The ReRAM cells with OTS selectors offer excellent endurance, low energy consumption, and high switching speed.
Resistive Random Access Memories (RAMs) or ReRAMs are a perfect solution for cost-sensitive applications, such as wearables and IoT devices. ReRAMs are a good fit for some low-end MCUs and consumer products with a lower memory density requirement. They offer faster, bit-alterable, erase-free operation and have a significantly lower read latency and faster write performance.
ReRAMs work on the principle called “memristor”. An electric current is applied across a material, which changes the resistance of that material. The resistance state can then be measured. The working relies on the principle of hysteresis.
There has been a lot of research to find appropriate materials and measure the resistance state of the cells. Weebit Nano has taken an important step towards commercialization of these discrete memory units. They claim to have developed the industry’s first commercial integration of an oxide-based ReRAM (OxRAM) cell with an ovonic threshold switching (OTS) selector.
OTS is a two-terminal thin film selector that acts like a resistor and switches between the two states: conductive stage and highly resistive stage (OFF condition). When a voltage higher than it’s threshold voltage is applied across the terminals, the device is in the conductive stage. When the current is reduced below the holding current density of the device, the selector recovers its high resistance state.
These selectors play an important role in memory chips. They are stacked between the layers of memory chips to enable optimized cell access within a memory array. The selectors aid in isolating memory cells. So only the specific cells that should be accessed are impacted, and all the other cells remain unaffected.
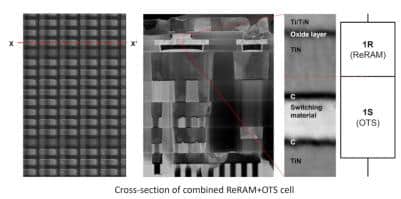
The OTS selectors provide high-current switching performance and therefore, using OTS selectors in ReRAMs is a significant step in improving the embedded non-volatile memories. The selector enables the smallest ReRAM bit cell, as well as excellent endurance, low energy consumption, and high switching speed.
Researchers believe that this technology will enable the implementation of 3D memory stacking and crossbar architectures in future developments.