A new generation of 1200 V SiC power modules delivers higher efficiency, lower EMI and improved thermal reliability for EV chargers, solar inverters, motor drives and telecom power systems.
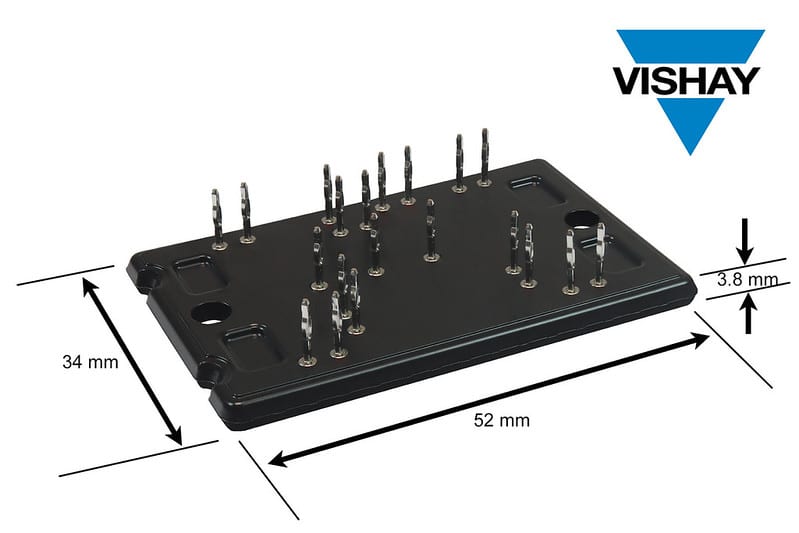

A new pair of 1200 V SiC MOSFET power modules by Vishay Intertechnology is pushing efficiency and reliability further for medium- to high-frequency power-conversion designs. Aimed at automotive, energy, industrial and telecom systems, the modules arrive in a compact PressFit package that reduces parasitic inductance, lowers EMI and supports faster, cleaner switching in high-density layouts. The low-profile format also cuts board height while aligning with industry-standard pin matrices, easing drop-in replacement for existing inverter and converter designs.
At the core of the update is a shift toward newer-generation silicon carbide MOSFETs paired with intrinsic SiC diodes offering low reverse-recovery behaviour. The result is reduced switching losses and improved conversion performance across common use cases: solar inverters, EV and HEV chargers, industrial motor drives, welding systems, UPS units, HVAC controls, large battery-storage platforms and telecom rectifiers. Designers also gain integrated temperature feedback through an onboard NTC thermistor, enabling tighter thermal monitoring during high-load operation.
The key features are:
- Silicon carbide-based power MOSFET design
- High blocking voltage with low on-resistance
- High-speed switching performance with low capacitance
The modules employ a moulded transfer construction designed for extended operating lifetimes and improved thermal resistance compared with legacy modules. This rugged packaging approach helps maintain reliability under thermal cycling and mechanical stress an increasingly important requirement as SiC adoption expands in harsh-environment and mission-critical power stages.
The line includes two configurations. A full-bridge inverter module delivers a 38 mΩ on-resistance and 35 A continuous drain current at 80 °C, supporting high-efficiency switching with low device capacitance. A three-phase inverter variant features 75 mΩ on-resistance and an 18 A continuous rating. Both devices support maximum junction temperatures up to 175 °C, enabling wider thermal headroom for compact system designs. The devices are RoHS-compliant and halogen-free, aligning with current sustainability and material-safety expectations.
By combining SiC performance characteristics with a space-saving topology and PressFit interconnects, the modules aim to simplify system upgrades as designers shift from silicon to SiC-based architectures. With medium- to high-frequency converters demanding higher efficiency, lower switching noise and greater thermal robustness, the new package approach signals a continued move toward tightly integrated, ruggedised SiC solutions for next-generation power electronics.