the development of an efficient and discreet spying device capable of transmitting audio over long distances.

The required components are listed in the Bill of Materials table.
| Bill of Materials | ||
| Components | Quantity | Description |
| IndusBoard Coin V1/V2 | 1 | 3cm development board |
| SIM800L module | 1 | 2G GSM module for communication |
| Li-Po battery (3.7V) with BMS module | 1 | Li-Po battery with BMS module |
| Microphone module | 1 | Captures audio for transmission |
Note: A UFL flexible GSM antenna can be attached to the device for better connectivity. In this case, it is not used as network connectivity is sufficient in the deployment area.
Code
Before writing the code, the required library must be installed. Follow these steps:
- Open Arduino IDE
- Go to Sketch >Include Library >Manage Libraries
- In the Library Manager, search for Adafruit FONA
- Click on Install next to the Adafruit FONA Library
- Once installed, restart the Arduino IDE to apply the changes
After installing the library, the FONA library must be included first, followed by the HardwareSerial library. Then, serial pins should be defined—any pins can be used, but by default, pins 43 and 44 are assigned for the SIM800L module. Finally, the baud rate must be set.
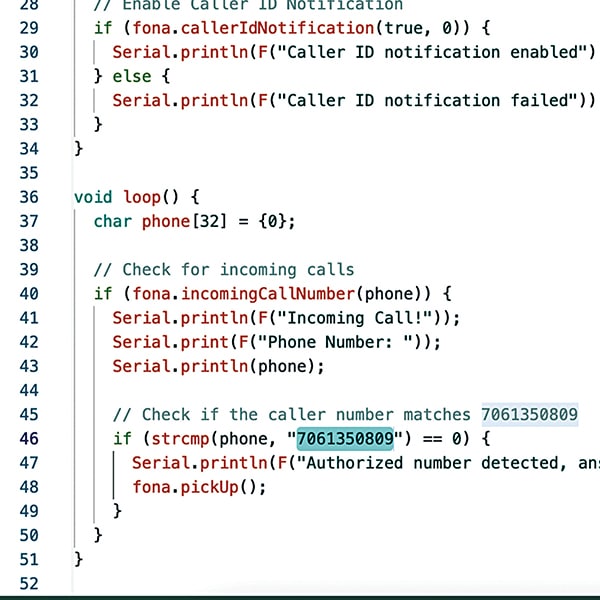
Fig. 2 shows the code snippet for the pin definition.

