An IGBT is a special type of power transistor used to control very high voltages and currents. It is the heart of electric vehicles, solar inverters, motor drives, industrial machines, and power systems. It combines the easy control of a MOSFET with the power handling of a bipolar transistor.
In this guide, you will learn:
- What an IGBT is in simple terms
- How it works inside
- Why it is better than MOSFETs in high power systems
- Where it is used in real life
- How engineers choose the right IGBT
Now, let us go deeper.
What Is an IGBT
IGBT stands for Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor.
It is a power semiconductor device used to turn large electrical currents on and off. Think of it as a very strong electronic switch that can control thousands of volts and hundreds of amps.
An IGBT has three main terminals:
- Gate
- Collector
- Emitter
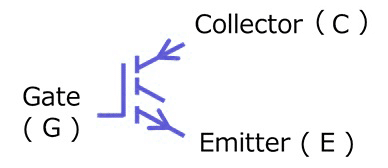
The gate controls the device. When a small voltage is applied to the gate, a much larger current flows between the collector and the emitter. This makes it possible to control huge amounts of power using a tiny control signal.
That is why IGBTs are used in heavy machines, electric cars, renewable energy systems, and industrial motor drives.
Why IGBTs Were Invented
Before IGBTs, engineers had two main options.
Bipolar transistors could handle high power, but they were hard to control. MOSFETs were easy to control, but they struggled at high voltage and high current.
IGBTs were created to combine the best of both.
They offer:
- Easy voltage based control like a MOSFET
- High power handling like a bipolar transistor
This combination makes IGBTs perfect for modern power electronics.
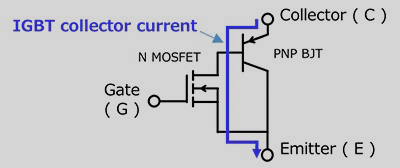
How an IGBT Works
When you apply a voltage to the gate, it creates an electric field. This field opens a channel that allows current to flow inside the device.
Once the channel opens, a bipolar transistor section inside the IGBT takes over and allows large current to flow from collector to emitter.
So in simple terms:
The MOSFET part turns the device on.
The bipolar part carries the heavy current.
This is why IGBTs can control massive power while still being easy to drive with simple electronics.
Why IGBTs Are So Powerful
IGBTs are popular because they solve real engineering problems.
They can handle very high voltage. Many IGBTs work at 600 V, 1200 V, or even more.
They can handle large current. Some IGBTs control hundreds of amps.
They waste less power at high load. At high current levels, IGBTs lose less energy as heat compared to MOSFETs.
They are reliable. IGBTs are designed to survive harsh electrical and thermal conditions.
That is why they are used in industrial and transportation systems that must run for years without failure.
IGBT vs MOSFET
This is one of the most searched questions.
Here is the simple answer.
MOSFETs are better for low voltage and high speed switching. IGBTs are better for high voltage and high power.
MOSFETs are used in:
- Phone chargers
- Laptop adapters
- Low-power power supplies
IGBTs are used in:
- Electric vehicles
- Solar and wind inverters
- Industrial motor drives
- Railway traction systems
If the system is big and powerful, IGBT usually wins.
In another article, we explained the difference between IGBT and MOSFET.
Where IGBTs Are Used in Real Life
You interact with IGBTs every day, even if you never see them.
- In electric vehicles, IGBTs control the motor that moves the car
- In solar inverters, they convert DC from panels into AC for the grid
- In air conditioners and washing machines, they control motor speed
- In factories, they run conveyor belts, pumps, and robotic arms
- In trains and metros, they control traction motors
Any system that needs to control large electrical power efficiently almost always uses IGBTs.
Why IGBTs Matter for Renewable Energy
Solar and wind systems depend on inverters to connect to the power grid. IGBTs are the main switching devices inside those inverters.
They:
- Convert DC to AC
- Control voltage and frequency
- Improve efficiency
- Reduce energy loss
Without IGBTs, modern renewable energy systems would be bigger, hotter, and far less efficient.
What Are the Limits of IGBTs
No device is perfect.
- IGBTs switch slower than MOSFETs
- They generate a small current tail when turning off
- They are not ideal for very high frequency applications
That is why IGBTs are usually used below about 50 kHz, while MOSFETs dominate high frequency designs.
Engineers choose based on voltage, current, and switching speed.
How Engineers Choose the Right IGBT
When selecting an IGBT, engineers look at:
- Maximum voltage rating
- Maximum current rating
- Switching frequency
- Thermal performance
- Package type
- Cost and availability
The goal is to get the best balance between efficiency, reliability, and price.
The Future of IGBT Technology
IGBTs continue to improve.
- New designs reduce switching losses
- Better materials allow higher temperatures
- Advanced packaging improves cooling
Even with new technologies like silicon carbide, IGBTs will remain critical for many large power systems for years to come.
Final Thoughts
The IGBT is one of the most important inventions in power electronics.
It quietly powers electric vehicles, clean energy, factories, trains, and heavy machines around the world.
If you understand IGBTs, you understand how modern electricity is controlled, converted, and delivered.
That is why IGBTs are not just components. They are the backbone of the electrified future.








