Unexpected electricity bills can often be frustrating. This smart energy monitor, built using an ESP32 microcontroller, measures real-time power consumption and predicts upcoming bills with the help of a machine learning model.
The system monitors electricity usage, along with temperature and humidity, displaying all data on a laptop through a clean and intuitive interface. It provides live updates, stores previous readings, and forecasts future bills based on actual consumption patterns and environmental conditions.
POC Video Tutorial
| Bill of Materials | ||
| Components | Quantity | Description |
| ESP32-S-Wrover-1 (U1) | 1 | Main controller for data acquisition and Wi-Fi |
| ACS712 current sensor (U2) | 1 | For measuring current usage |
| ZMPT101B voltage sensor | 1 | For measuring voltage |
| DHT22 sensor (U3) | 1 | For ambient temp/humidity |
| Breadboard | 1 | For circuit assembly |
| Jumper wires | – | As required |
| USB cable | 1 | For programming ESP32 |
| Power supply/power bank | 1 | To power the ESP32 if not using USB |
Designed for homes, hostels, and small offices, this affordable and user-friendly system helps manage both energy usage and budget more effectively. The components are listed in the Bill of Materials table, and the prototype is shown in Fig. 1.

Smart Energy Meter Circuit and working
Fig. 2 illustrates the system workflow. The IoT-based ESP32 energy monitor and bill predictor functions by measuring voltage, current, temperature, and humidity using sensors such as ACS712 and DHT11. The ESP32 processes these readings to calculate real-time power, energy usage, and load. The data is then transmitted via HTTP to cloud platforms, where energy consumption can be monitored through a dashboard.
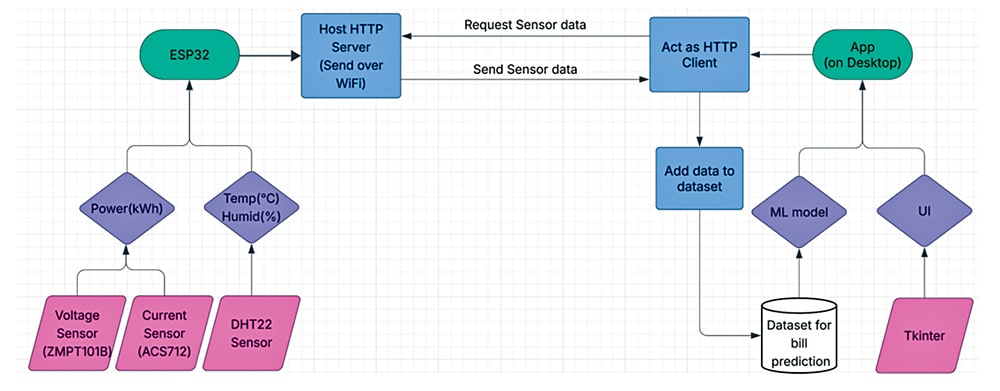
A machine learning model analyses past usage to predict upcoming electricity bills and generates alerts for high consumption or abnormal load spikes. Operating continuously, the system provides real-time insights that help optimise energy usage and prevent unexpected bill increases.
Fig. 3 shows the circuit diagram of the IoT-based ESP32 energy monitor and bill predictor. It is built around the ESP32 microcontroller and employs three main sensors: the ZMPT101B voltage sensor, the ACS712 current sensor, and the DHT22 temperature and humidity sensor. The phase (live) wire passes through the IP+ and IP– terminals of the ACS712, while the phase and neutral wires are connected to L (pin 4) and N (pin 5) of the ZMPT101B. Together, these sensors enable the accurate calculation of energy consumption (kWh).
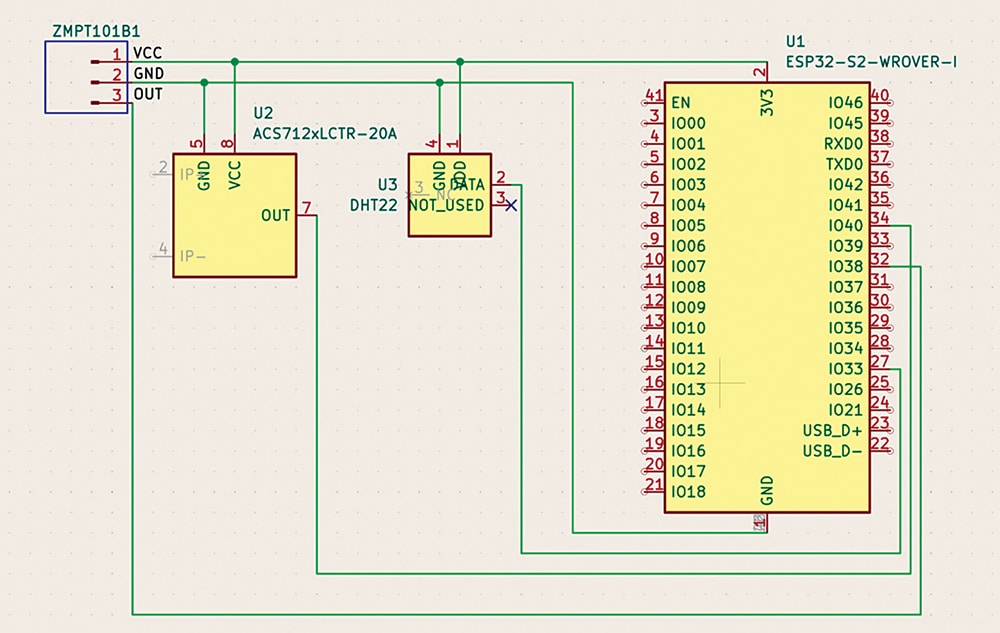
(EFY note: It is advisable to first test the circuit using a 9W LED bulb before connecting it to household appliances for full-scale monitoring.)
Software Implementation: ESP32 Web Server and UI