Within the loop, the device checks for incoming calls. If the incoming call matches the designated phone number configured for spying, the device automatically answers and begins streaming audio. This enables remote listening to conversations and sounds from the device’s location. The phone number can be set within the code.
Fig. 3 shows the code snippet for setting up the phone number.
Circuit Design
The IndusBoard Coin acts as the central controller, interfacing with the SIM800L module for GSM communication. The microphone is connected to the SIM800L’s audio input, allowing captured sound to be transmitted over a call.
Fig. 4 shows the circuit diagram for the long-range spy device.
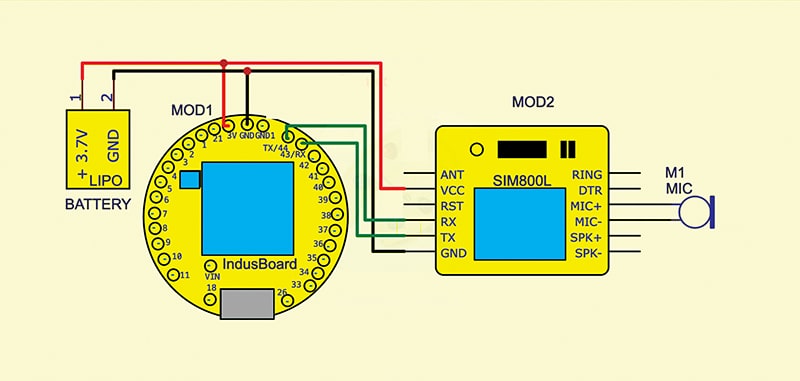
Power connections must be carefully managed. The IndusBoard Coin operates at 3.3V, whereas the SIM800L module requires a stable 4V power supply. To achieve this, a voltage regulator can step down the Li-Po battery’s voltage. The voltage regulator connects the battery to the IndusBoard Coin and the SIM800L module. The microphone module is connected to the SIM800L’s MIC+ and MIC- pins to ensure precise audio transmission.
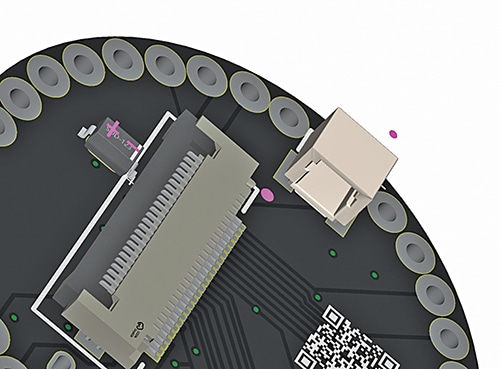
Note: If using the IndusBoard Coin V2.1, it has an in-built battery connector. The battery can be directly plugged in using the built-in BMS module on that connector.
Fig. 5 shows the battery connector on the IndusBoard Coin V2.1.
Construction and Testing
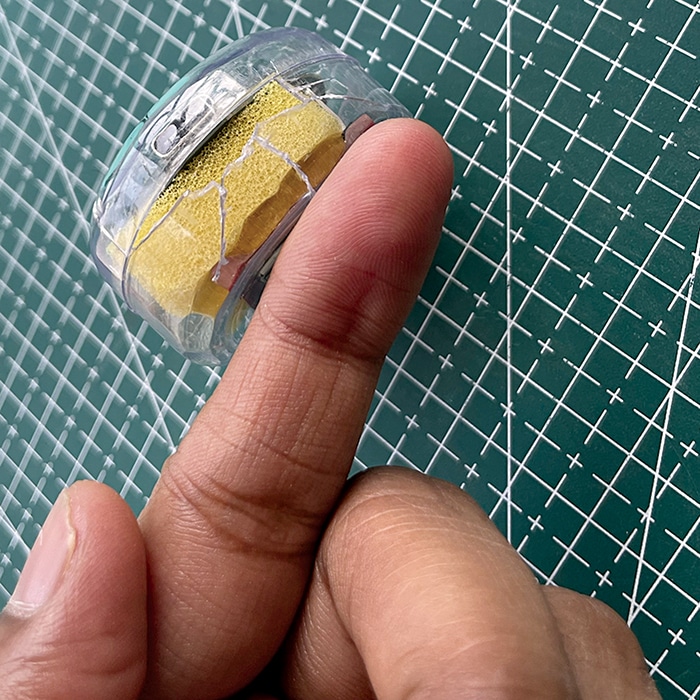
After soldering the SIM800L, battery, and microphone, all components are fixed within a 3cm enclosure. The coin comes in a 3cm circular case, where the components are placed before sealing the entire setup. Five to seven small holes should be made in the case to allow sound to enter.
Fig. 6 shows how the device is set up within the enclosure.
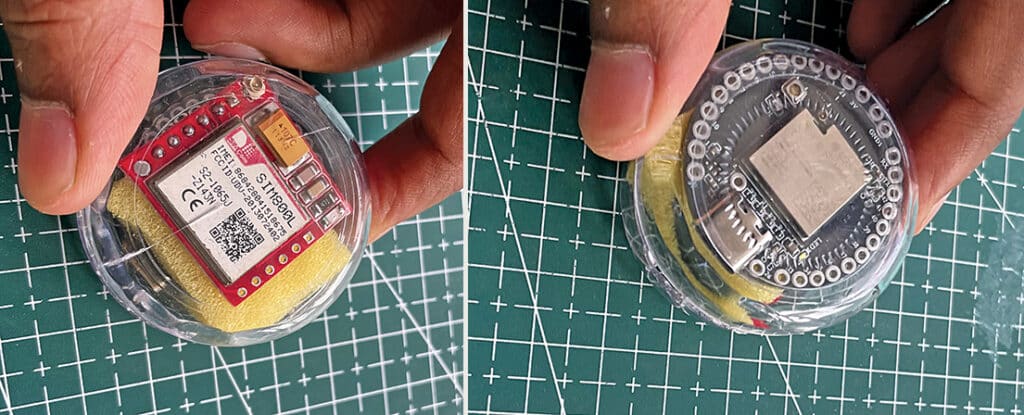

A SIM card with a voice call pack must be inserted before charging the battery. The device requires a few seconds to connect to the network. When surveillance is needed, calling the configured phone number enables audio monitoring.
EFY note: This device is intended strictly for ethical security applications. Any unauthorised use of surveillance is illegal.
Ashwini Kumar Sinha, an IoT and AI enthusiast, is a Tech Journalist at EFY.







Can you modify the above diagram for automatic water pump on or off for 3 tanks using single motor pump