GPU clusters are slowing down with network problems and stalled jobs. A new design could solve it all and make large AI clusters run smoothly.
In this modern era of Artificial Intelligence (AI) we have seen clusters of large General Purpose Units (GPUs). Now for building these large clusters AI teams face many challenges like networking sprawl. Servers use separate Network Interface Cards (NICs), Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe) switches, and rail switches, all connected in narrow, isolated paths that do not work well together. This setup limits bandwidth, creates cross-GPU congestion, and makes the system fragile. If one GPU link fails it can halt the entire job. As clusters scale, device hops multiply, load distribution becomes uneven, incast events rise, and total cost of ownership increases. Expensive GPUs often sit under-used because the network cannot keep up.
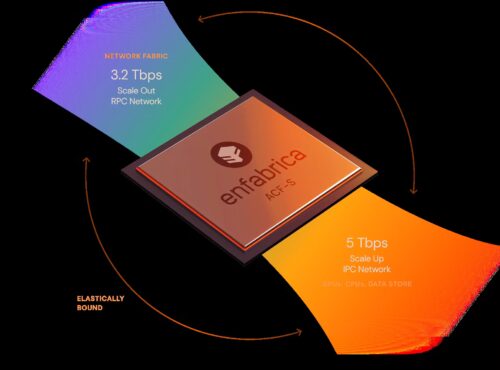
Enfabrica’s ACF-S steps in to solve this bottleneck. It replaces multiple components with a single 3.2 Tbps Multi-GPU SuperNIC that gives GPUs access to 8× elastic bandwidth. Instead of routing data through several devices, ACF-S moves traffic directly and distributes it evenly across GPUs. This reduces data-movement latency, cuts device hops by up to 66%, and keeps network-to-GPU traffic congestion-free. For users running large training jobs, this means jobs stop failing due to link flaps and clusters stay productive even under heavy load.
The technology works for data centers scaling multi-GPU nodes as well as teams trying to control cost while growing their AI footprint. By collapsing NICs, PCIe switches, and other components into one architecture, ACF-S reduces CapEx by up to 29% and OpEx by as much as 55%. It also aligns with upcoming standards, supporting PCIe Gen5 and CXL 2.0+ today, with PCIe Gen6 and CXL 3.0 on the way.
ACF-S sits at the center of Enfabrica’s EMFASYS platform, which unifies compute, memory, and interconnect paths for AI workloads. For operators building dense GPU clusters and struggling with network limitations, the design offers a practical way to scale performance without multiplying complexity.